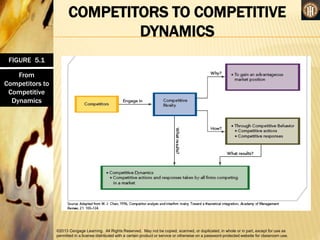
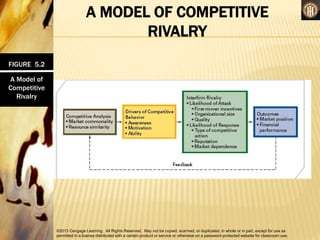
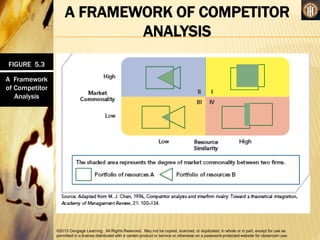
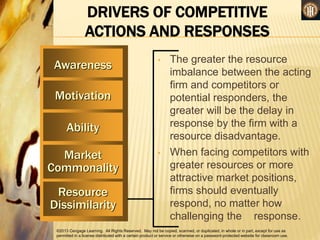
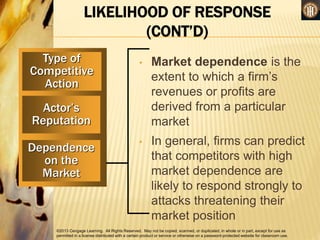
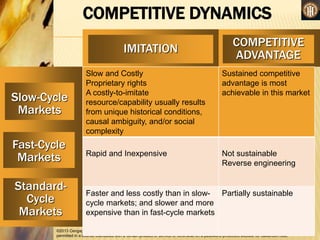
Competitive rivalry and dynamics involve the ongoing actions and responses between firms competing in the same markets. Competitors are firms offering similar products and targeting similar customers. Competitive rivalry increases during economic downturns as customers seek value and escapism. Analysis of competitors considers market commonality, such as competing in multiple markets, and resource similarity, like comparable capabilities. Drivers of competitive actions are a firm's awareness of mutual dependence with rivals and its motivation to act based on potential gains or losses.