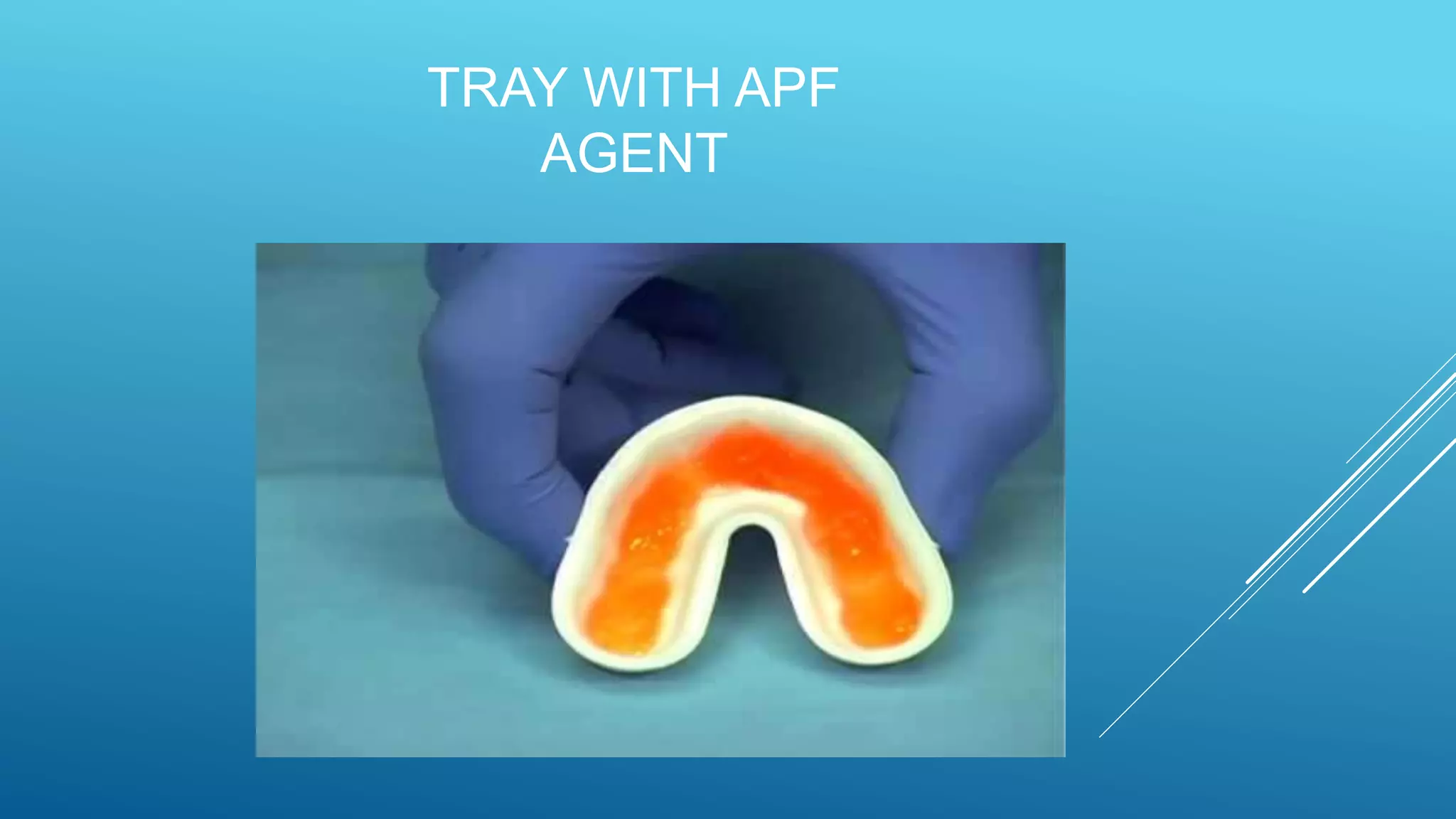
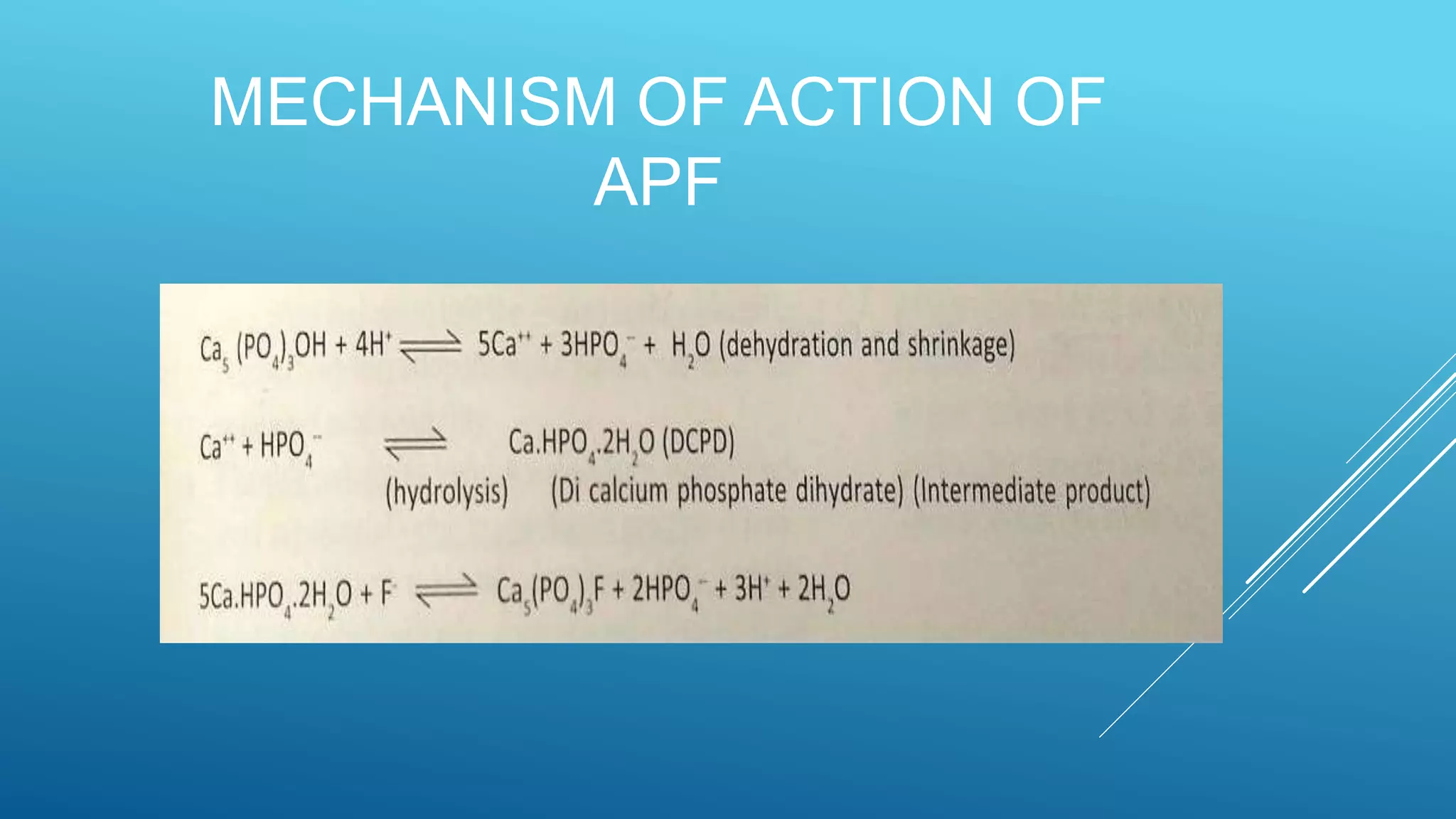
This document discusses acidulated phosphate fluoride (APF), a topical fluoride treatment used to prevent tooth decay. It is presented in two forms - a 1.23% fluoride solution with a pH of 3.0 or a gel with 1.23% fluoride and a pH between 4-5. APF is indicated for caries-active individuals and is applied using trays or cotton rolls, keeping the teeth wet for 4 minutes. It works by increasing fluoride uptake into enamel and providing topical fluoride to teeth. While effective, it has drawbacks like an acidic taste and potential to irritate tissues.

![APF-ACIDULATED PHOSPHATE
FLUORIDE
GUIDED BY: SUBMITTED BY:
DR. BHARATH BHUSHAN SIR SHASHWAT PANCHAL
DR. KHUSHBOO BARJATYA MA’AM BATCH: 2017-2018
DR. BINTI CHAND MA’AM ROLL NO: 63
DR. PREENE JUNEJA MA’AM POSTING BATCH: [G]
DR. ABHILASHA M. TRIPATHI
DR. HARIOM MEENA SIR](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/apf-acidulatedphosphatefluoride-200307074258/75/Apf-acidulated-phosphate-fluoride-2-2048.jpg)