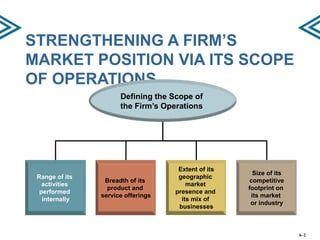
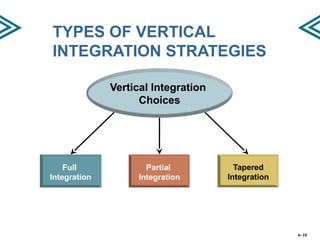
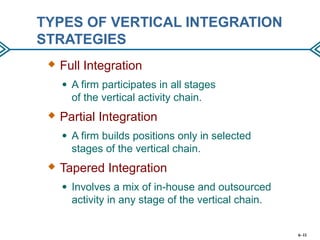
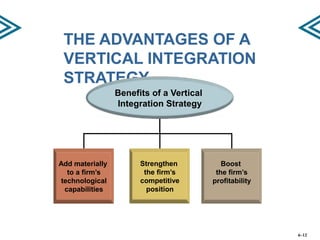
This document discusses strategies for strengthening a company's competitive position through expanding the scope of its operations. It describes horizontal and vertical integration strategies, as well as outsourcing. Horizontal integration involves merging with or acquiring companies in similar product/service areas to expand geographic coverage or product offerings. Vertical integration involves participating in multiple stages of the value chain, either fully, partially, or through a tapered approach. The benefits and risks of these strategies are outlined. Outsourcing involves farming out value chain activities to specialists to improve flexibility and reduce costs and risks, though it can also reduce control and resources.