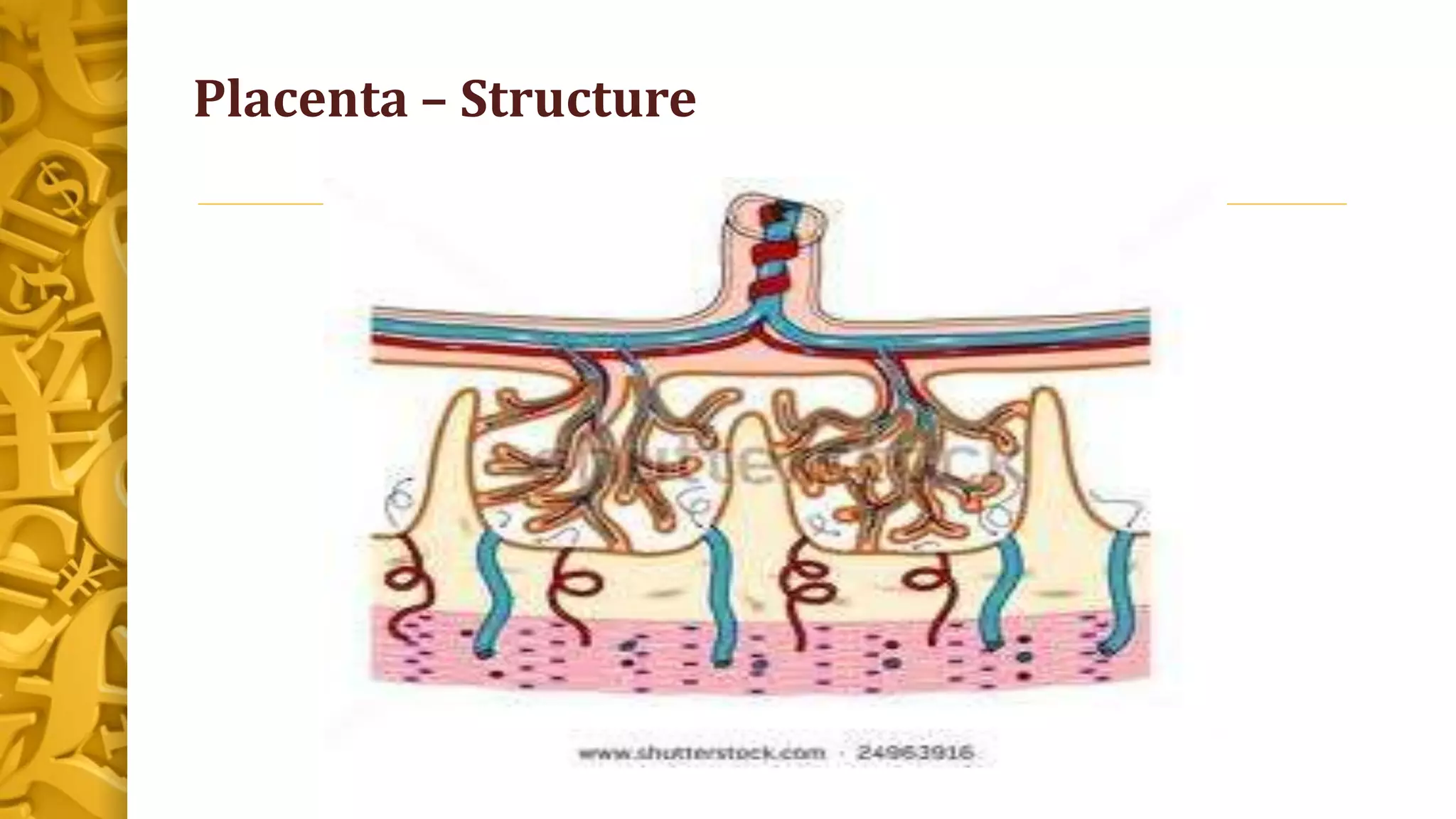
The placenta develops from small projections called chorionic villi on the blastocyst that proliferate and erode into the walls of maternal blood vessels by the 17th day of gestation. By 10 weeks of gestation, the placenta has fully developed and each villus and its branches form cotyledons that allow for respiratory, nutritive, excretory, and endocrine functions by mechanisms like diffusion, active transport, and phagocytosis. The mature placenta is a discoid structure weighing around 500g that is the site of gas, nutrient, waste, and antibody exchange between mother and fetus.