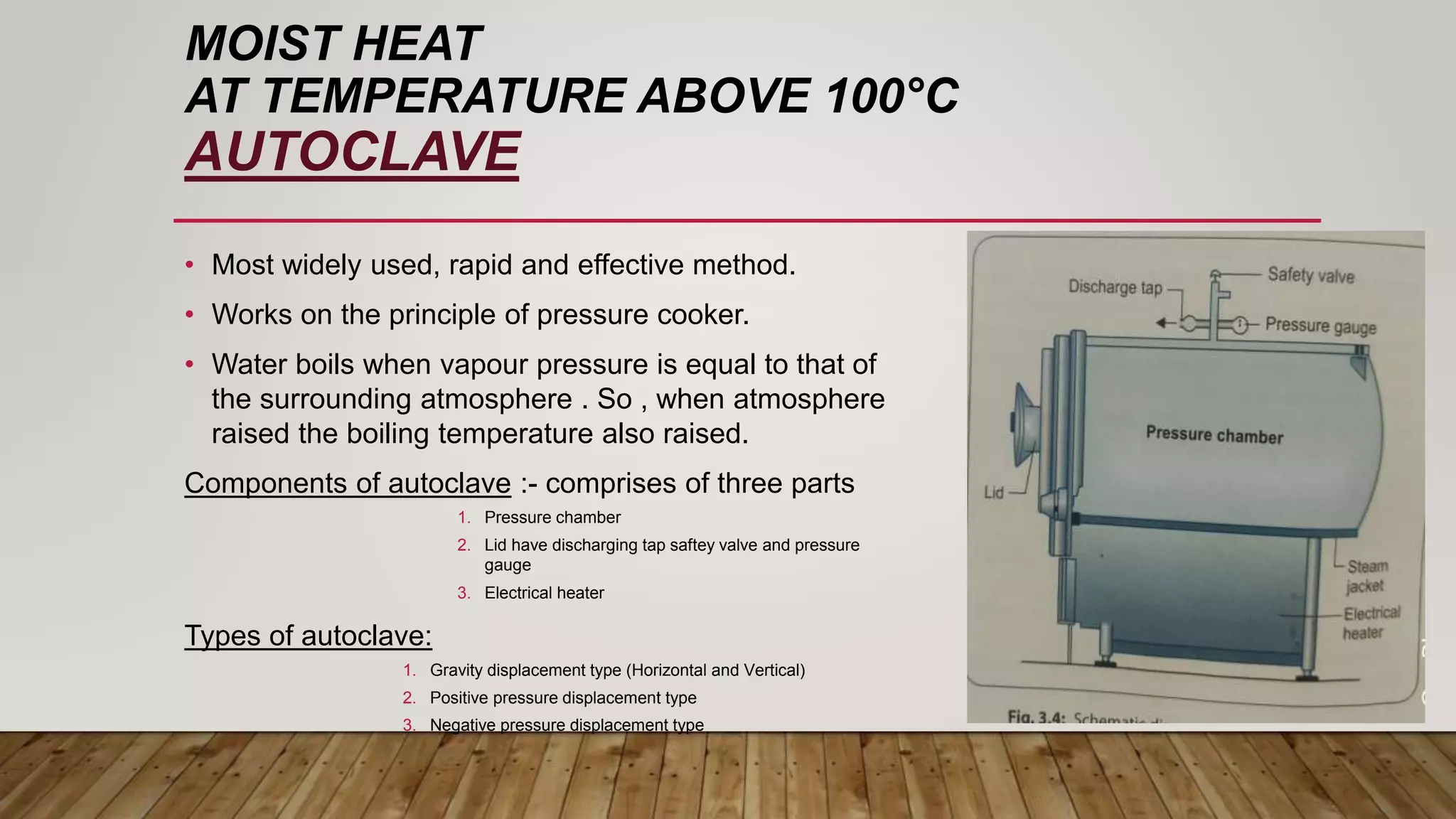
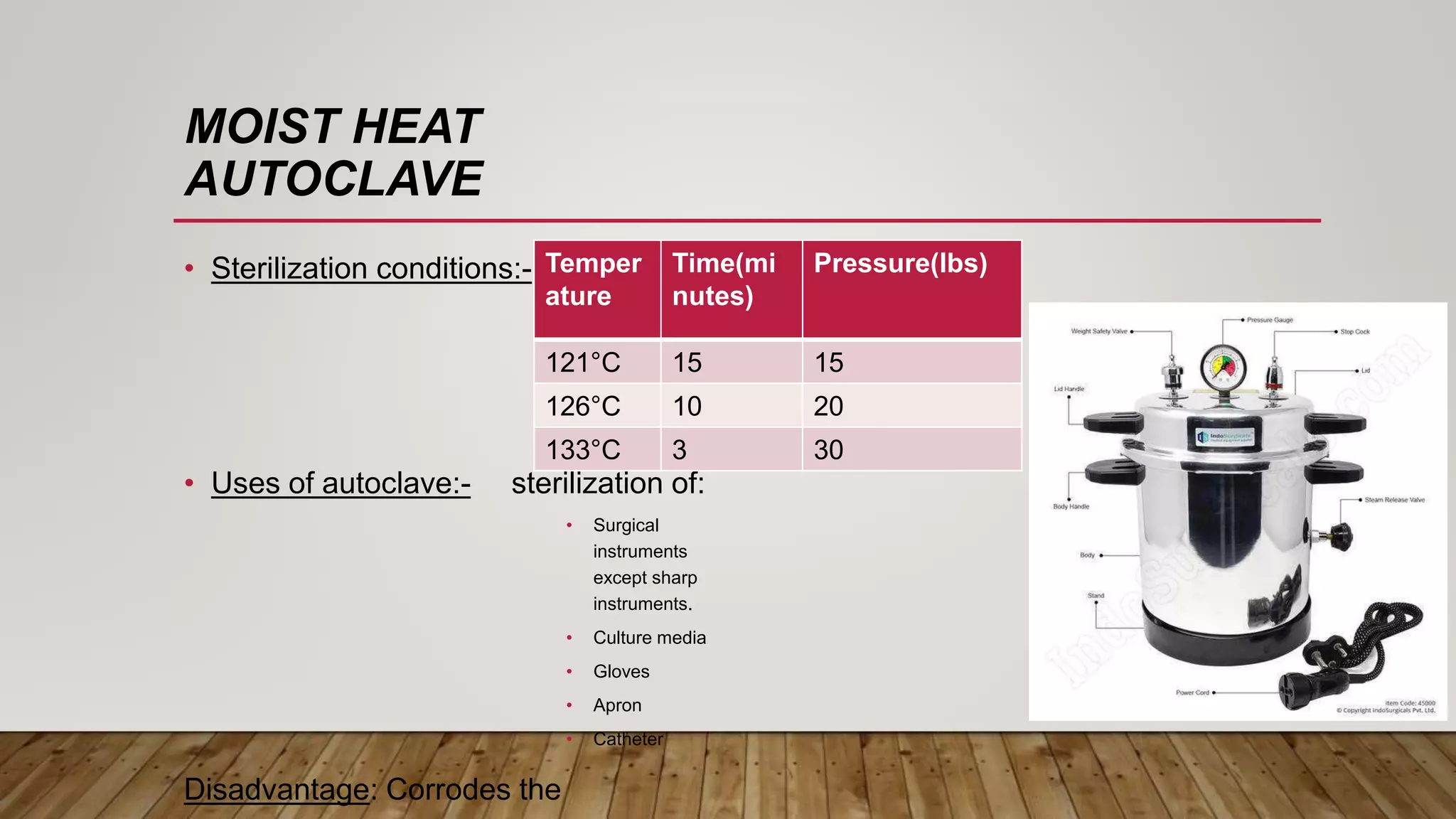
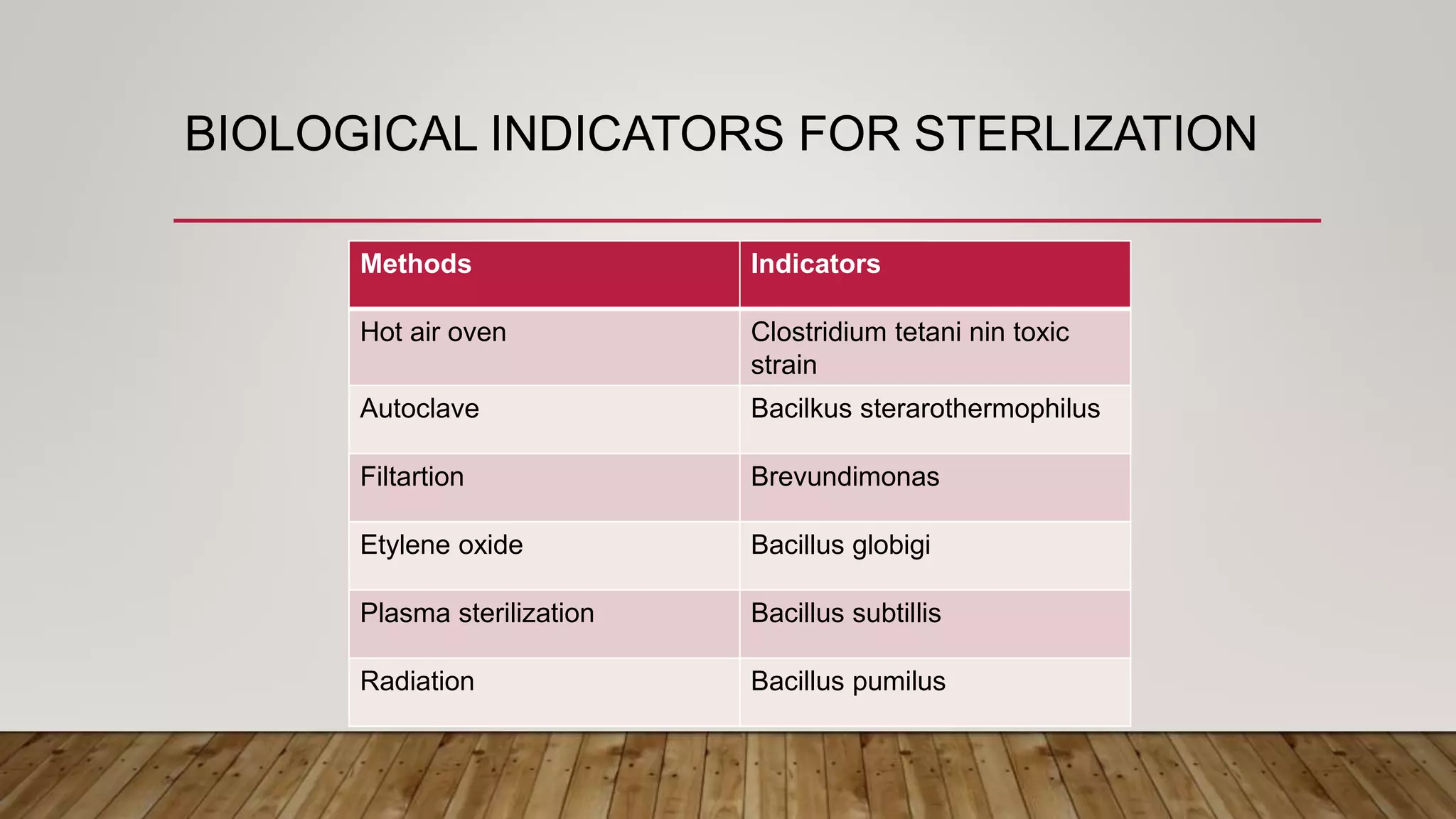
This document provides information about sterilization methods and guidelines. It defines sterilization as a process that destroys all microorganisms. It discusses factors that influence sterilization efficacy like organism load and resistance. Physical sterilization methods covered are heat, radiation, filtration and ultrasonic sterilization. Chemical methods discussed are aldehydes, oxidizing agents, gas sterilization and plasma sterilization. It also covers Spaulding's classification of medical devices and recommended sterilization methods for critical, semi-critical and non-critical devices.