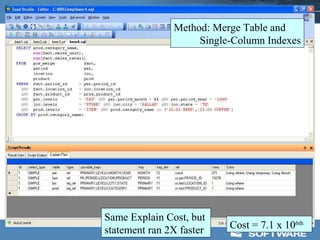
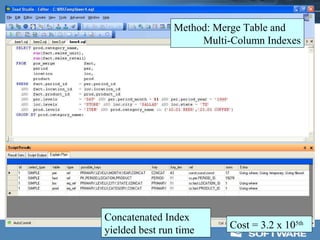
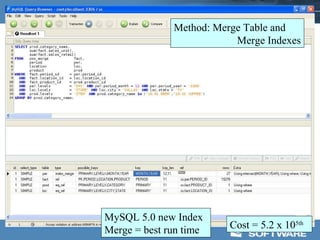
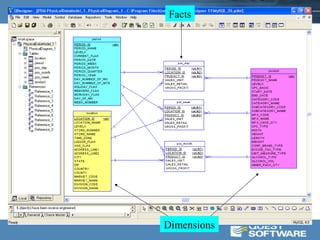
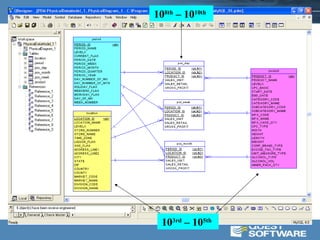
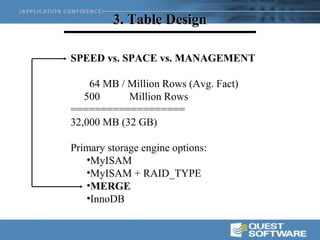
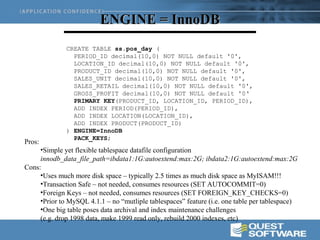
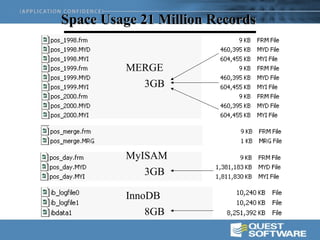
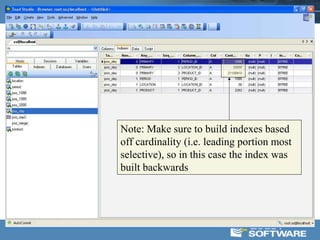
This document discusses optimizing data warehouse star schemas with MySQL. It provides tips for database design including using a star schema approach with dimension and fact tables. It recommends MySQL 5.x, optimizing the MySQL configuration file, designing tables and indexes effectively, using the correct data loading architecture, analyzing tables, writing efficient query styles, and examining explain plans. Optimizing these areas can help ensure fast query performance from large data warehouses built with MySQL.













![MyISAM Key Cache Magic
1. Utilize two key caches:
•Default Key Cache – for fact table indexes
•Hot Key Cache – for dimension key indexes
command-line option:
shell> mysqld --hot_cache.key_buffer_size=16M
option file:
[mysqld]
hot_cache.key_buffer_size=16M
CACHE INDEX t1, t2, t3 IN hot_cache;
2. Pre-Load Dimension Indexes:
LOAD INDEX INTO CACHE t1, t2, t3 IGNORE LEAVES;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/starschema-mysql-130415073056-phpapp02/85/Star-schema-my-sql-21-320.jpg)