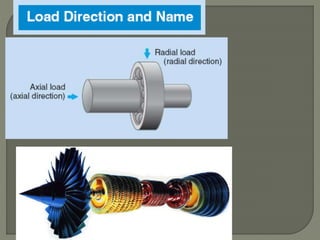
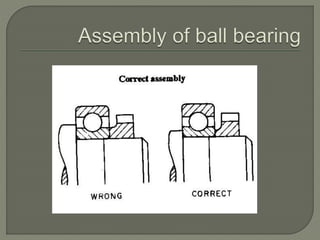
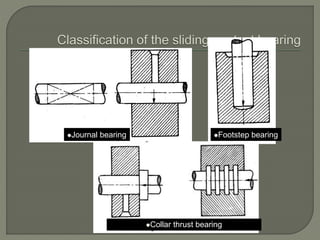
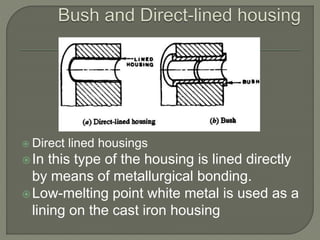
The document discusses the functions, classifications, and types of bearings, highlighting the differences between sliding contact bearings and rolling or anti-friction bearings. It emphasizes the importance of bearings in providing support and facilitating power transmission in rotating shafts, as well as detailing specific types like journal and thrust bearings and their respective applications. The text outlines the advantages and disadvantages of various bearing types, including high costs and lubrication requirements for effective functionality.