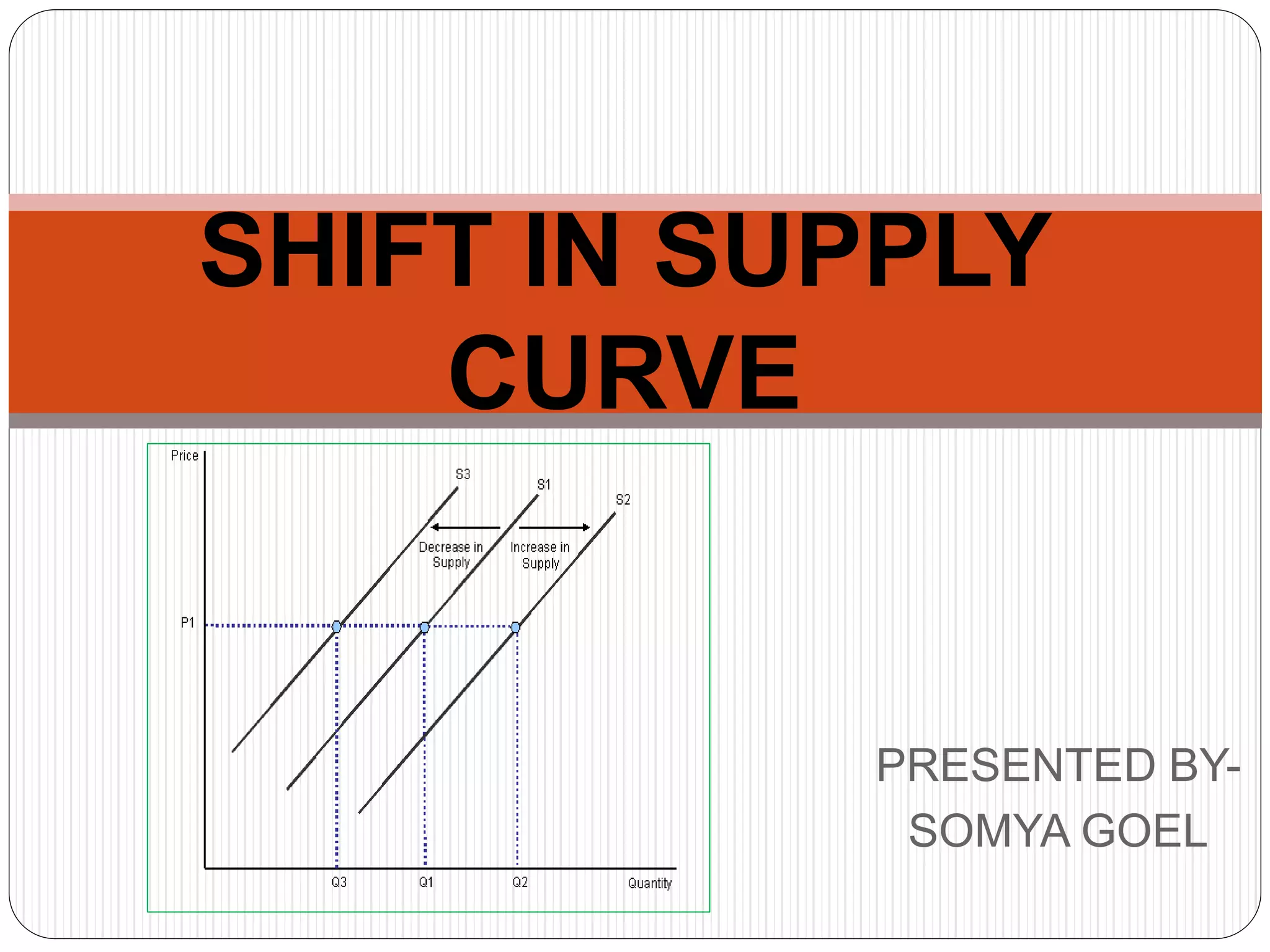
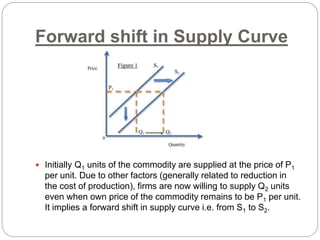
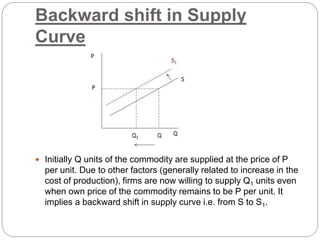
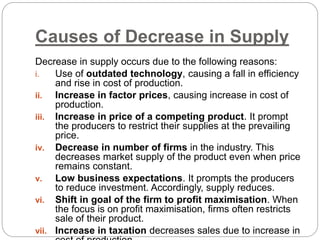
This document discusses shifts in supply curves, which refer to changes in the quantity supplied of a commodity even when its own price remains constant. An increase in supply is indicated by a forward shift of the supply curve, caused by factors that reduce production costs and increase the willingness of firms to supply more units at the same price. A decrease in supply is shown by a backward shift of the supply curve and can be caused by factors that increase costs and decrease firms' willingness to supply units at a given price. The document provides examples of specific factors that can lead to increases or decreases in supply.