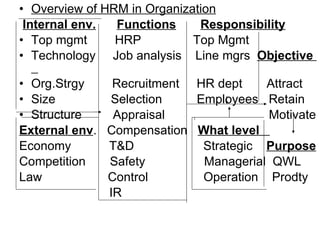
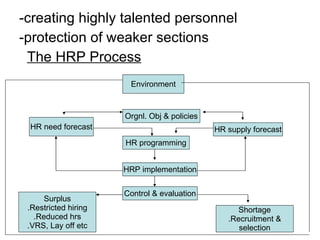
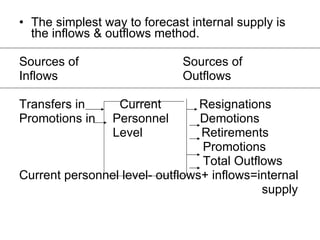
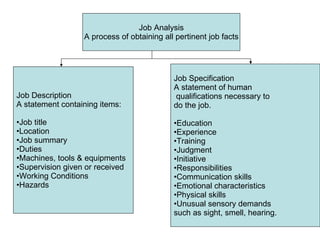
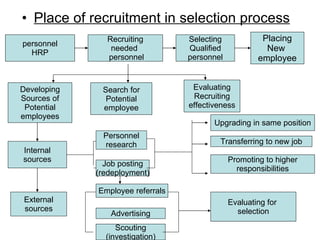
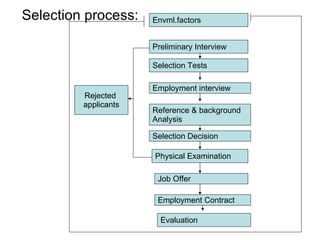
The document provides an introduction to human resource management (HRM). It discusses the key activities of HRM including human resource planning, recruitment, selection, training and development, performance appraisal, compensation, and employee welfare. It also covers the importance of HRM for organizations, individuals, and society. Different models of HRM and its objectives and functions within an organization are described. The processes of job analysis, recruitment, and selection are also summarized.