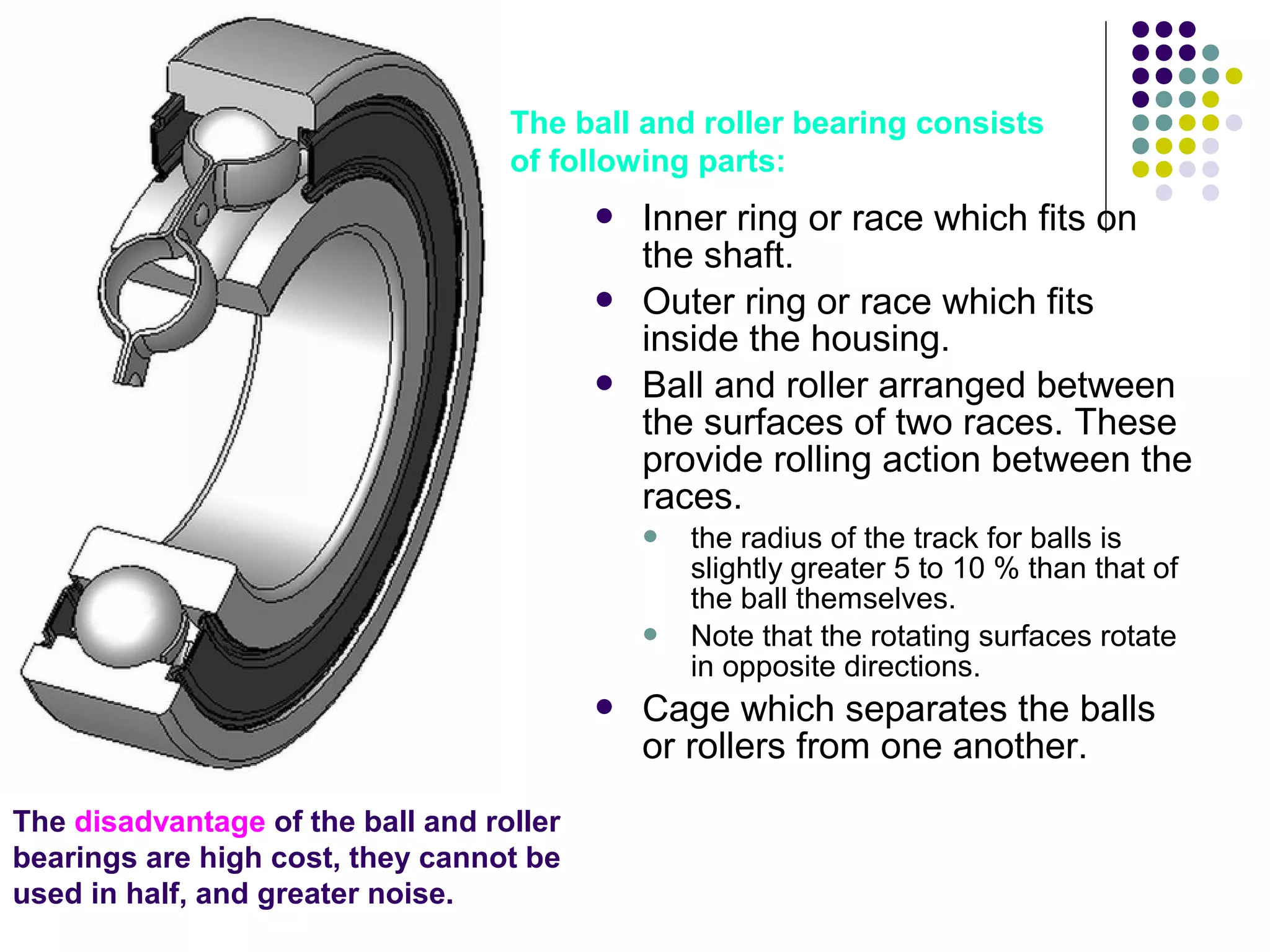
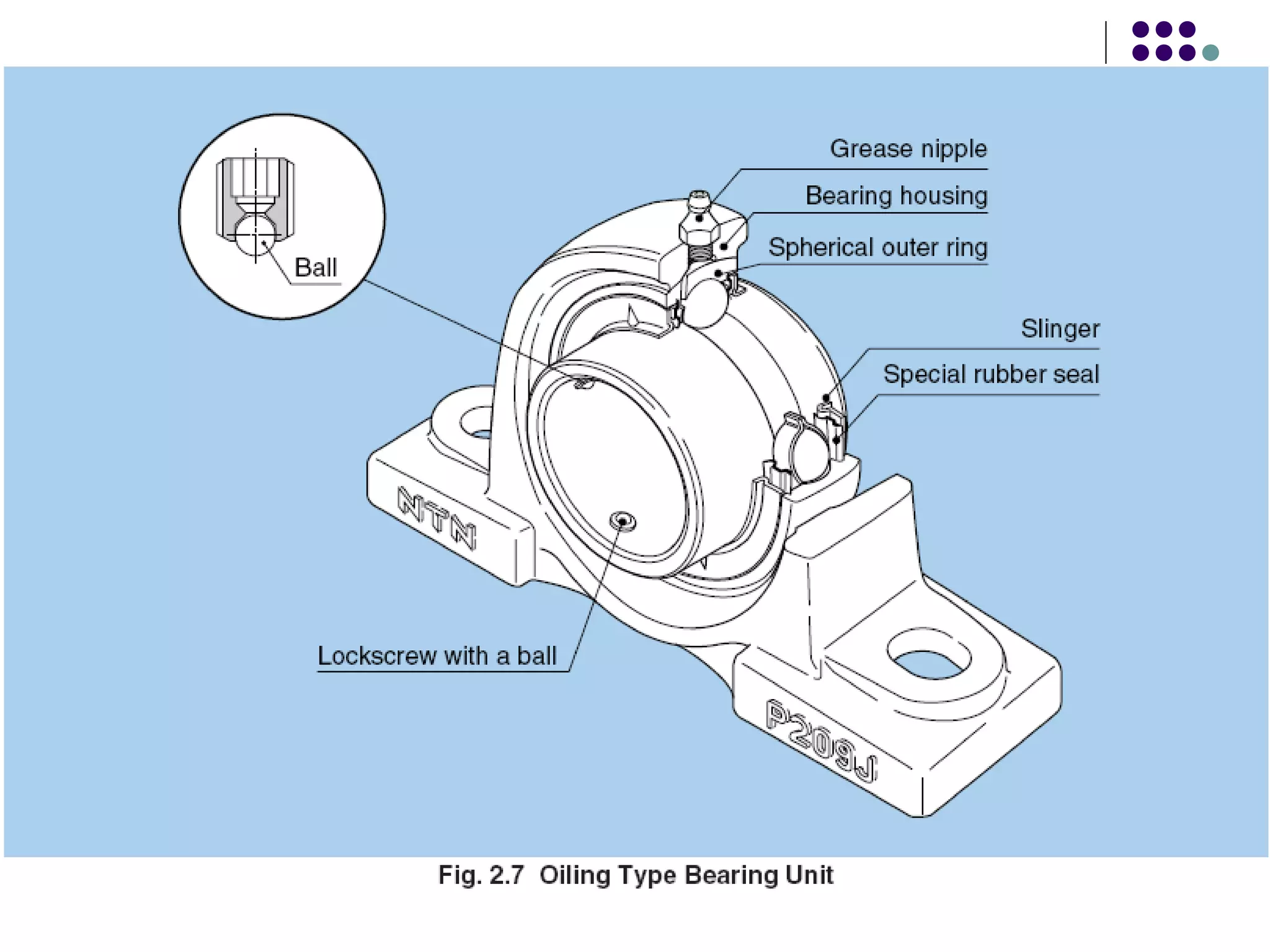
This document discusses bearings and their functions. It describes how bearings support rotating shafts and reduce friction to allow for smooth rotation. There are two main types of bearings - plain/slider bearings which have a large contact area and high friction, and rolling/ball bearings which have less contact area and lower rolling friction. Ball and roller bearings are further described as having races, balls/rollers, and a cage that separates the balls to reduce friction. Common ball and roller bearing types and their applications are also outlined.