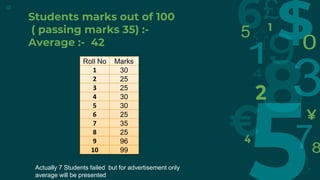
The document provides an overview of statistics, defining it as the collection, presentation, analysis, and interpretation of numerical data. It distinguishes between descriptive statistics, which present numerical data, and inferential statistics, which make inferences about populations based on sample observations. Additionally, it highlights the applications and limitations of statistics, emphasizing issues related to data misinterpretation and reliance on small sample sizes.