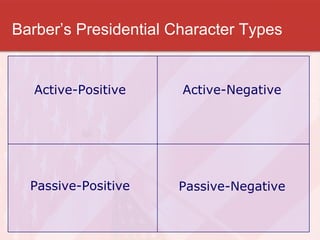
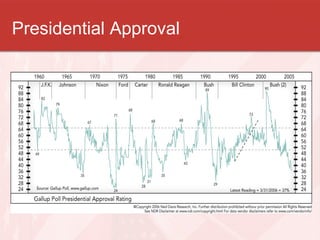
This document discusses models of presidential power and the modern presidency. It describes the Whig Model, which favors a passive approach, and the Stewardship Model, which favors an active leadership role. It also outlines Barber's four presidential character types: active-positive, active-negative, passive-positive, and passive-negative. Additionally, it examines informal presidential powers like the ability to persuade and "go public," and discusses the importance of public approval and qualities of great presidents like vision and consensus-building. The role of the vice presidency has increased over time from an insignificant position to one with more responsibilities.