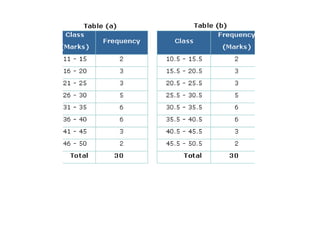
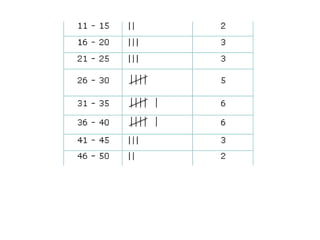
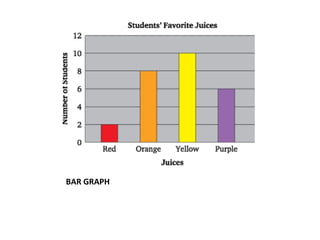
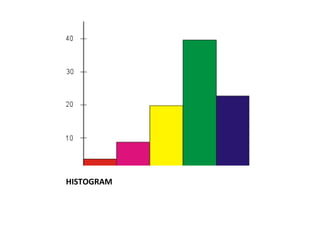
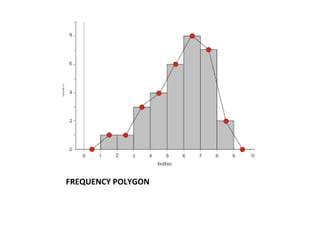
This document provides an introduction to basic statistical concepts. It defines statistics as the study of numerical data and notes that while it uses mathematics, statistics arises from practical situations. The founder of modern statistics is identified as Ronald Fisher. Primary data is defined as data collected directly from sources, while secondary data is collected from existing sources. Key concepts explained include range, frequency, frequency tables, bar graphs, histograms, frequency polygons, and measures of central tendency like mean, median and mode. An example is provided to illustrate calculating these measures.