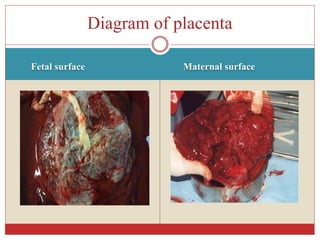
The document provides information about the placenta, including its definition, characteristics, development, structure, functions, and conclusions. It defines the placenta as the structure developed in the pregnant uterus through which the fetus derives nutrition and establishes a connection between the mother and fetus via the umbilical cord. Key points covered include that the placenta is discoid, hemochorial and deciduate in nature. It develops from 6-12 weeks of gestation from the chorion frondosum and decidua basalis. At term, it is circular, 15-20cm in diameter, and weighs about 500g. Its functions include the transfer of nutrients and oxygen to the fetus, excretion of fetal waste