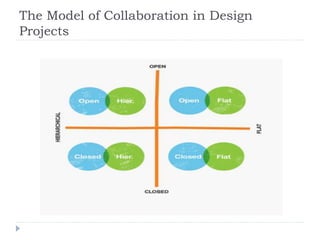
This document discusses design collaboration and the key elements involved. It describes collaboration as involving motivation, diversity, sharing, communication, support, and problem solving. The design process is also outlined, involving discover, define, develop, and deliver phases. Different models of collaboration are presented, including open/hierarchical, open/flat, closed/hierarchical, and closed/flat. Social networking technologies and mechanisms for conversation, coordination, and collaborative ethnography are also covered.