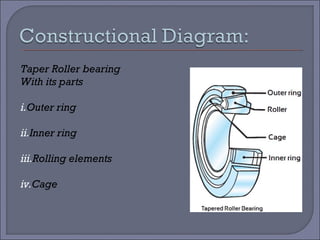
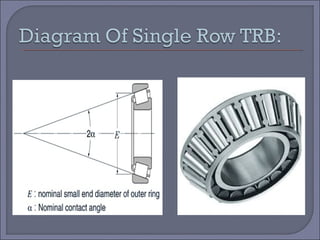
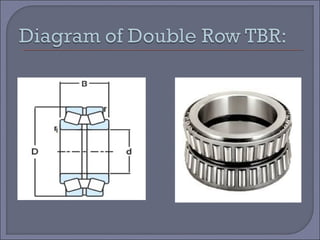
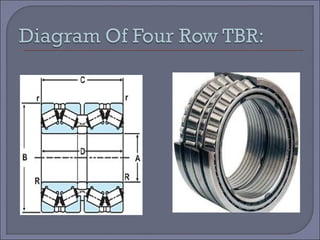
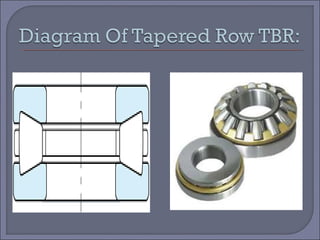
The document discusses taper roller bearings, which can take both axial and radial loads. Taper roller bearings are composed of an inner race, outer race, rolling elements, and a cage. They are available in single, double, and four row configurations. Taper roller bearings are used in heavy duty applications like construction equipment, axles, gearboxes, and engine motors due to their ability to handle large loads and their durability.