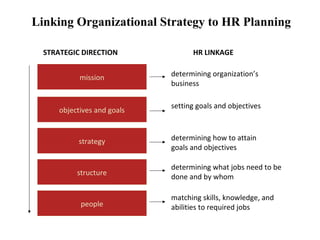
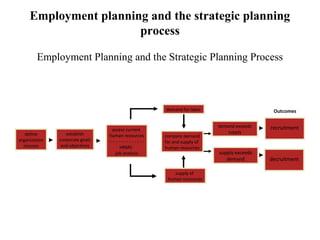
Human resource planning is a process by which an organization ensures it has the right number and type of employees with the necessary skills and abilities to implement organizational strategies and achieve objectives. It involves assessing the current workforce, determining future labor demand and supply, and matching them to identify any gaps. Key aspects of HR planning include conducting a job analysis, developing succession plans, forecasting future needs and availability of workers, and integrating planning with the organization's overall strategic direction. The goal is to competitively position the organization by having a workforce that can adapt to changing business requirements.