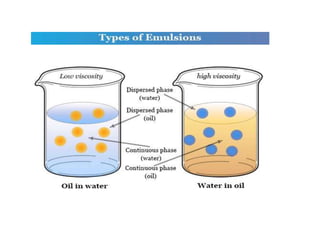
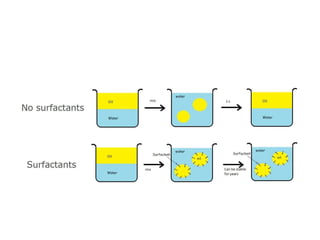
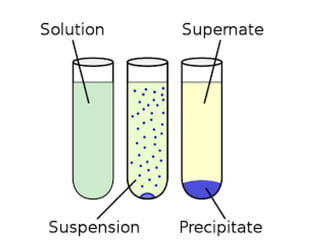
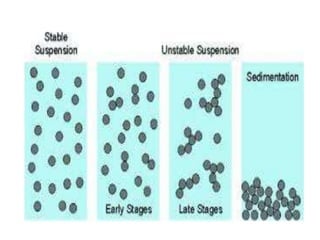
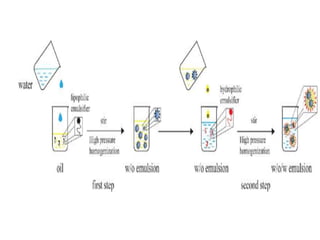
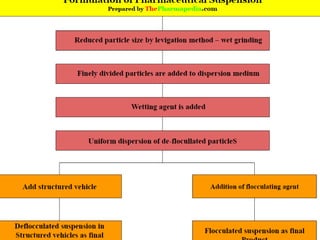
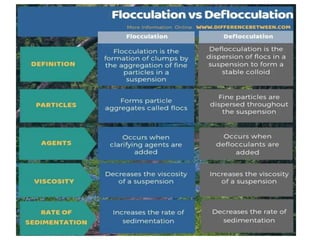
Biphasic liquid dosage forms contain two immiscible phases, a dispersed solid or liquid phase within a continuous liquid phase. Suspensions and emulsions are examples. They are used to deliver drugs that are poorly soluble and allow inclusion of multiple incompatible ingredients. Compared to monophasic forms, biphasic forms contain distinct phases rather than a single homogeneous phase. They exhibit higher bioavailability than other dosage forms but are also bulkier and more costly to produce.