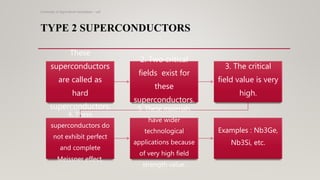
The document discusses superconductors, which are materials that lose all electrical resistance below a critical temperature. It describes how superconductivity was discovered in 1911 by Kammerlingh Onnes. The key properties of superconductors are zero resistance, the Meissner effect of expelling magnetic fields, and ability to levitate objects. There are two types of superconductors based on their critical magnetic field properties. Applications include MRI, maglev trains, and particle accelerators. Advantages are efficient power transmission and small devices, while limitations are the need for extremely low temperatures and brittleness.