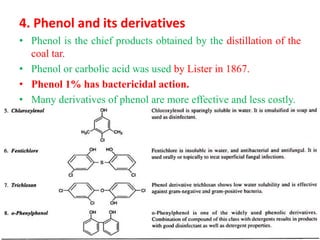
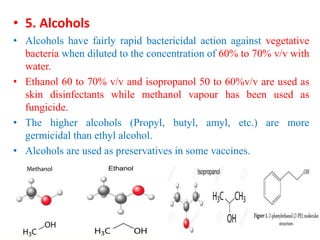
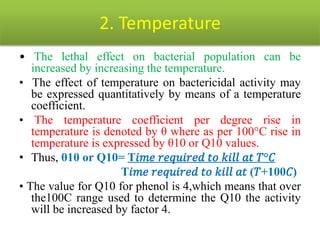
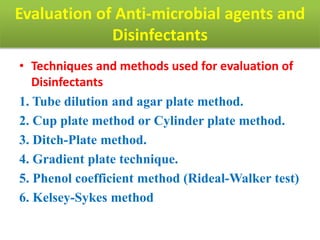
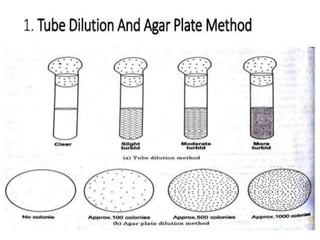
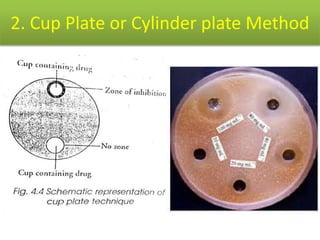
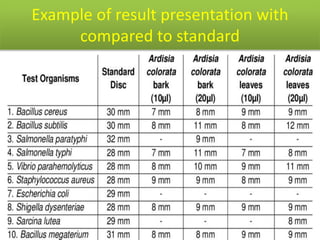
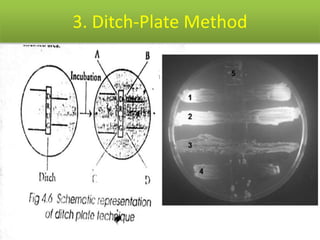
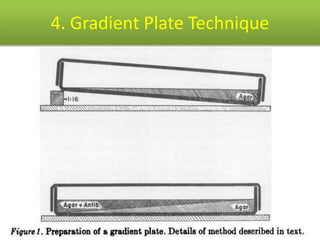
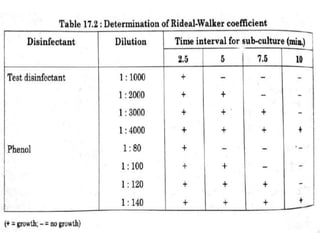
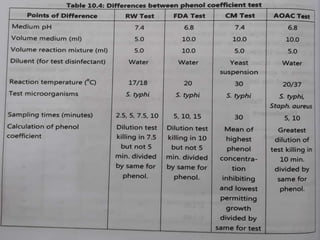
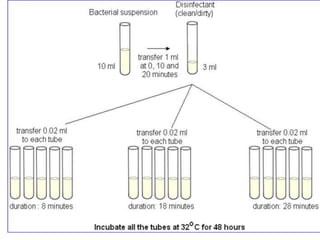
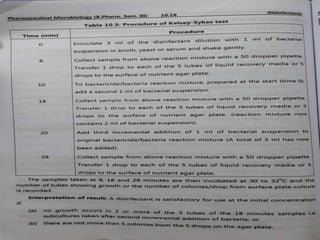
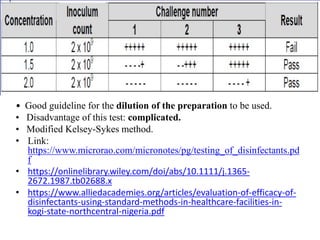
This document discusses disinfectants, providing information on their introduction, ideal characteristics, classification, modes of action, factors affecting disinfection, and methods of evaluation. It classifies disinfectants into nine main categories including acids, halogens, heavy metals, phenols, alcohols, aldehydes, quaternary ammonium compounds, dyes, and detergents/soaps. It also describes several common evaluation methods such as tube dilution, cup plate, gradient plate, and Kelsey-Sykes methods.