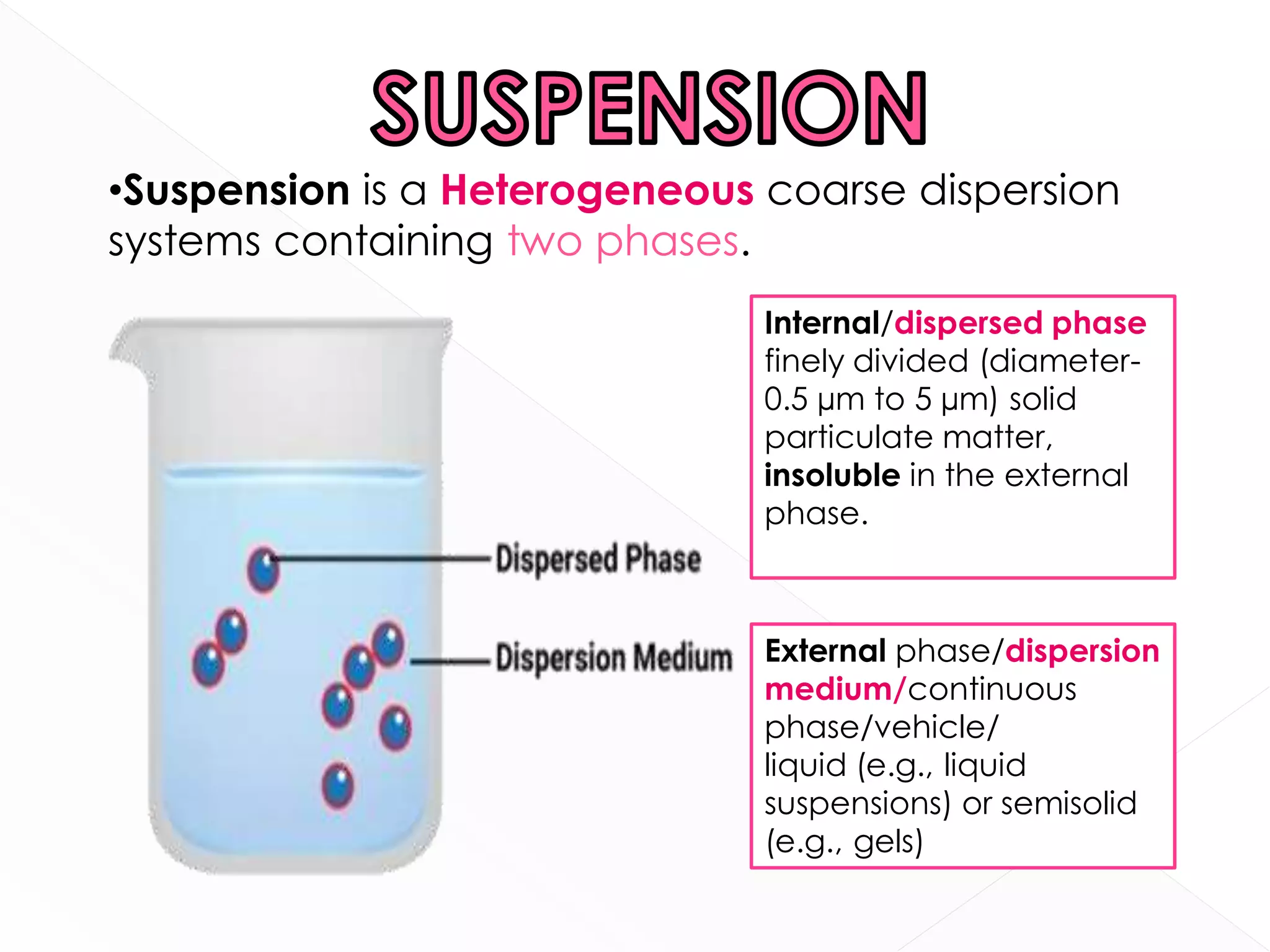
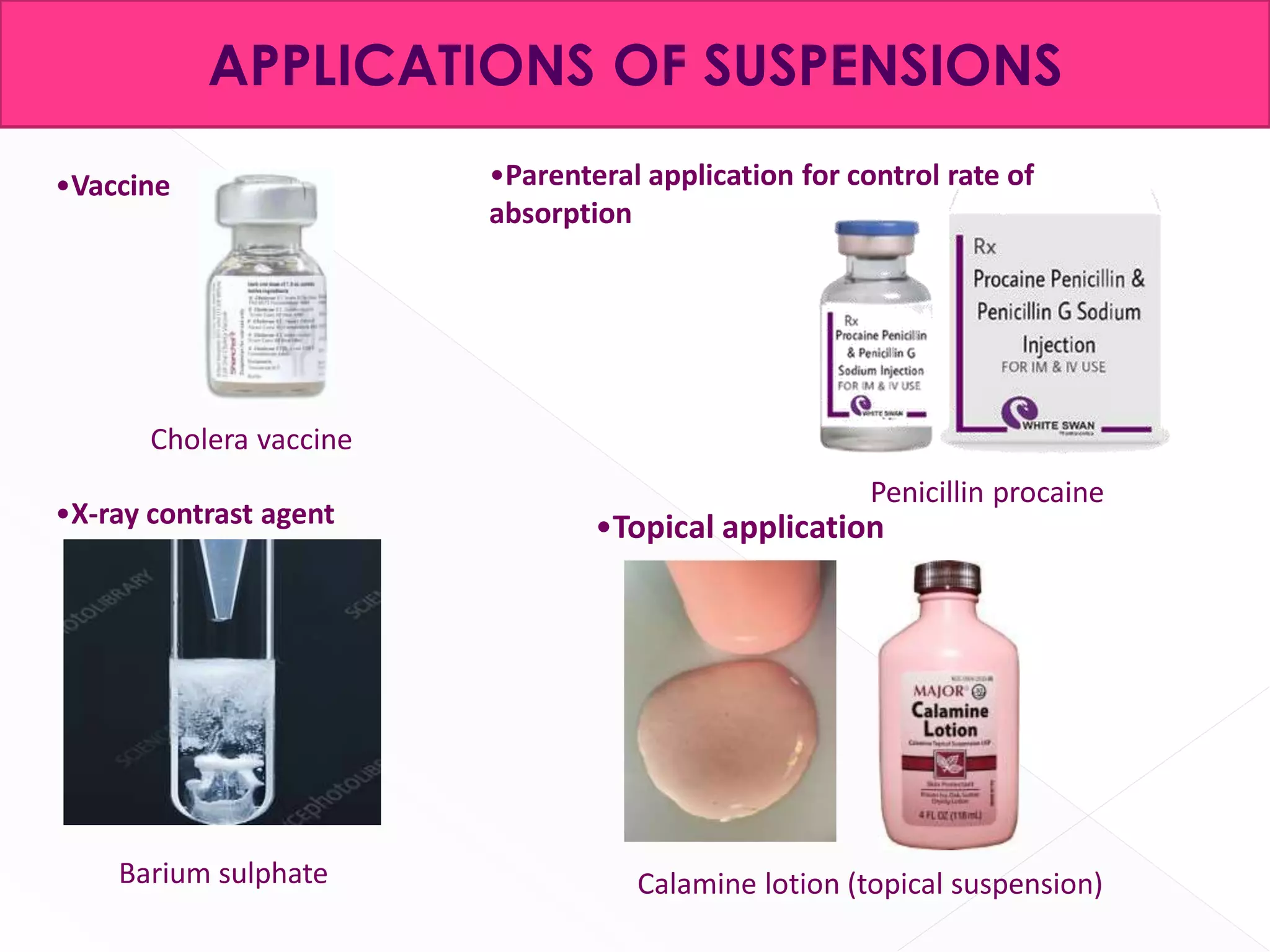
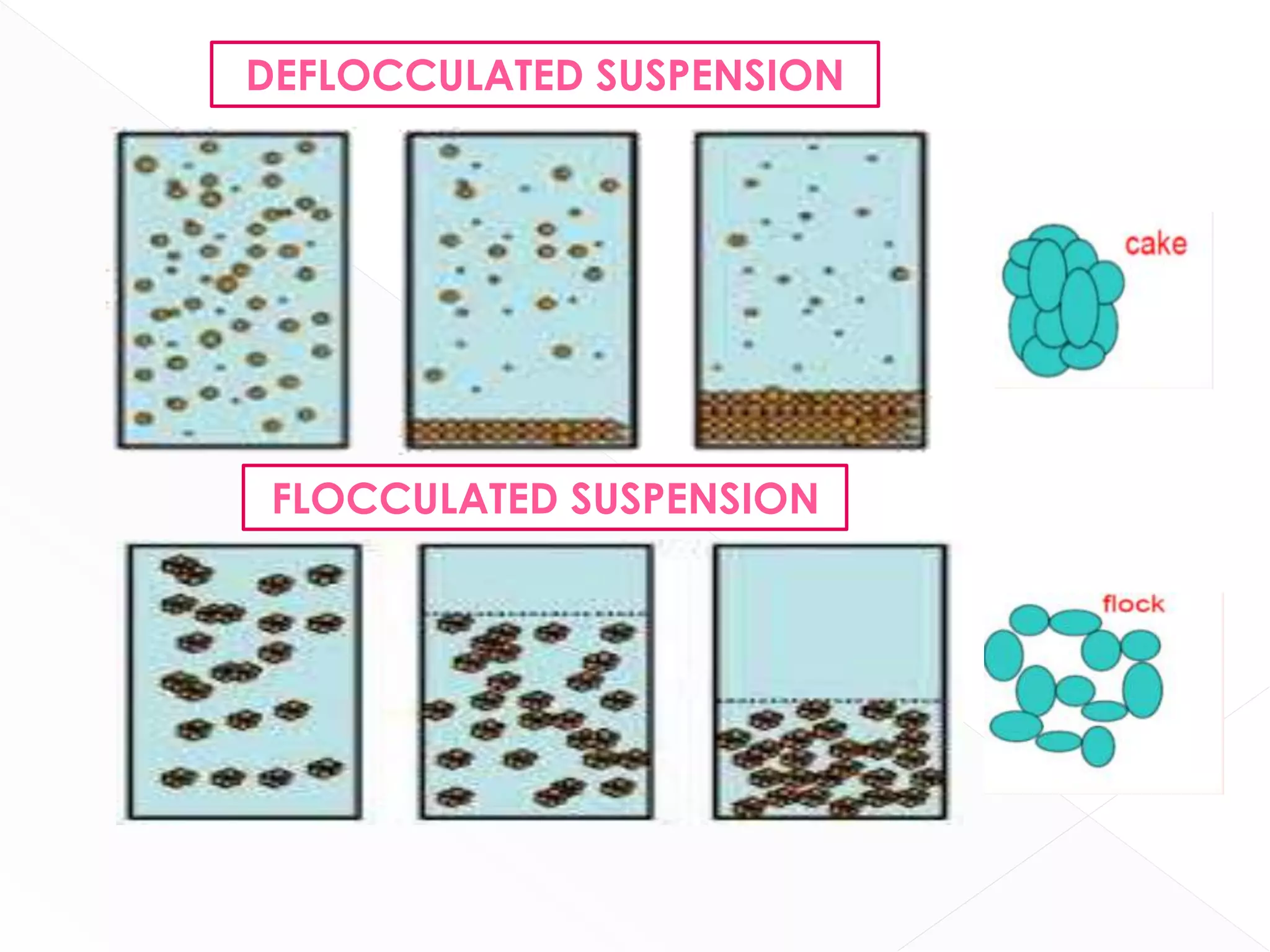
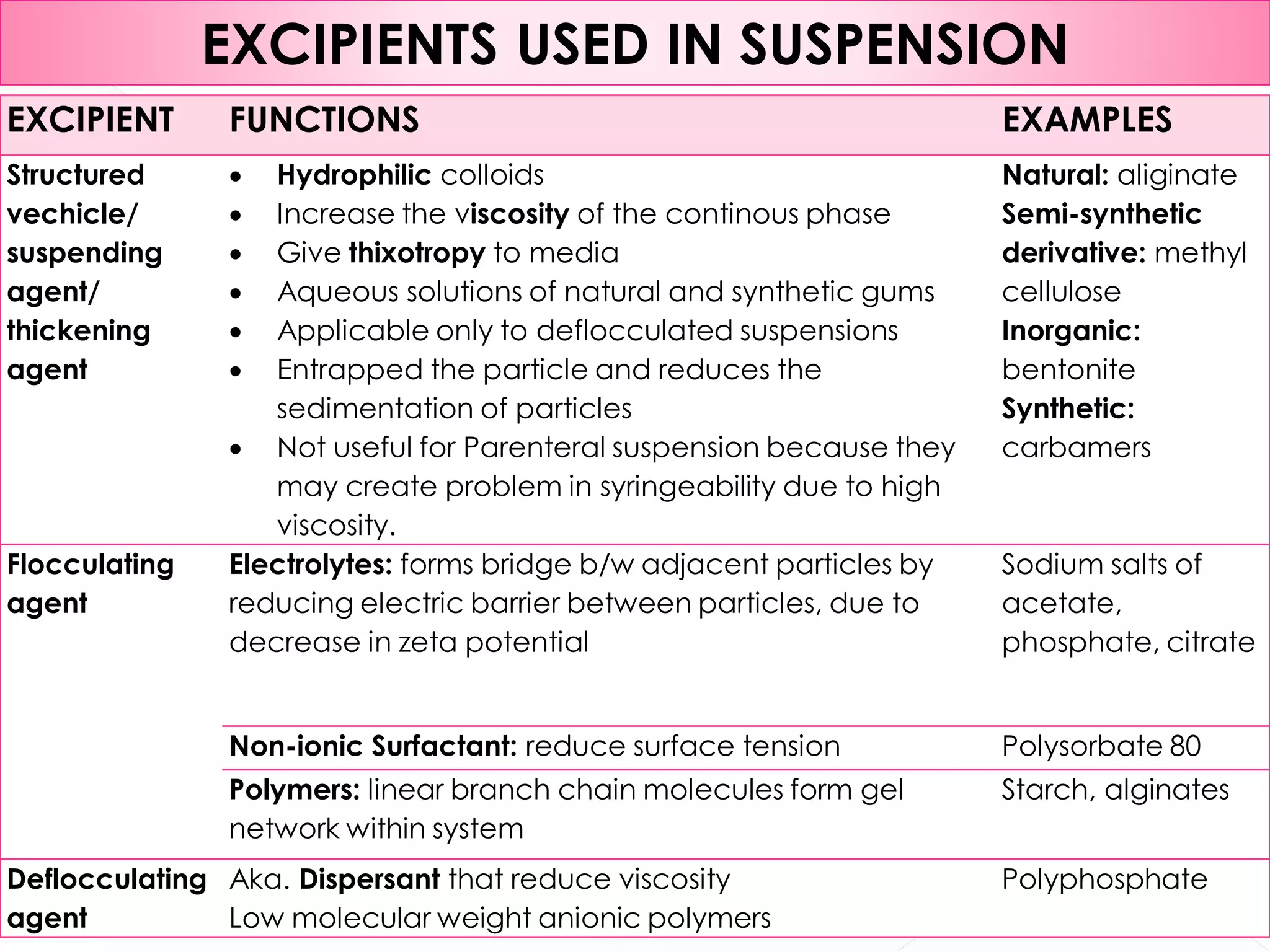
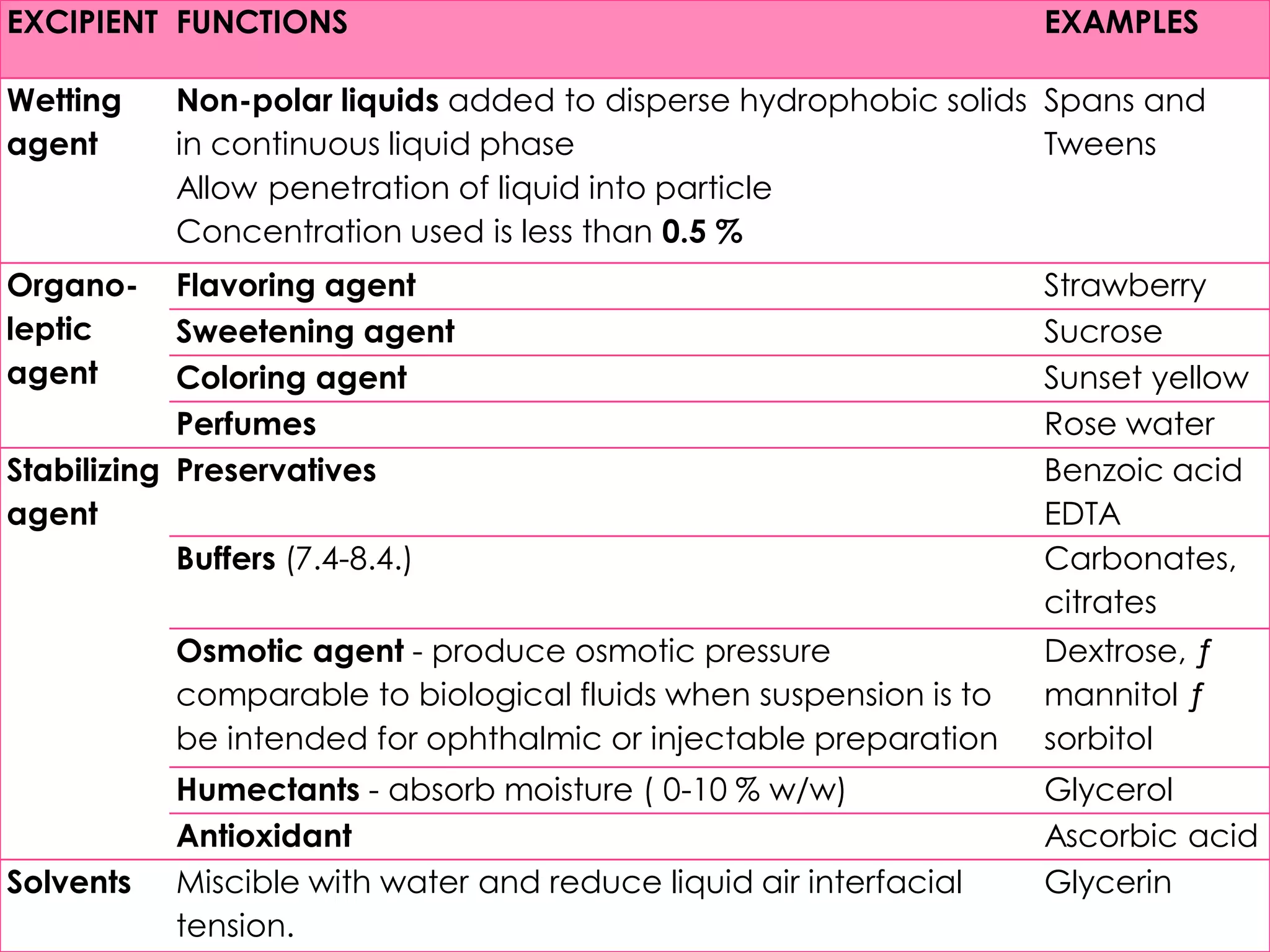
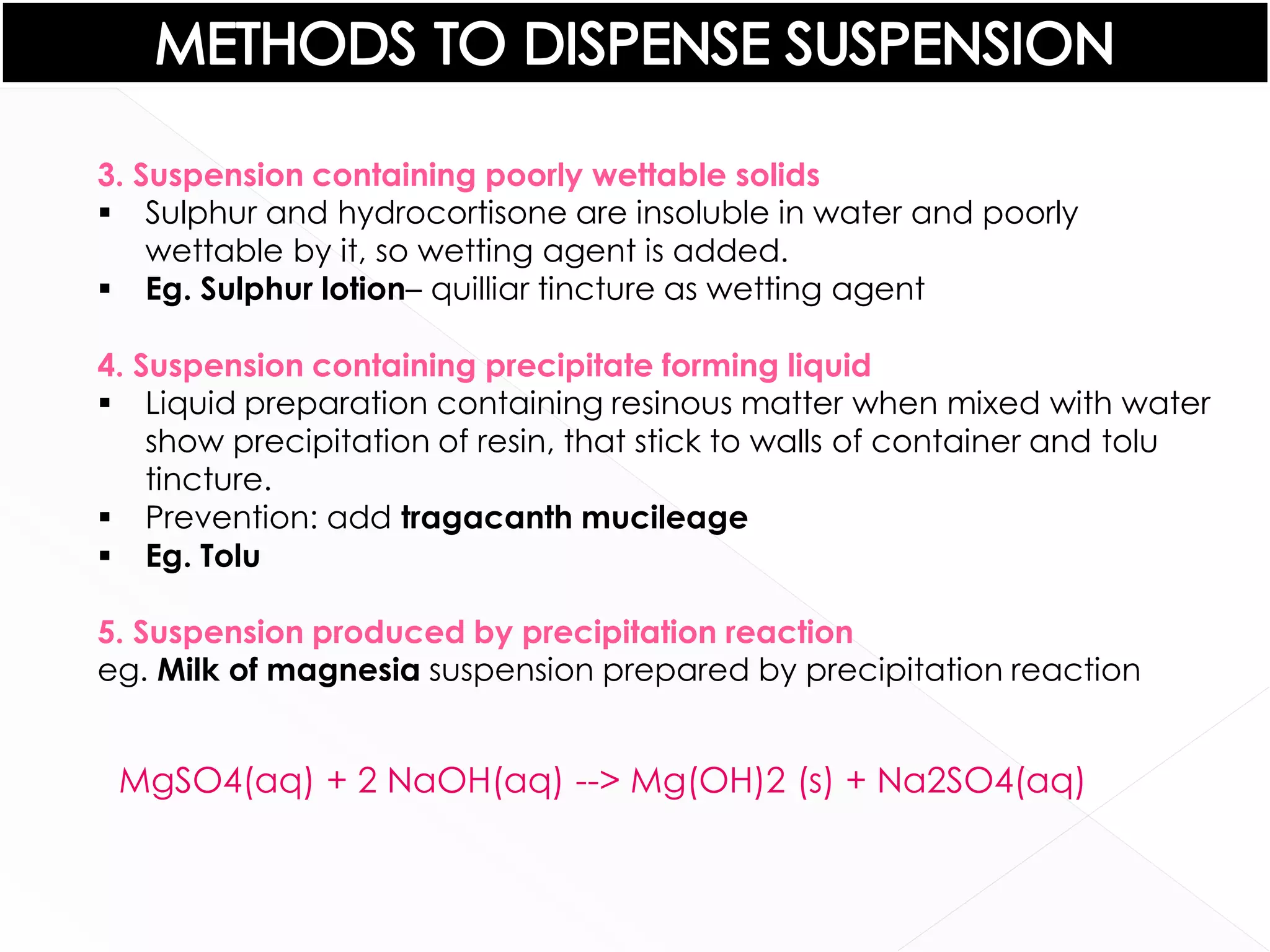
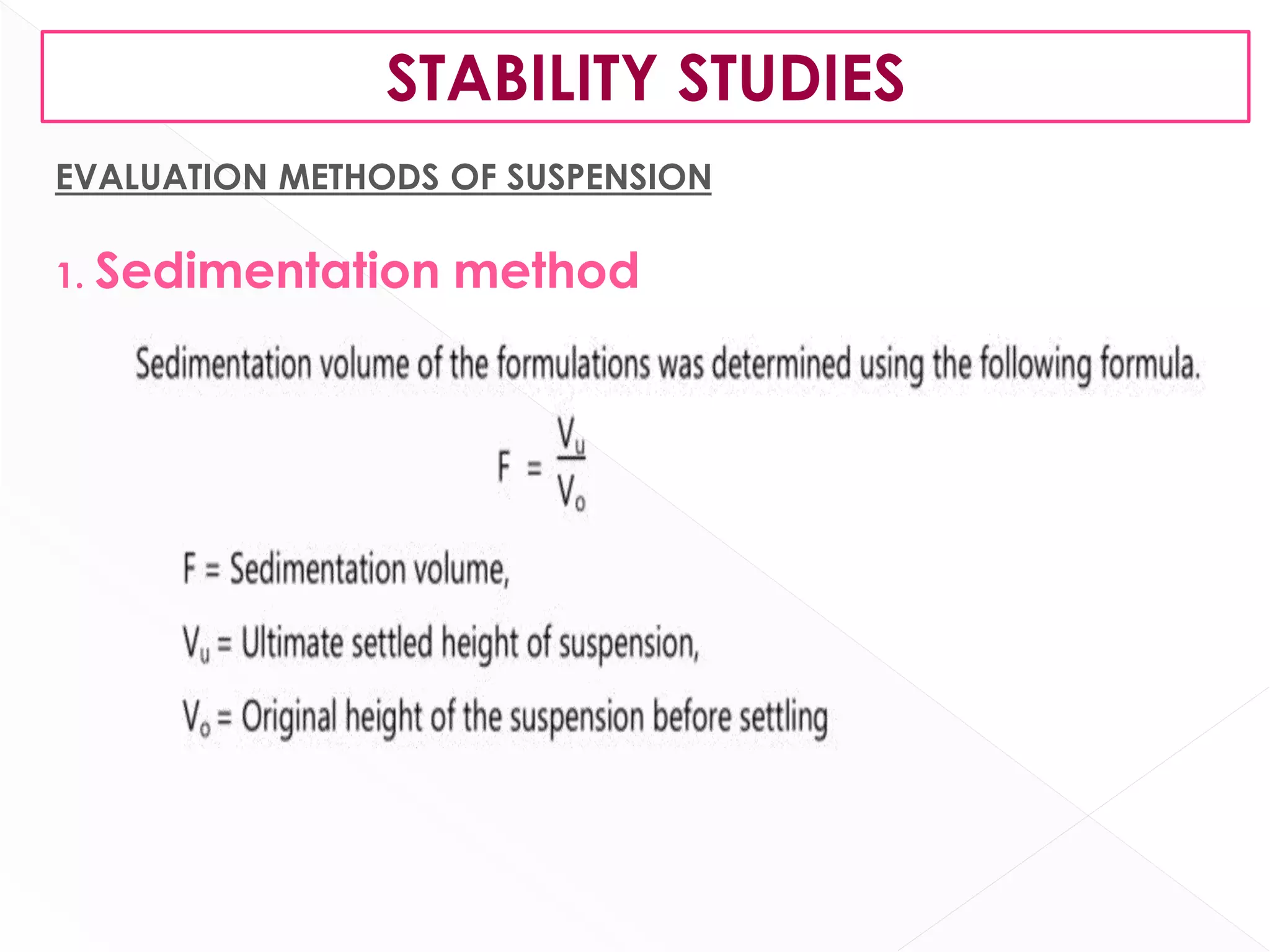
This document discusses the characteristics and classification of suspensions, which are heterogeneous dispersions containing solid particles in a liquid or gel medium. It outlines the ideal qualities, applications, and formulation methods of suspensions, including their use as pharmaceuticals and the types of excipients involved. The key factors influencing suspension stability, such as deflocculation, flocculation, and ingredient selection, are also highlighted.