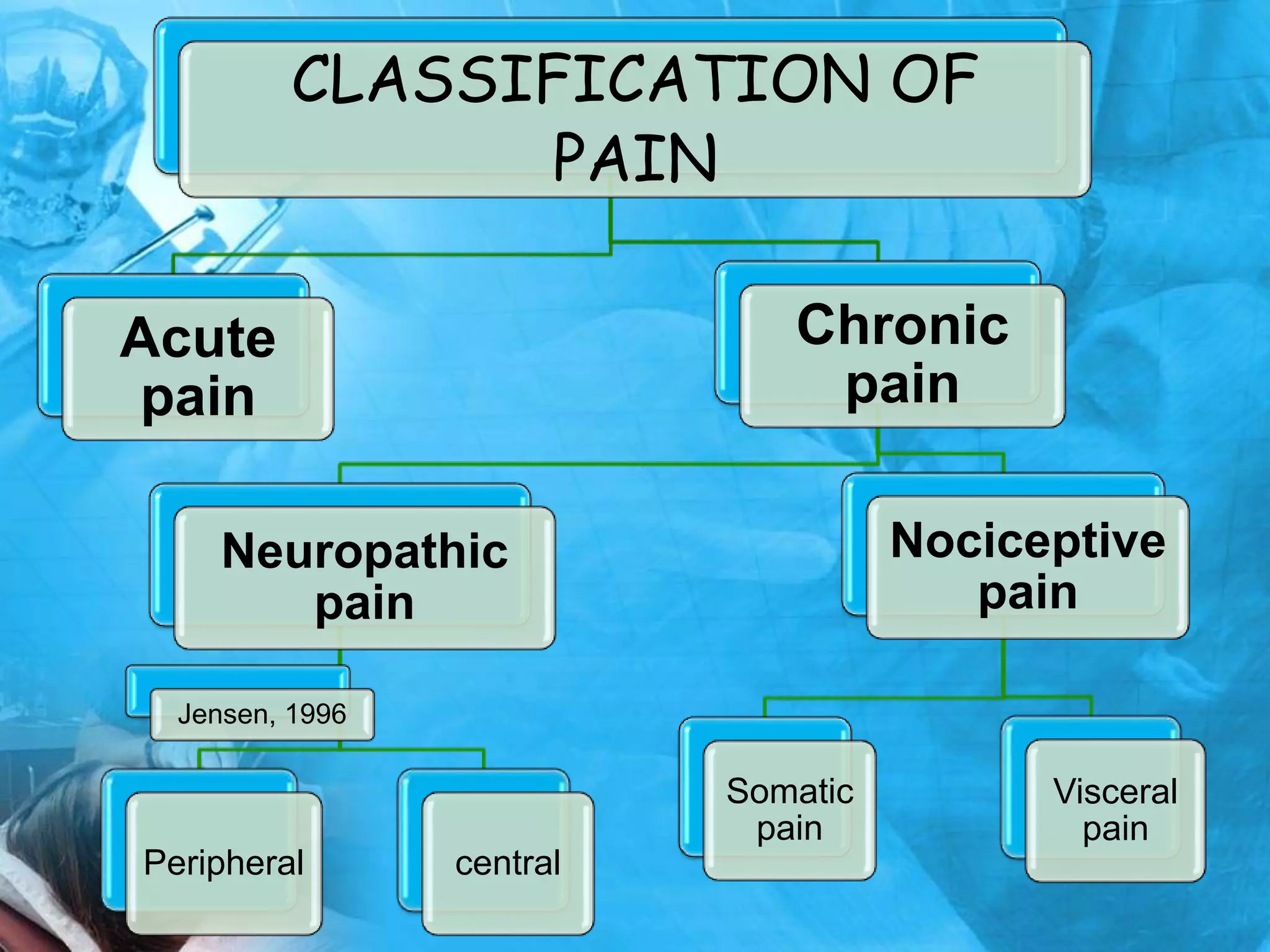
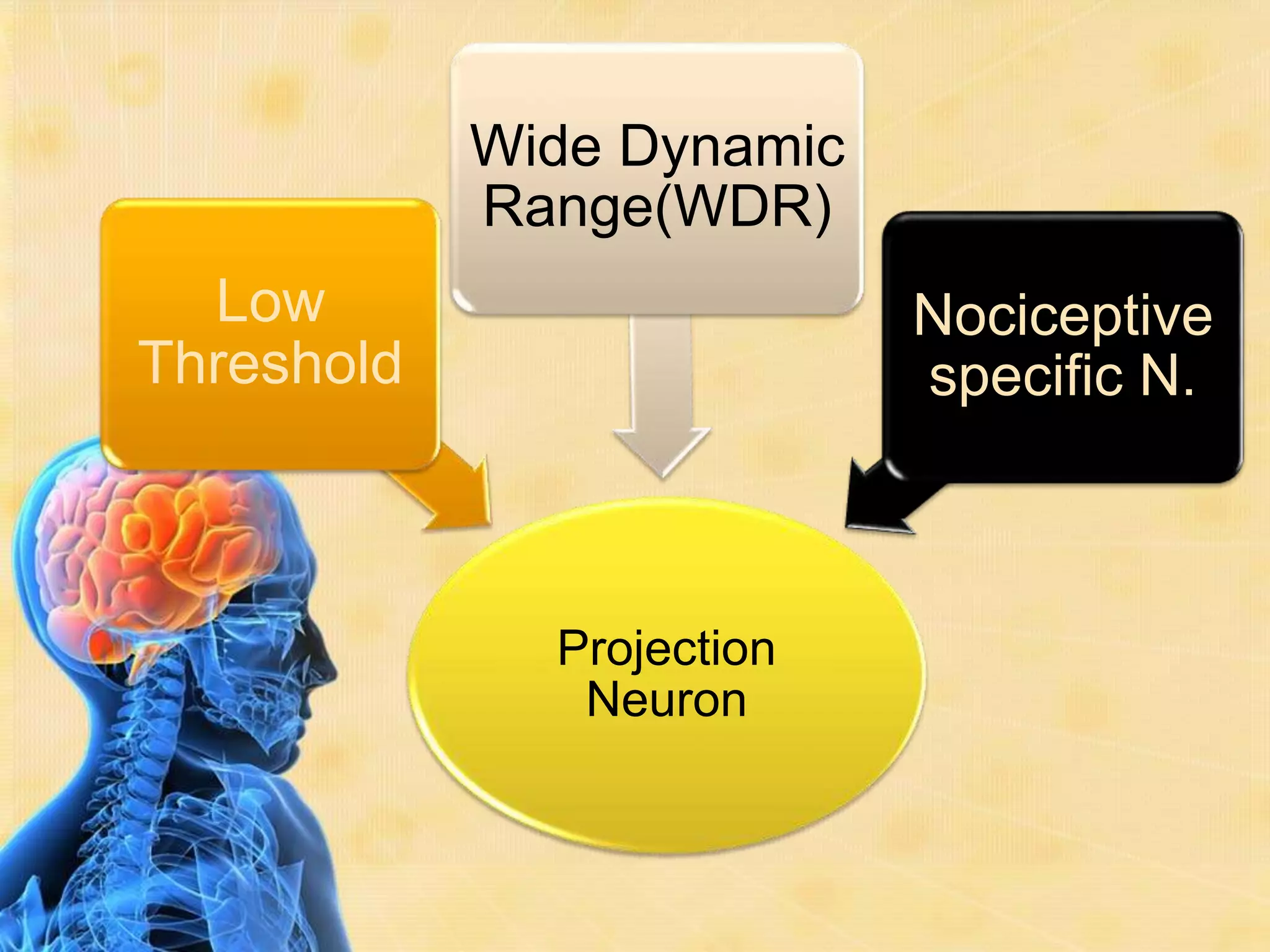
This document provides an overview of the physiology of pain. It begins with a brief history of pain theories, then defines pain and discusses its classification. The document outlines the mechanism of pain perception, including the roles of sensory receptors, neurons, and ascending and descending pain pathways in the spinal cord and brain. It also addresses factors that affect pain perception as well as electrophysiology concepts like action potentials. The document concludes by discussing pain in unborn children and referencing additional resources.