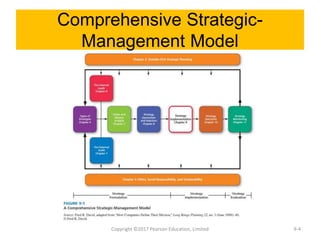
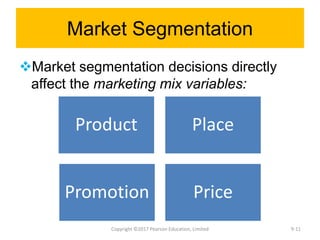
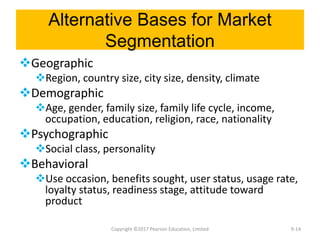
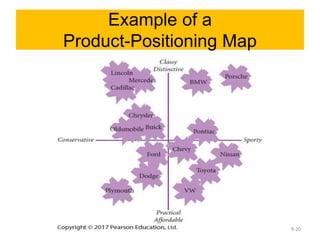
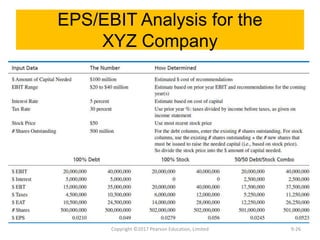
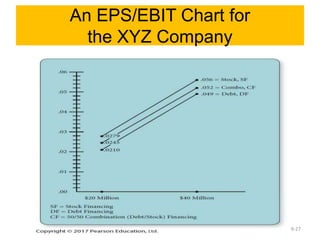
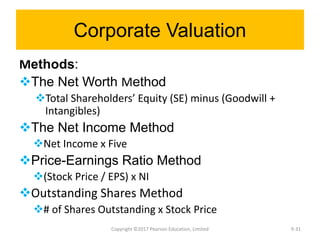
This document discusses strategy implementation tools including social media marketing, market segmentation, product positioning, finance and accounting issues, projected financial statements, corporate valuation methods, decisions around IPOs and cash management, and research and development. Specifically, it covers how these tools can help analyze strategies, acquire needed capital, evaluate strategic impacts, and determine a firm's value.