Embed presentation
Downloaded 105 times


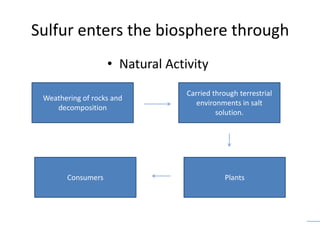
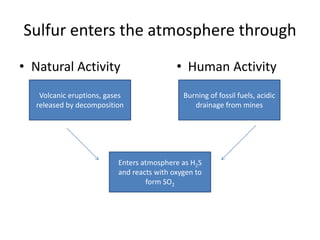
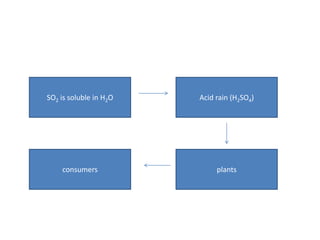
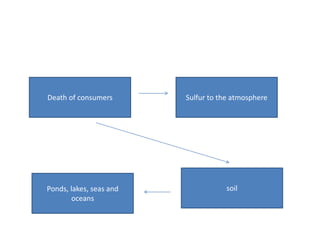
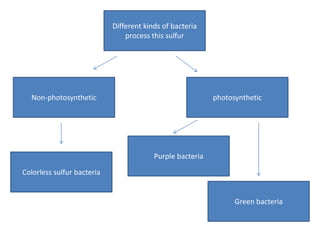
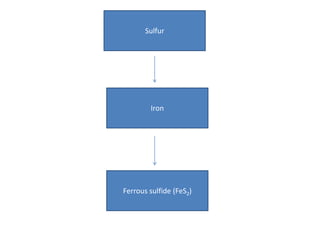
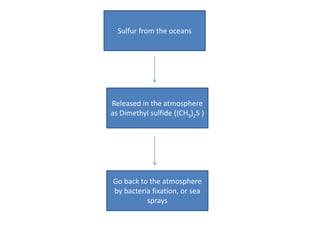
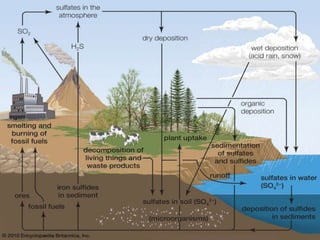

The sulfur cycle has both sedimentary and gaseous components. Sulfur enters the biosphere through natural processes like rock weathering and volcanic eruptions or through human activities like burning fossil fuels. It cycles through terrestrial and marine environments and can be found in soil, oceans, plants, and animals. Various bacteria play important roles in processing and transforming sulfur as it moves between the atmosphere, lithosphere, hydrosphere, and biosphere.









