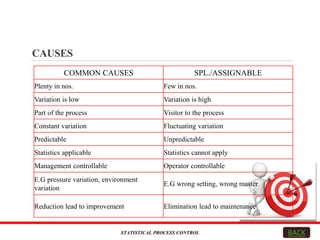
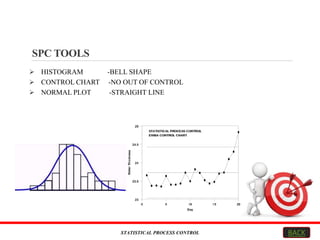
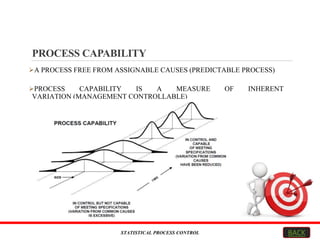
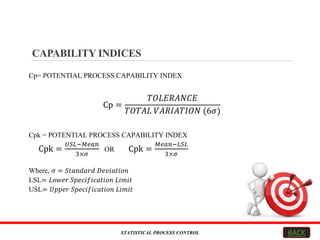
This document explains Statistical Process Control (SPC), focusing on its objectives, methodologies, tools, and applications across various industries. SPC aims to enhance product quality and efficiency by monitoring processes, reducing waste, and improving customer satisfaction. Key tools include control charts, and the method is widely applicable in fields like automotive, healthcare, and software engineering.