This document provides an overview of stealth technology, including its history, types of signatures that stealth aims to reduce, and methods used. It discusses radar absorbent materials and structures, as well as techniques to decrease infrared, acoustic, visual and other signatures. Examples of stealth aircraft like the F-117 and ships are given. Advantages like reduced detection and disadvantages like high costs are outlined. India's developments of stealth helicopters and aircraft are summarized. The future potential of stealth, including South Korea's KF-X fighter, is also examined.



















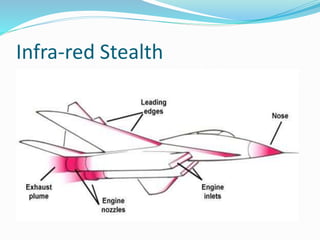
![Infrared Signature
Infra-red radiation are emitted by all matter above
absolute temperature zero.
Hot zones such as engine exhaust , wing surface
[friction due to air ] get heated which rather
increases the visibility.
These part should be kept cool as possible it can
be.
Option would be mixing of cool air with the hot
engine exhaust .](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/stealthtechnology-160206120149/85/Stealth-technology-23-320.jpg)