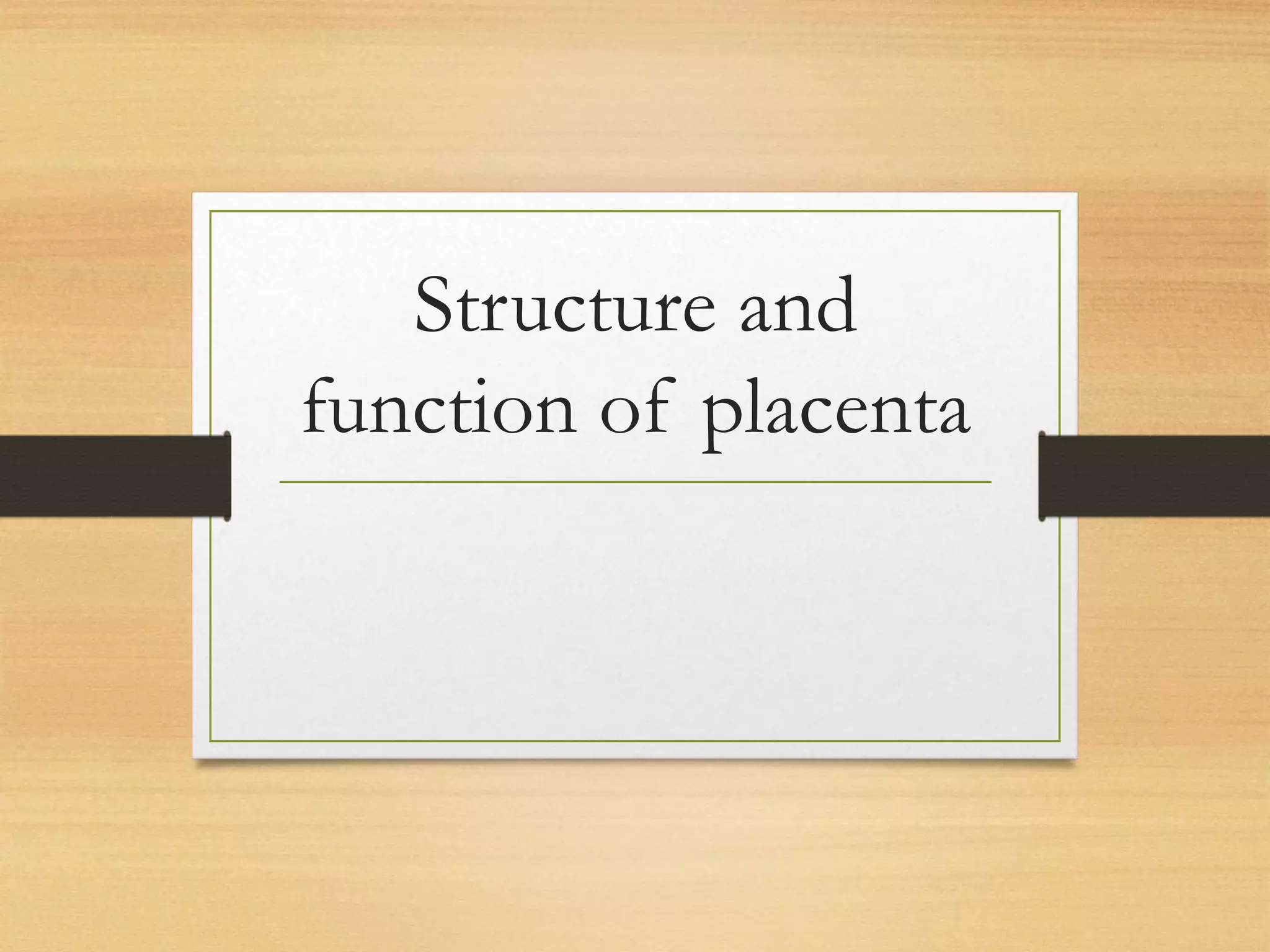
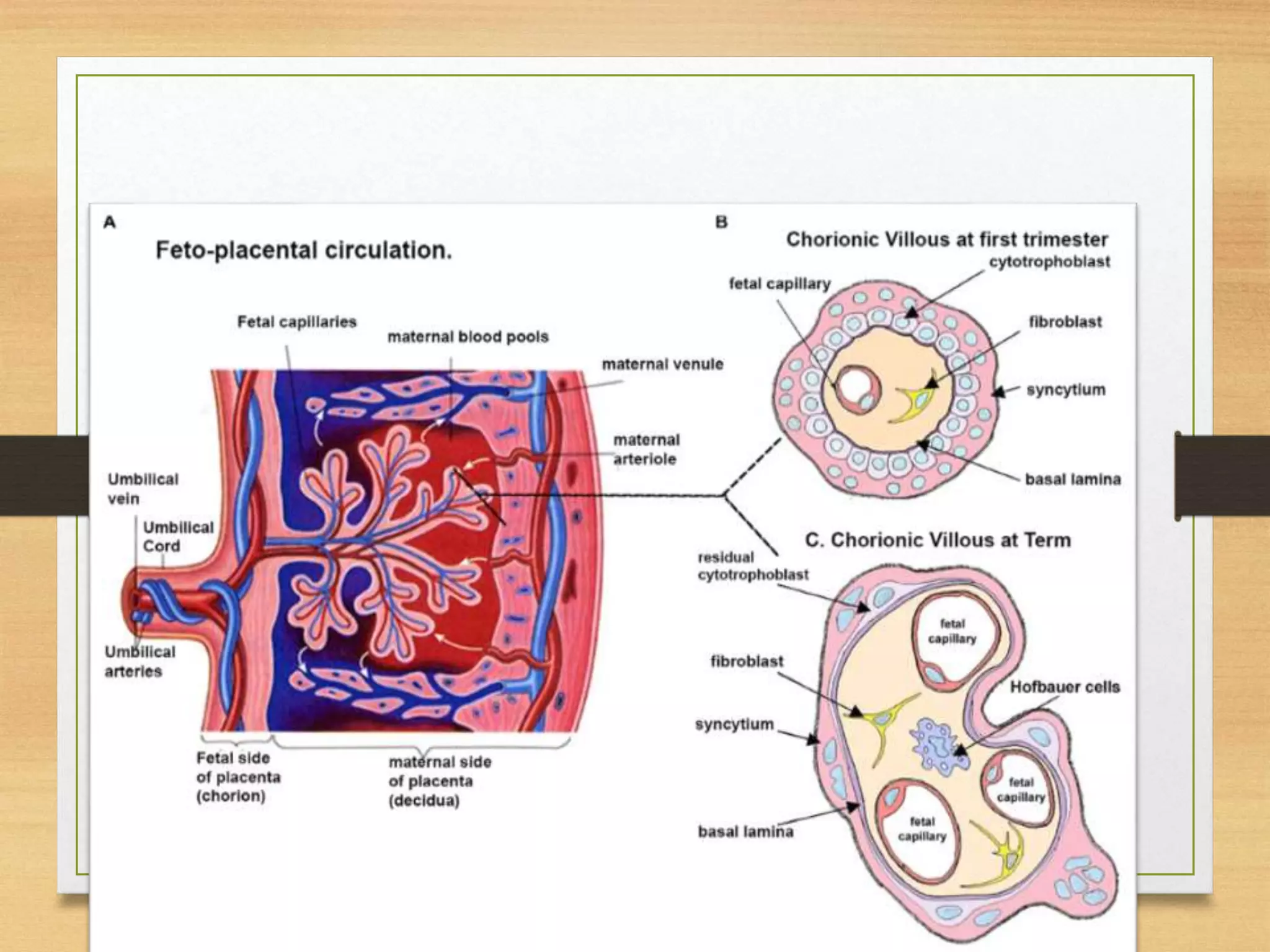
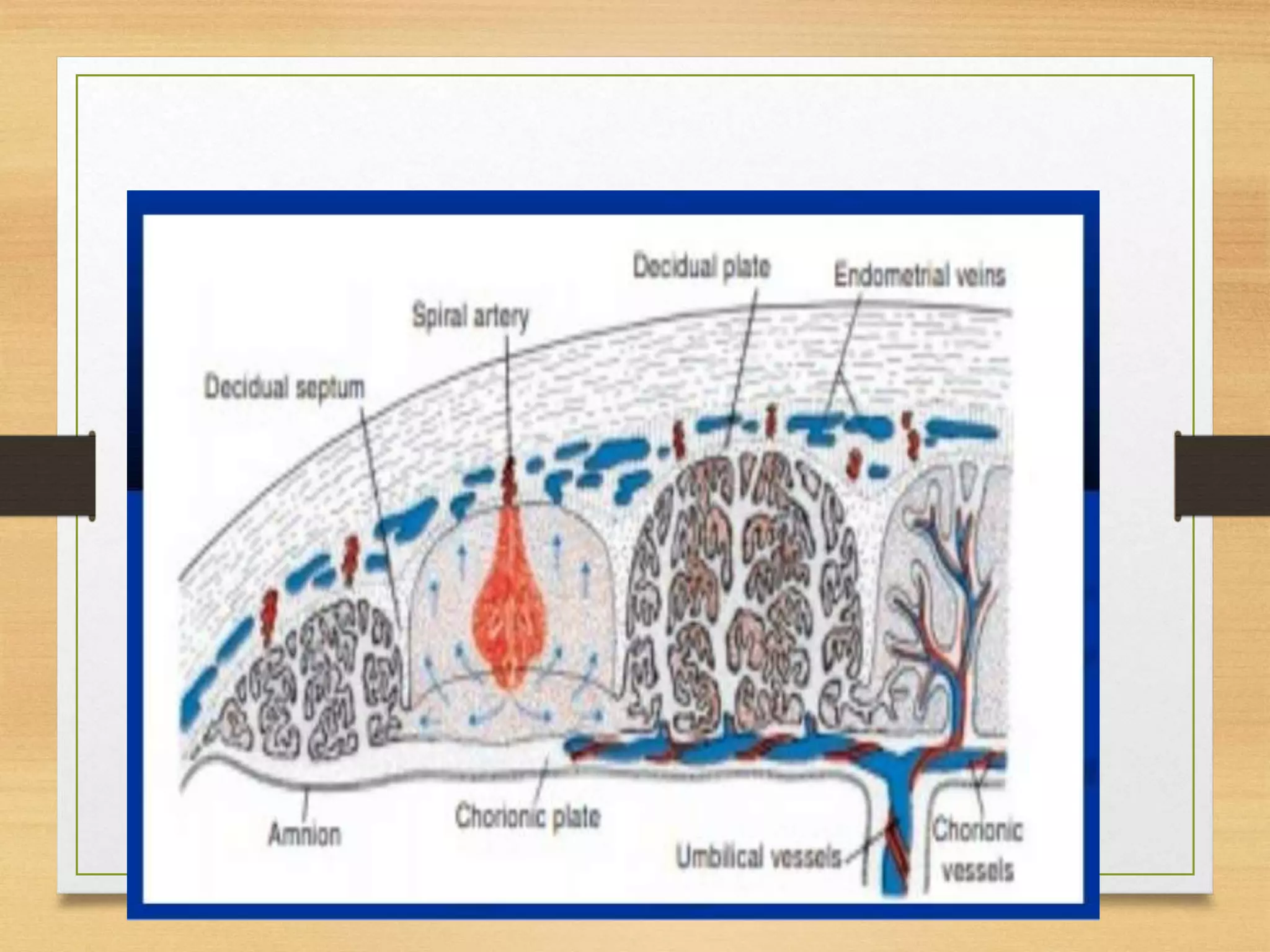
The placenta has fetal and maternal portions separated by chorionic and decidual plates. Between the plates are intervillous spaces containing maternal blood. During months 4-5, decidual septa divide the placenta into compartments called cotyledons. The placenta exchanges gases, nutrients, electrolytes and antibodies between mother and fetus. It also produces hormones like progesterone and estrogen to maintain pregnancy.