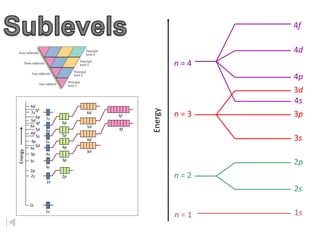
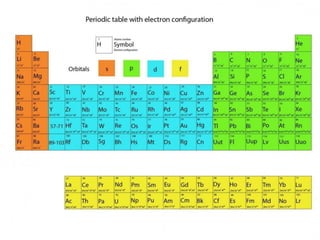
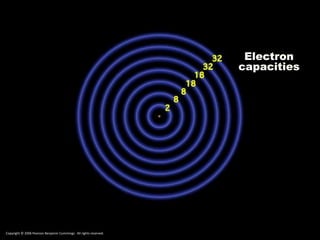
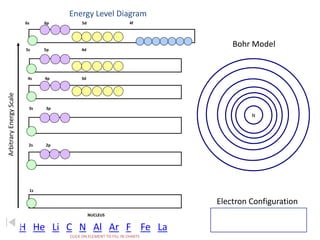
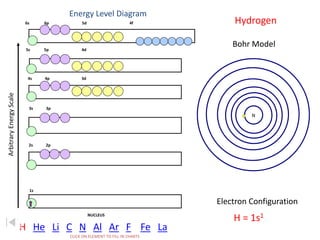
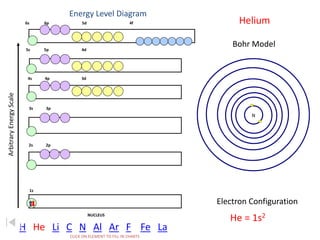
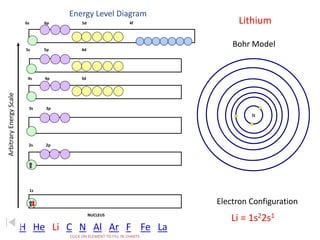
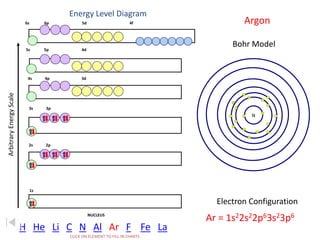
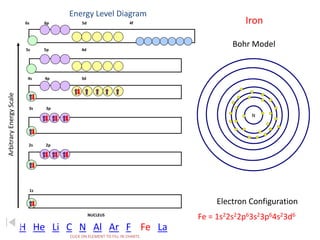
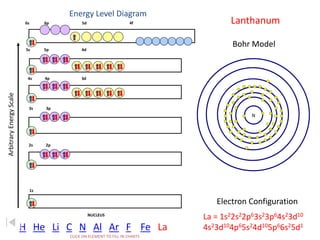
The document discusses electron configurations, which describe the arrangement of electrons in an atom's orbitals. Electron configurations are used to represent atoms in their ground state or as ions after gaining or losing electrons. Many of an element's physical and chemical properties can be correlated to its unique electron configuration, especially the valence electrons in the outermost shell. Knowing the electron configuration of an atom or ion allows us to better understand its bonding abilities, magnetism, and other chemical properties.





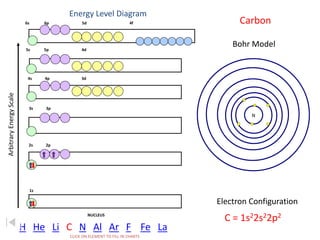
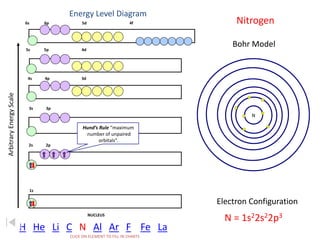
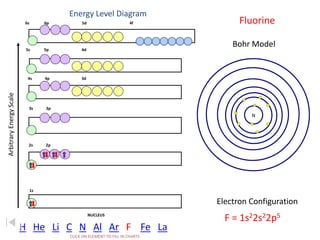
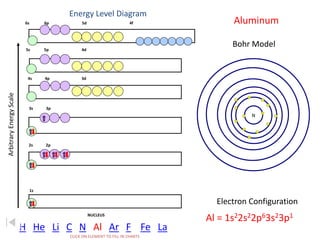
![neon's electron configuration (1s22s22p6)
[Ne] 3s1
third energy level
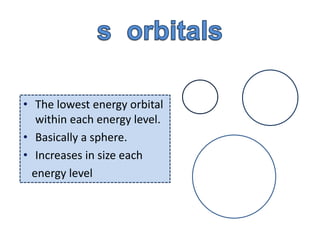
one electron in the s orbital
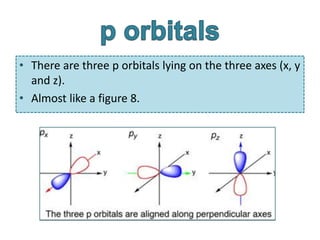
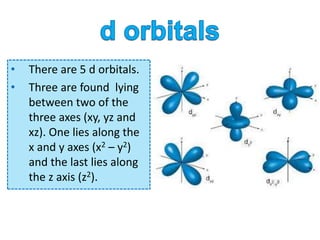
orbital shape
A
B
C
D
Na = [1s22s22p6] 3s1 electron configuration](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/electronconfig-141019083232-conversion-gate02/85/Electron-config-25-320.jpg)