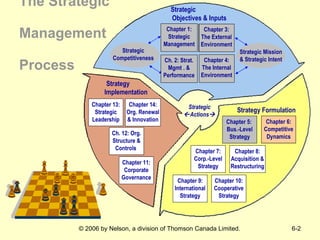
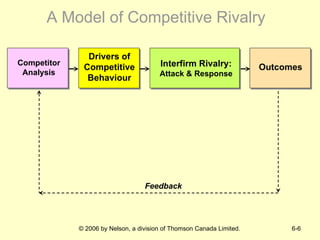
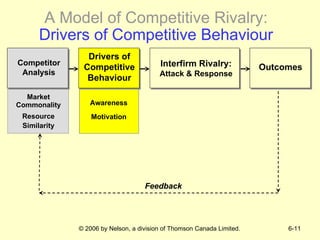
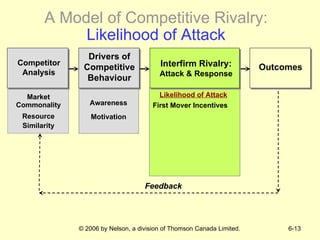
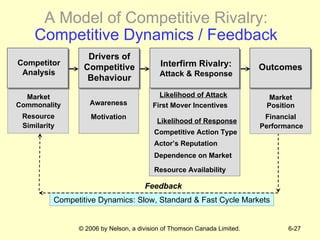
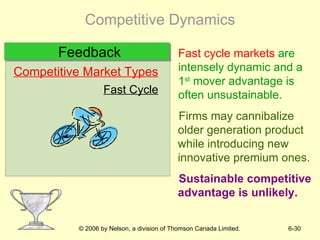
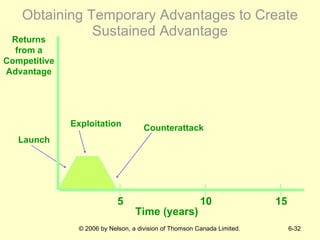
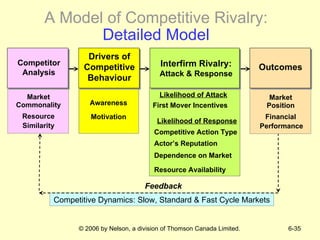
The document discusses competitive dynamics and rivalry between firms. It defines key concepts like competitors, competitive behavior, and competitive actions/responses. It presents a model of competitive rivalry that examines factors like market commonality, resource similarity, and the drivers, likelihood, and outcomes of attack and response behaviors between firms competing in an industry. It also describes different types of competitive dynamics that can occur in slow, standard, or fast-cycle markets and how they influence competitive advantage.