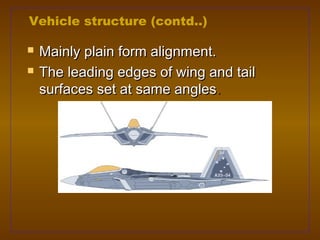
Stealth technology aims to make aircraft and vehicles difficult to detect on radar. It achieves this through shaping the vehicle to deflect radar waves, using radar absorbing materials to absorb radar signals, and minimizing heat emissions from engines. Key aspects of stealth technology include flat aircraft surfaces to deflect radar signals, re-entrant triangles and serrations in external airframes, and radar absorbing paints and materials. While stealth technology has advanced, it requires significant investment and its effectiveness in combat situations remains to be fully proven.