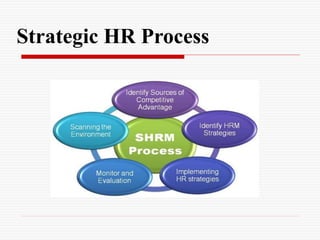
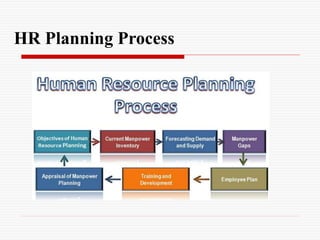
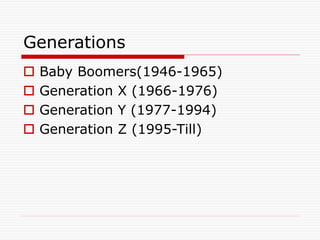
The document discusses the strategic role of human resource management. It outlines the strategic HR planning process which includes scanning the external and internal environment, identifying sources of competitive advantage, developing HR strategies, implementing strategies, and monitoring/evaluating performance. It also discusses the HR planning process of determining objectives, analyzing current staffing, forecasting needs, analyzing gaps, developing employment/action plans, providing training, and appraising the process. Finally, it outlines the evolving roles of HR managers in areas like recruitment, training, compensation, workplace safety, and employee relations.