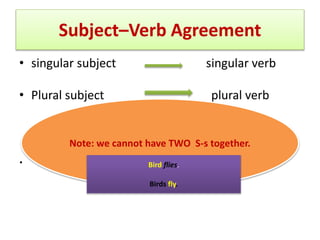
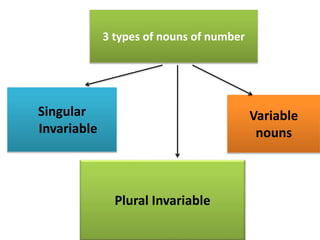
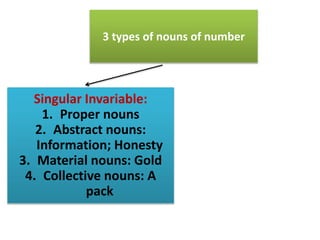
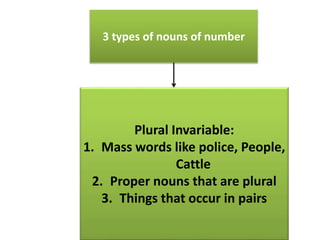
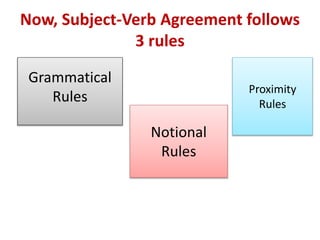
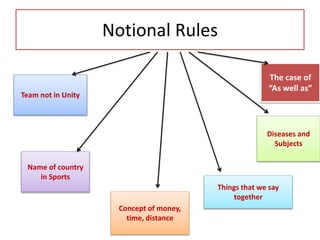
The document discusses subject-verb agreement and the different types of nouns. It covers three main types of nouns: singular invariable nouns, plural invariable nouns, and variable nouns. It also discusses the three main rules for subject-verb agreement: grammatical rules, notional rules, and rules of proximity. Notional rules are used when the subject is a collective noun where members are not united, the name of a country in sports, concepts involving amounts of time/money/distance, things that are said together, and names of diseases/subjects.




![Variable Nouns
Variable nouns are easy to recognize. They have
singular forms [taking singular], and plural
forms (taking plural verbs)
• A village gives you a closer life to nature.
• Villages are the worst victims of epidemic.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/subjectverbagreement-190606164642/85/Subject-verb-agreement-9-320.jpg)
![Solve
1. Homework ___ [is/are] boring.
2. The police ___ completed the investigation.
3. The Alps ___ in Italy.
4. A pair of Rayban sunglasses ___ around 8K.
5. Someone ___ left a bunch of flowers.
6. None of you __ going to the party.
7. Is there anyone who ___ not written
the notes?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/subjectverbagreement-190606164642/85/Subject-verb-agreement-10-320.jpg)


![Grammatical Rules: Special Cases
Some = Can be Singular or plural, depending on the context
Eg.:
1. Someone is standing over there.
[Some = Someone; Used for particular individuals]
2. Some never learn to behave.
[Some = some people; used in general statements]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/subjectverbagreement-190606164642/85/Subject-verb-agreement-14-320.jpg)




![IV.
Some things come together to form a concept. Take
for example: a dish.
Eg.: Cornflakes and milk is his favourite
breakfast.
Here, cornflakes + milk = a dish.
• Peace and harmony is important for domestic
life. [ peace and harmony = same thing]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/subjectverbagreement-190606164642/85/Subject-verb-agreement-21-320.jpg)






![Examples
• Either He or his friends are responsible for this.
[Friends> plural >near verb > Are]
• Either his friends or he is responsible.
Not only a criminal, but also the police get
beaten by mob.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/subjectverbagreement-190606164642/85/Subject-verb-agreement-28-320.jpg)




![“Of” Continued
Case 3: Percentages [Most; Some] before OF
In case of Most / Some, what we mean is %
percentage.
Most = 80%
Some = maybe 20 %
Percentage is like fraction. 20% = 1/5th](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/subjectverbagreement-190606164642/85/Subject-verb-agreement-33-320.jpg)



![A special note on “OF” contd.
Example:
1. Colours of the rainbow ARE beautiful.
[colours> plural]
2. The view of the rainbow IS beautiful.
[View> singular]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/subjectverbagreement-190606164642/85/Subject-verb-agreement-37-320.jpg)