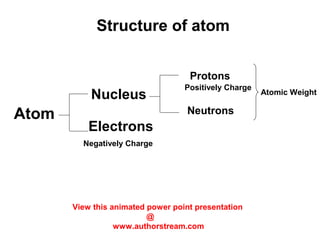
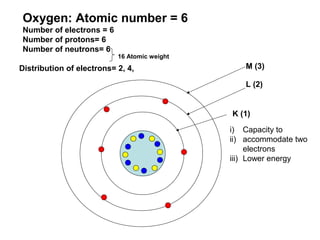
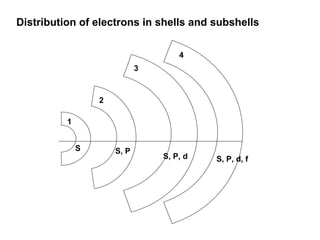
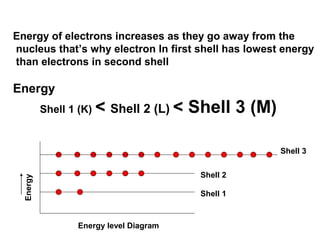
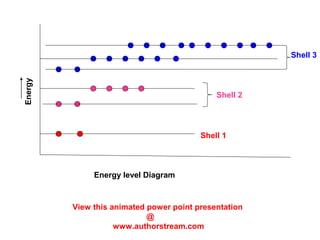
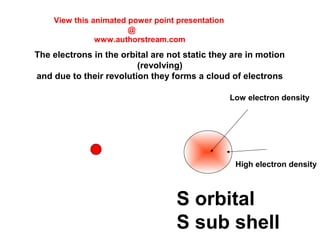
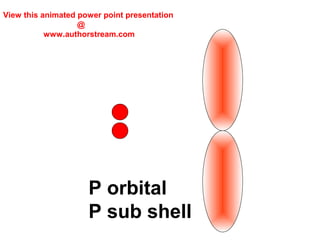
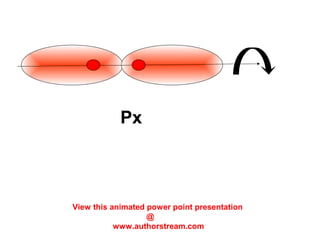
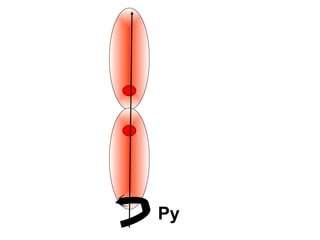
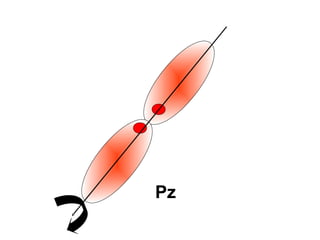
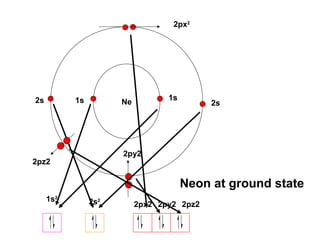
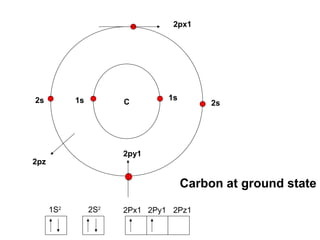
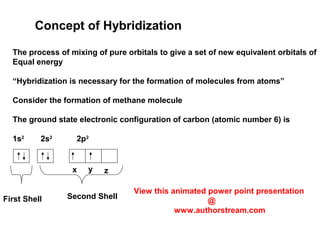
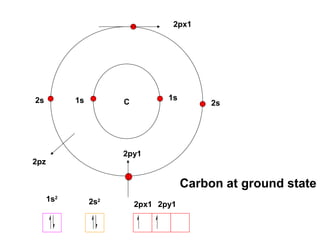
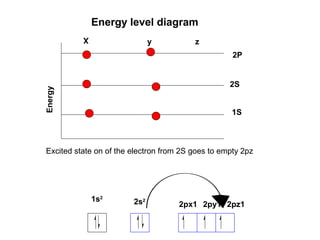
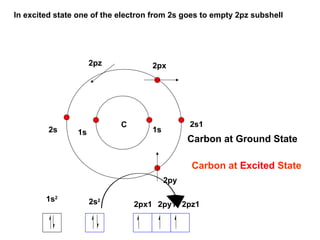
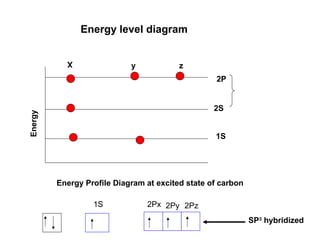
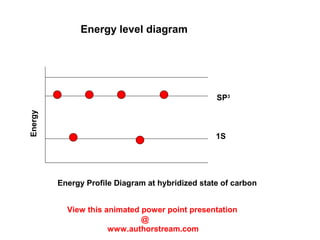
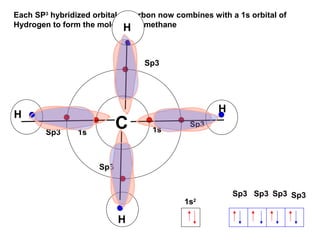
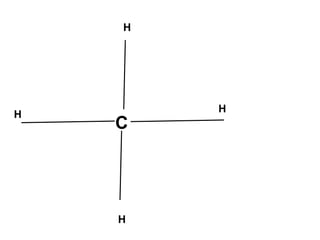
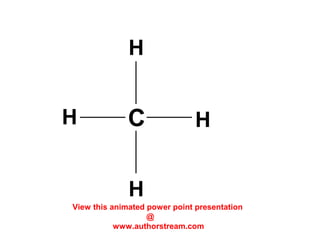
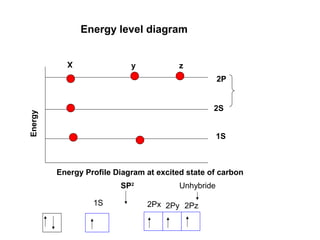
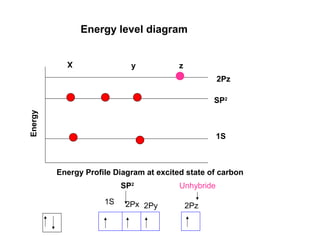
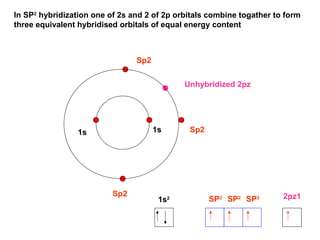
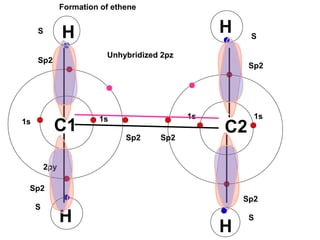
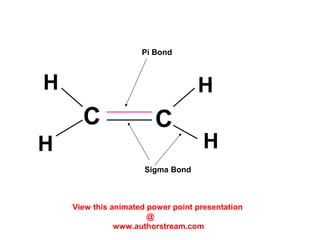
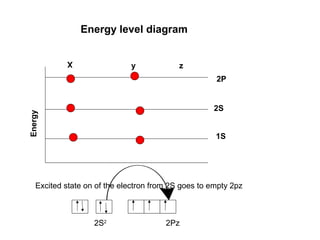
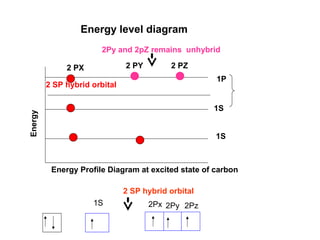
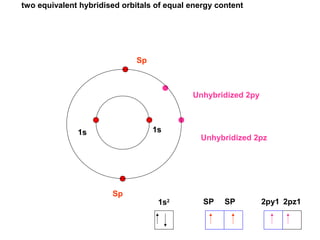
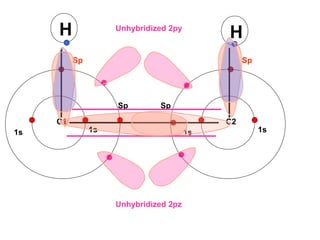
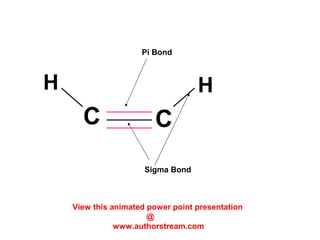
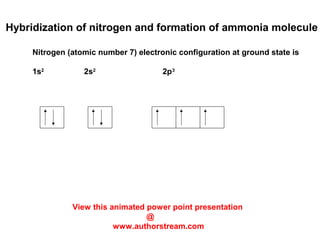
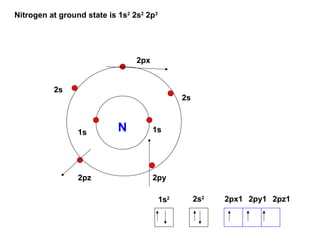
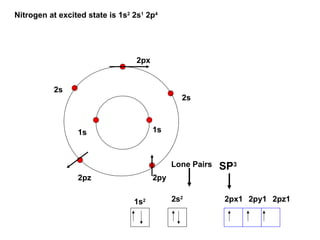
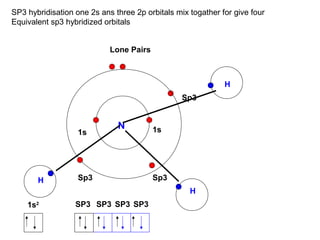
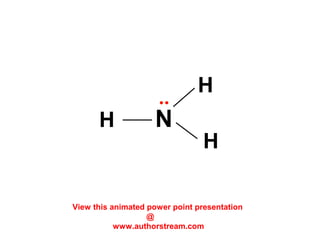
The document discusses the structure of atoms, including atomic orbitals and hybridization. It provides examples of sp, sp2, and sp3 hybridization in carbon and nitrogen. Sp hybridization forms two equivalent orbitals and is seen in acetylene. Sp2 hybridization forms three equivalent orbitals and one unhybridized p orbital, as seen in ethene. Sp3 hybridization forms four equivalent orbitals, as in methane and ammonia. The document is intended to explain these concepts for an audience learning about organic chemistry.