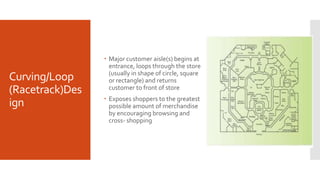
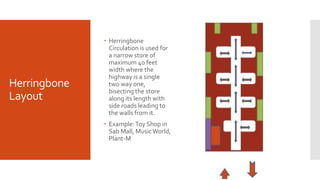
Store design involves both the exterior and interior of a store. The exterior includes elements like the store's location, signage, entrance, windows, and doors. The interior considers the layout, displays, and visual merchandising used. There are several common store layout types - free flow, grid, loop, spine, and herringbone - that each guide customer movement in different ways. Effective store design balances objectives like increasing sales while making products easy for customers to find.