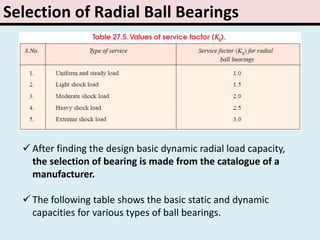
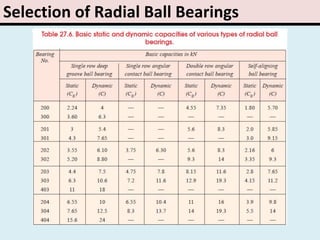
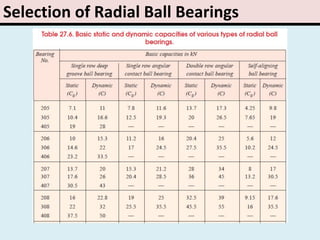
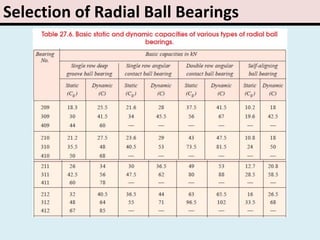
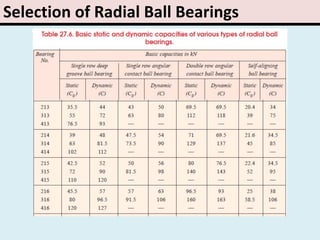
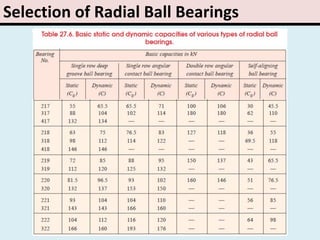
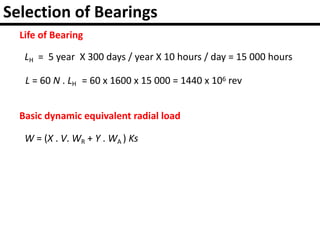
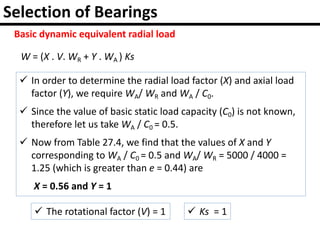
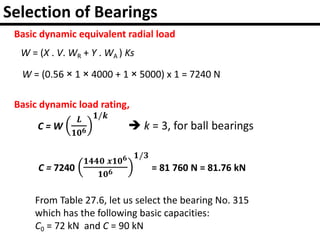
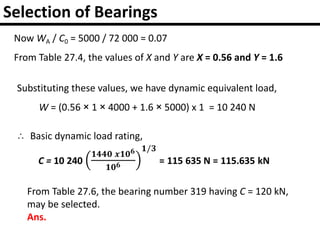
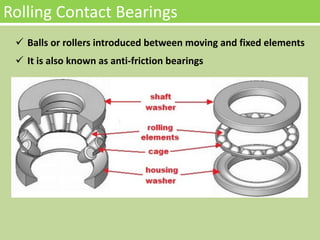
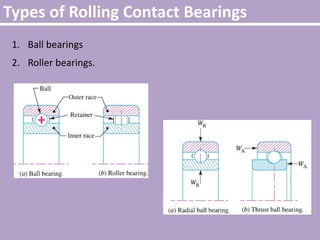
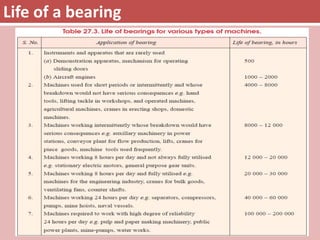
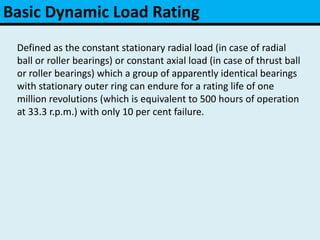
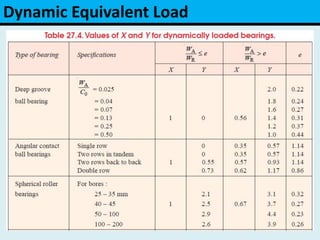
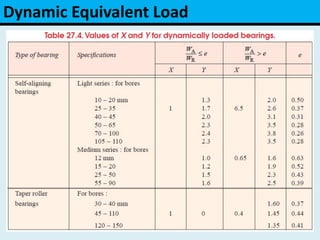
The document provides an overview of rolling contact bearings, detailing advantages such as low friction and ease of maintenance, alongside disadvantages including noise at high speeds and initial costs. It describes various types of bearings, their materials, lubrication methods, and essential parameters for load rating and selection process. The text includes formulas for calculating static and dynamic loads, and specific examples to illustrate bearing selection based on operational conditions.





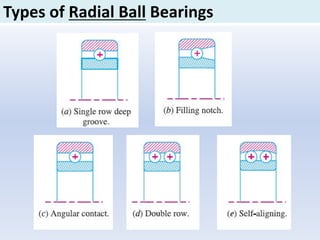
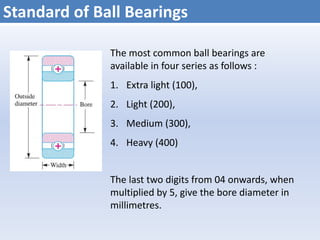
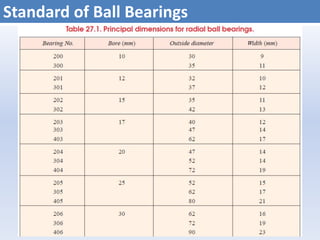
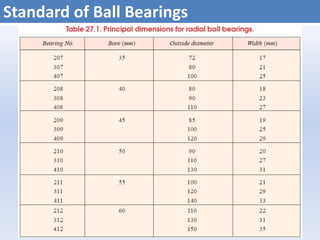








![Dynamic Load Rating
L = Rating life,
C = Basic dynamic load rating,
W = Equivalent dynamic load,
k = 3, for ball bearings,
k = 10/3, for roller bearings.
LH = Life in working hours
N is the speed in r.p.m.
L = 60 N . LH [revolutions]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rollingcontactbearings-180310145359/85/Rolling-contact-bearings-28-320.jpg)