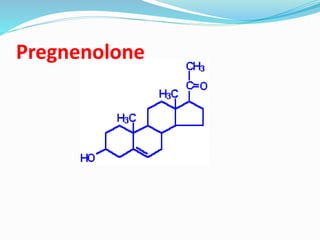
Steroid hormones, derived from cholesterol, are essential for various body functions and produced in the adrenal cortex, testis, and ovary. They are lipid-soluble, allowing them to diffuse across membranes shortly after synthesis and play critical roles in metabolism, reproductive functions, and responses to stress and inflammation. Key types include glucocorticoids, mineralocorticoids, androgens, estrogens, and progestogens, each with specific biological functions.