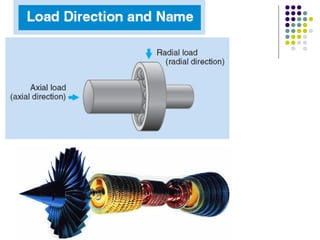
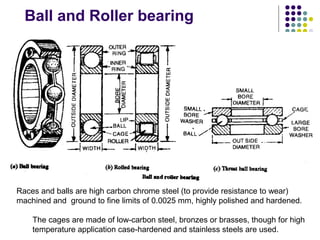
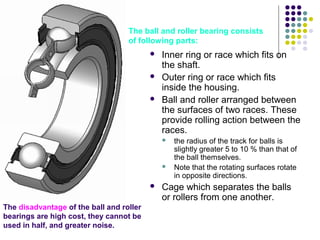
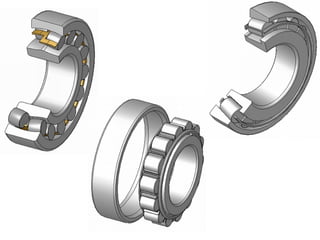
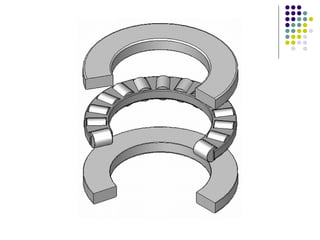
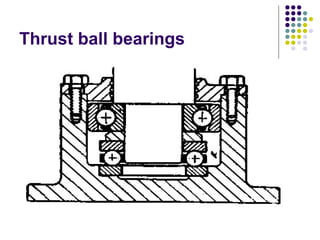
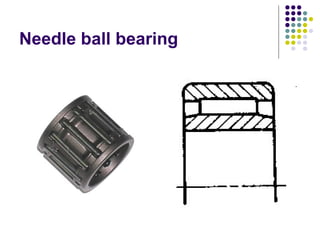
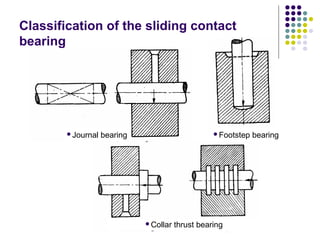
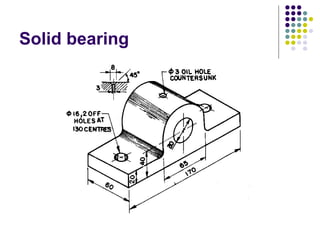
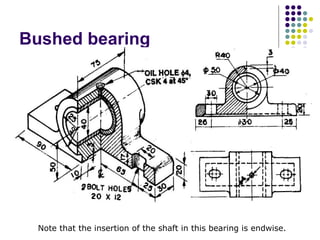
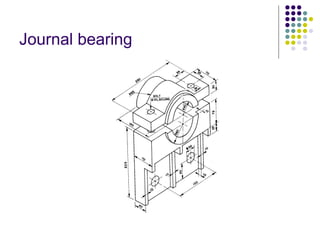
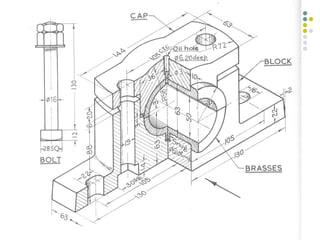
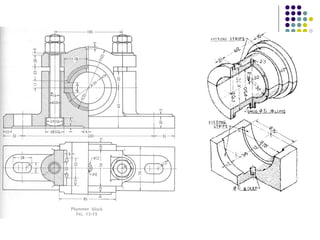
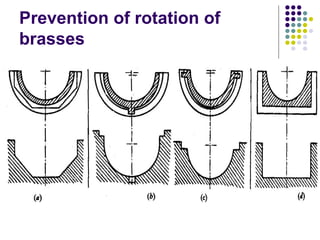
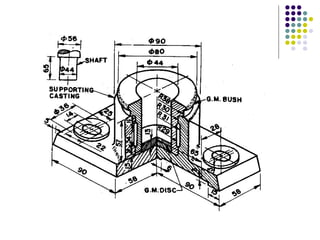
Bearings support rotating shafts and allow them to rotate with minimal friction. There are two main types: plain/slider bearings where the shaft slides against the bearing, and rolling element bearings like ball or roller bearings where balls or rollers allow the shaft and bearing to roll against each other with lower friction. Rolling element bearings have lower starting torque needs and friction compared to plain bearings. Journal, footstep, and thrust bearings are types of plain bearings that support axial or radial loads on vertical or horizontal shafts. Proper lubrication is important for all bearing types to reduce friction.