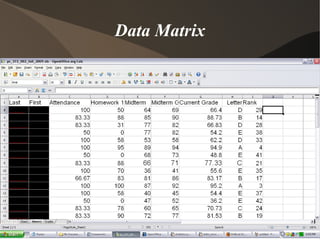
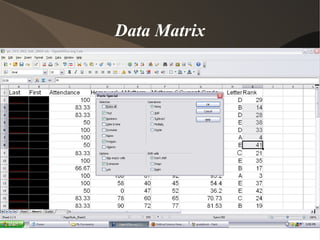
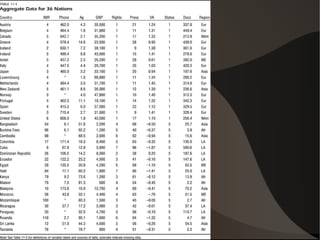
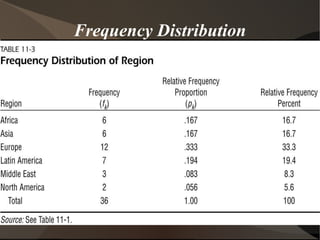
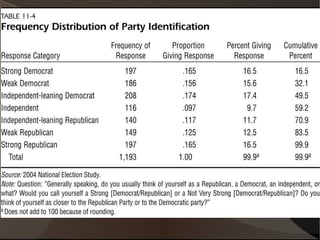
This document discusses key concepts in statistics. It introduces how data is organized in matrices and describes four data types: nominal, ordinal, interval, and ratio. It also discusses frequency distributions to describe variable values as proportions or percentages. Probability and odds are defined, where probability is the likelihood of an event and odds are expressed as ratios comparing outcomes. Key statistical concepts like descriptive statistics, inference, and different ways of organizing data are covered at a high level.