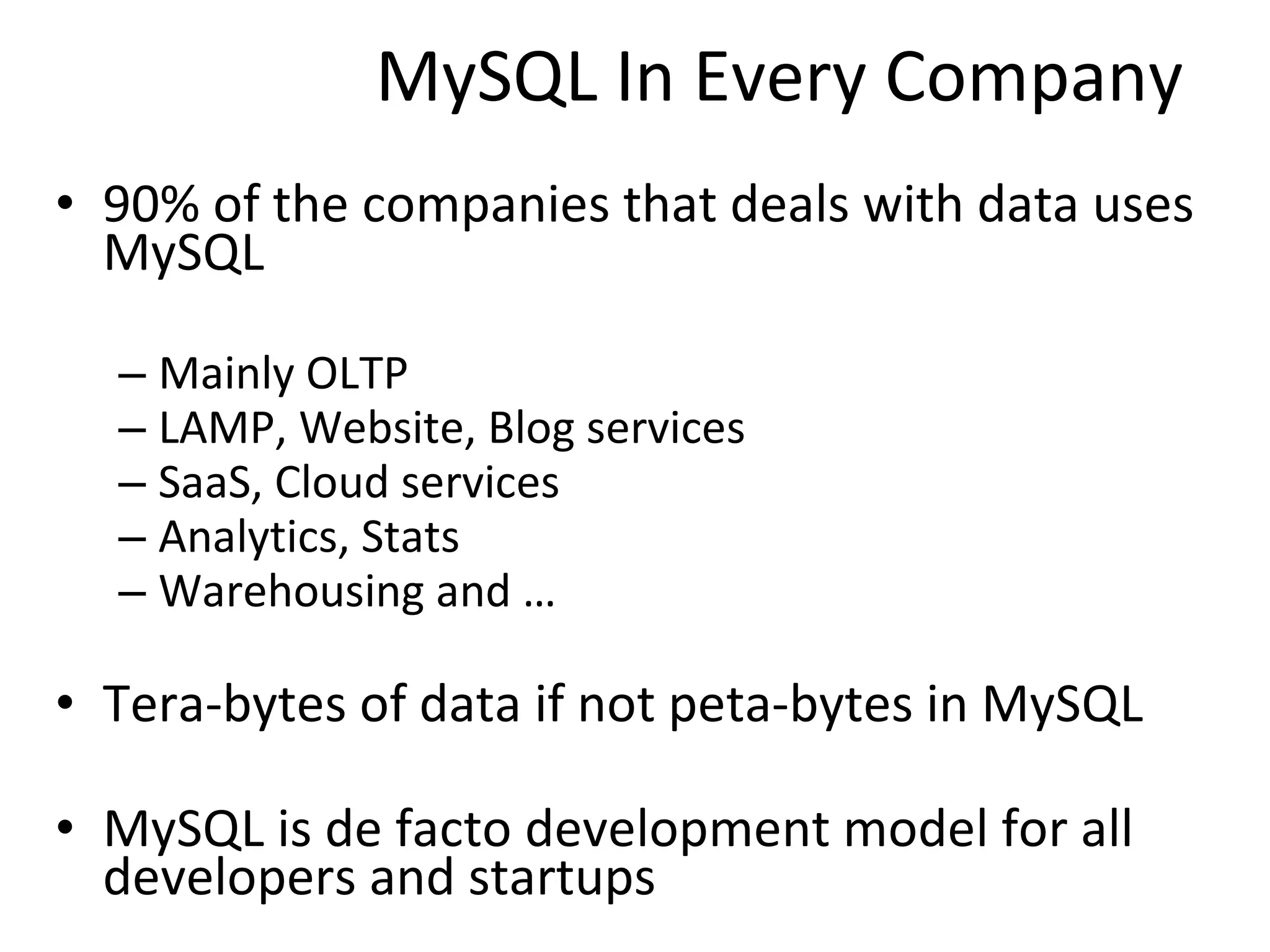
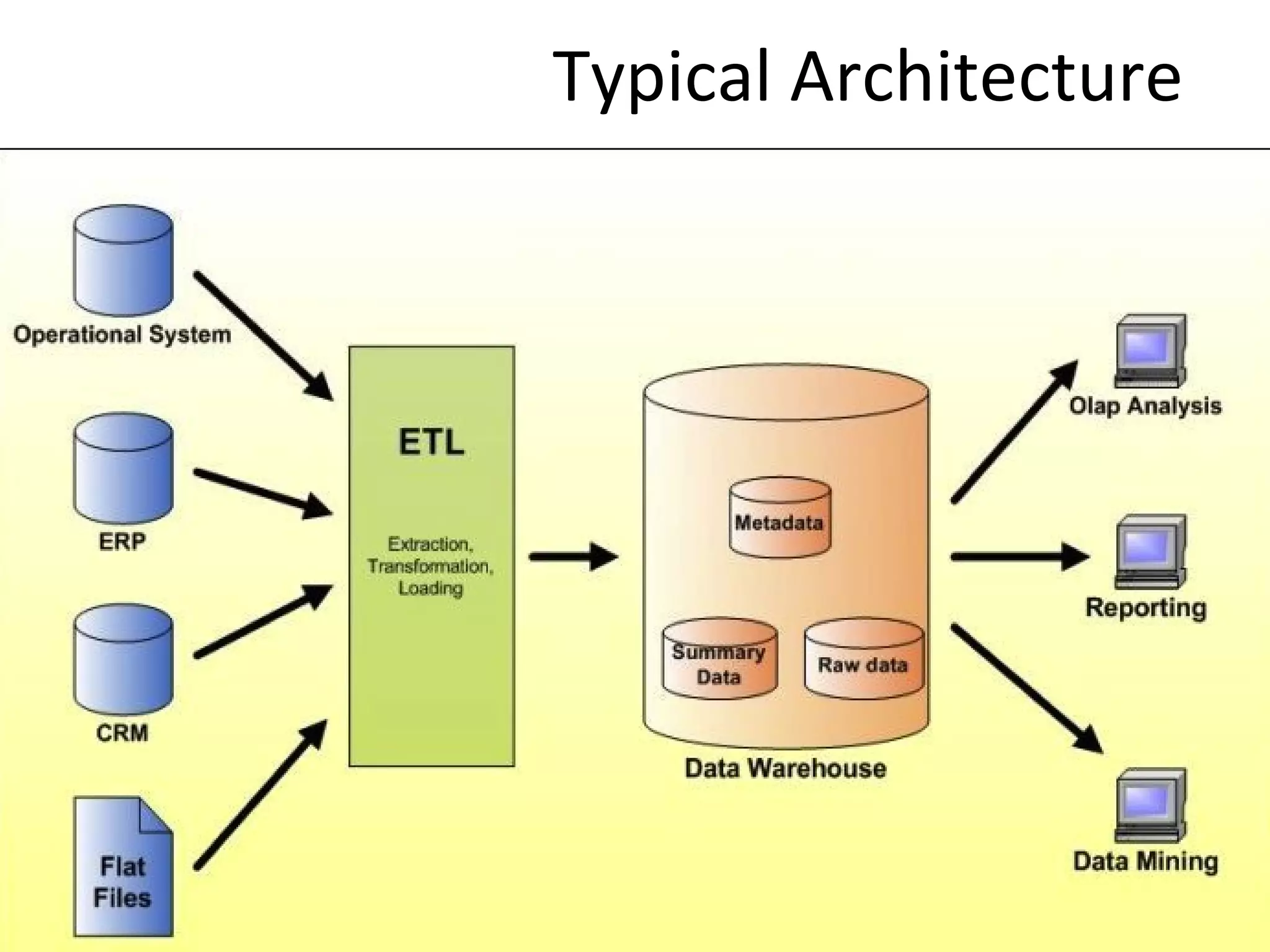
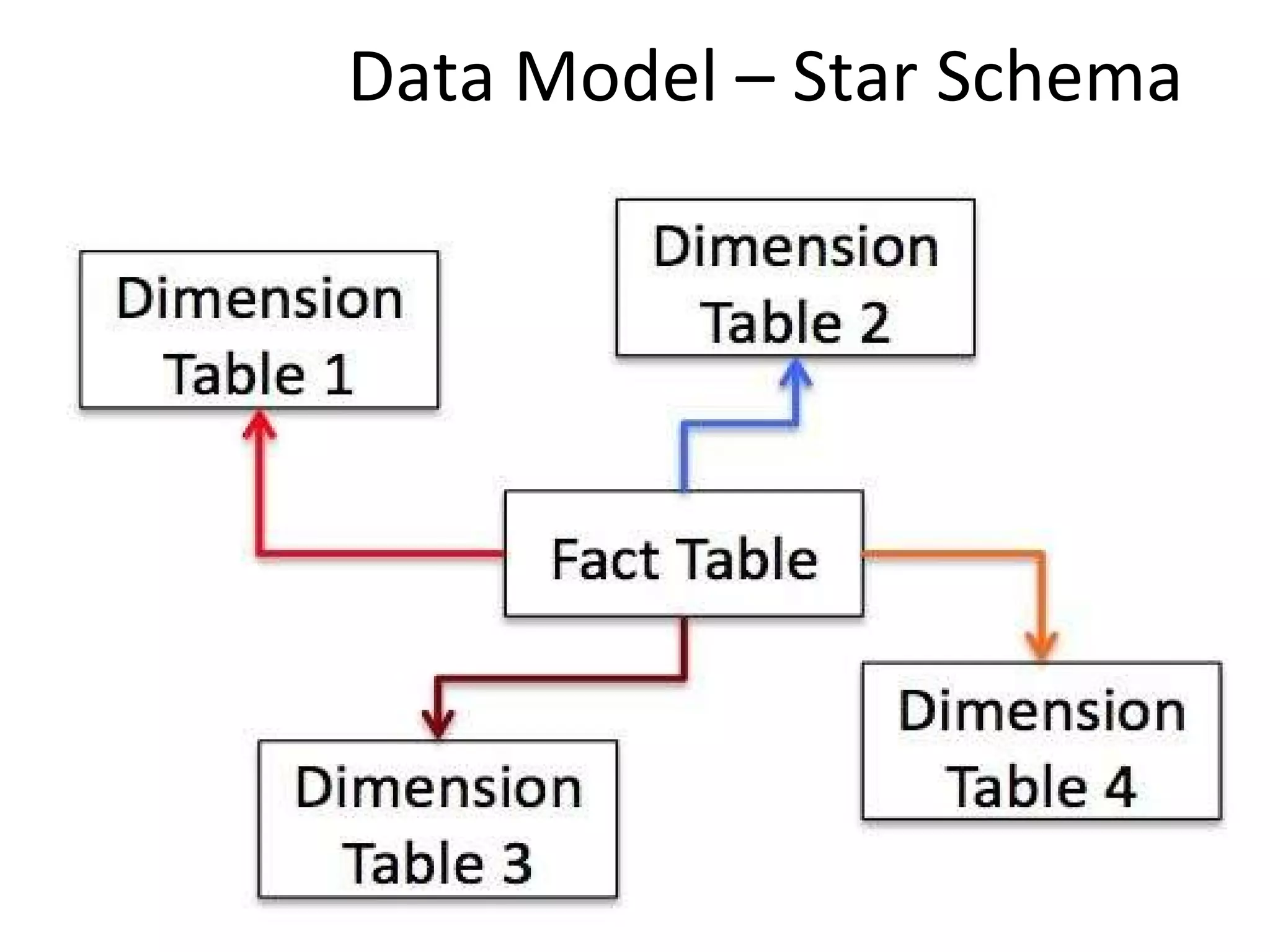
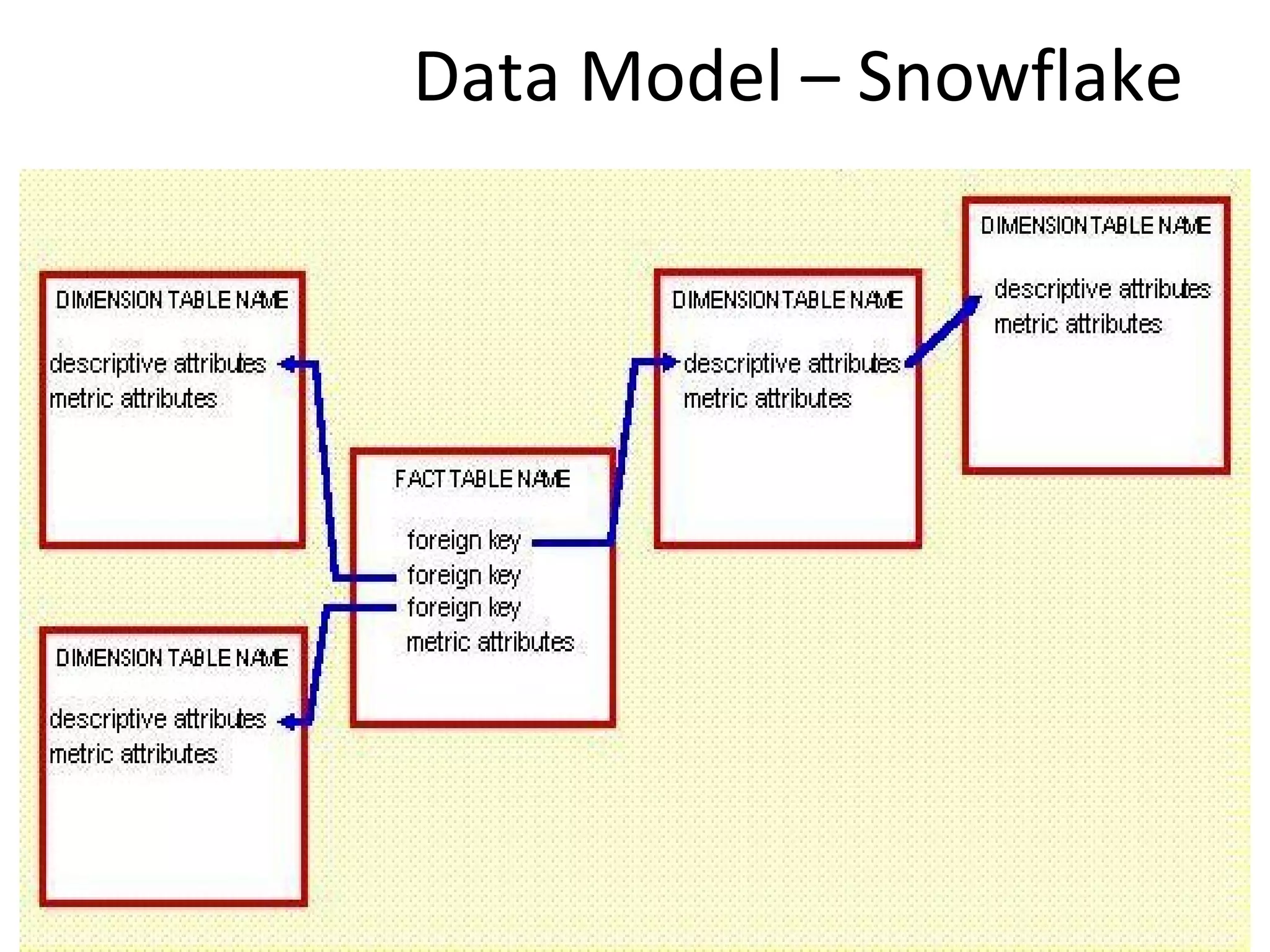
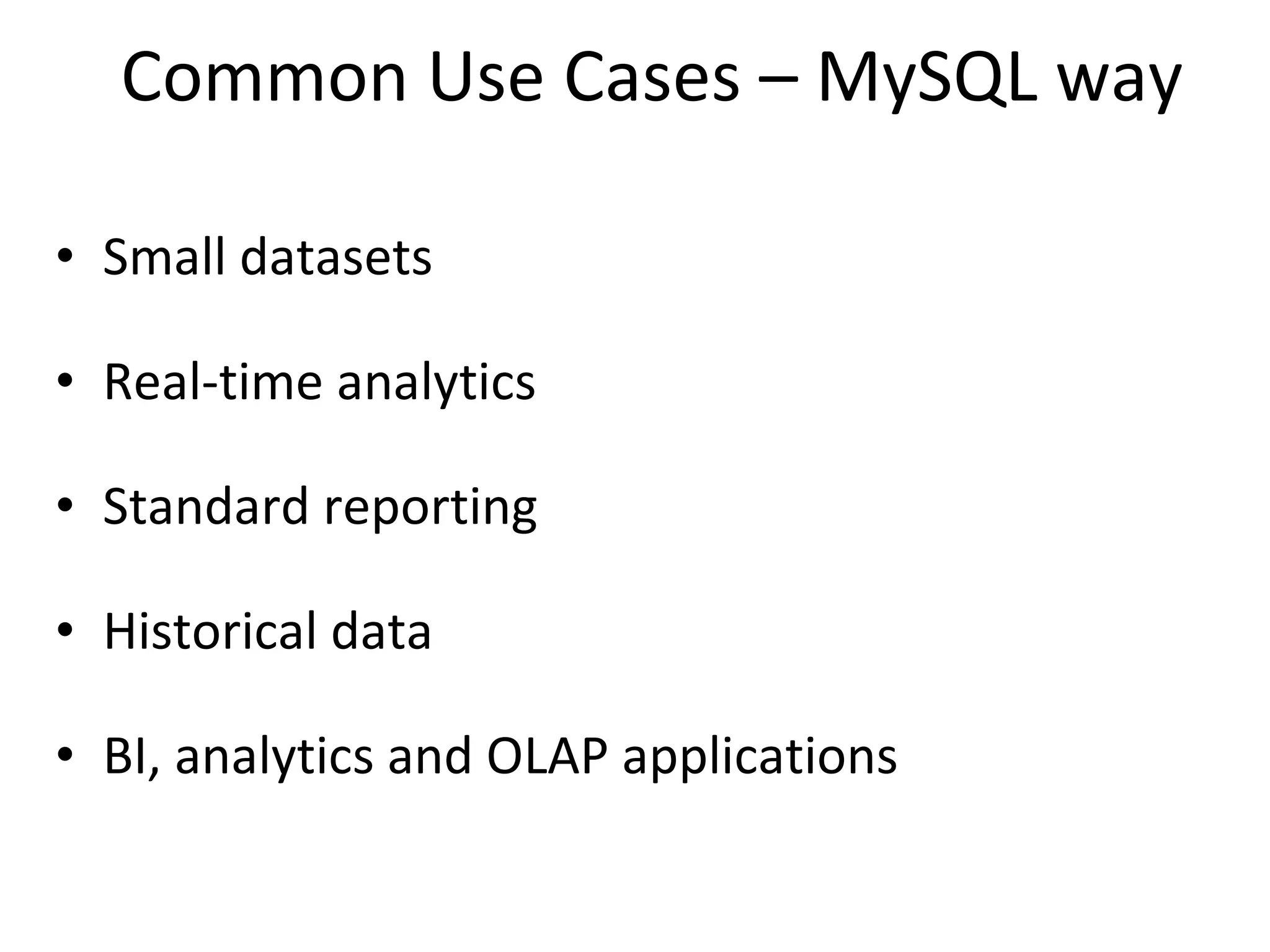
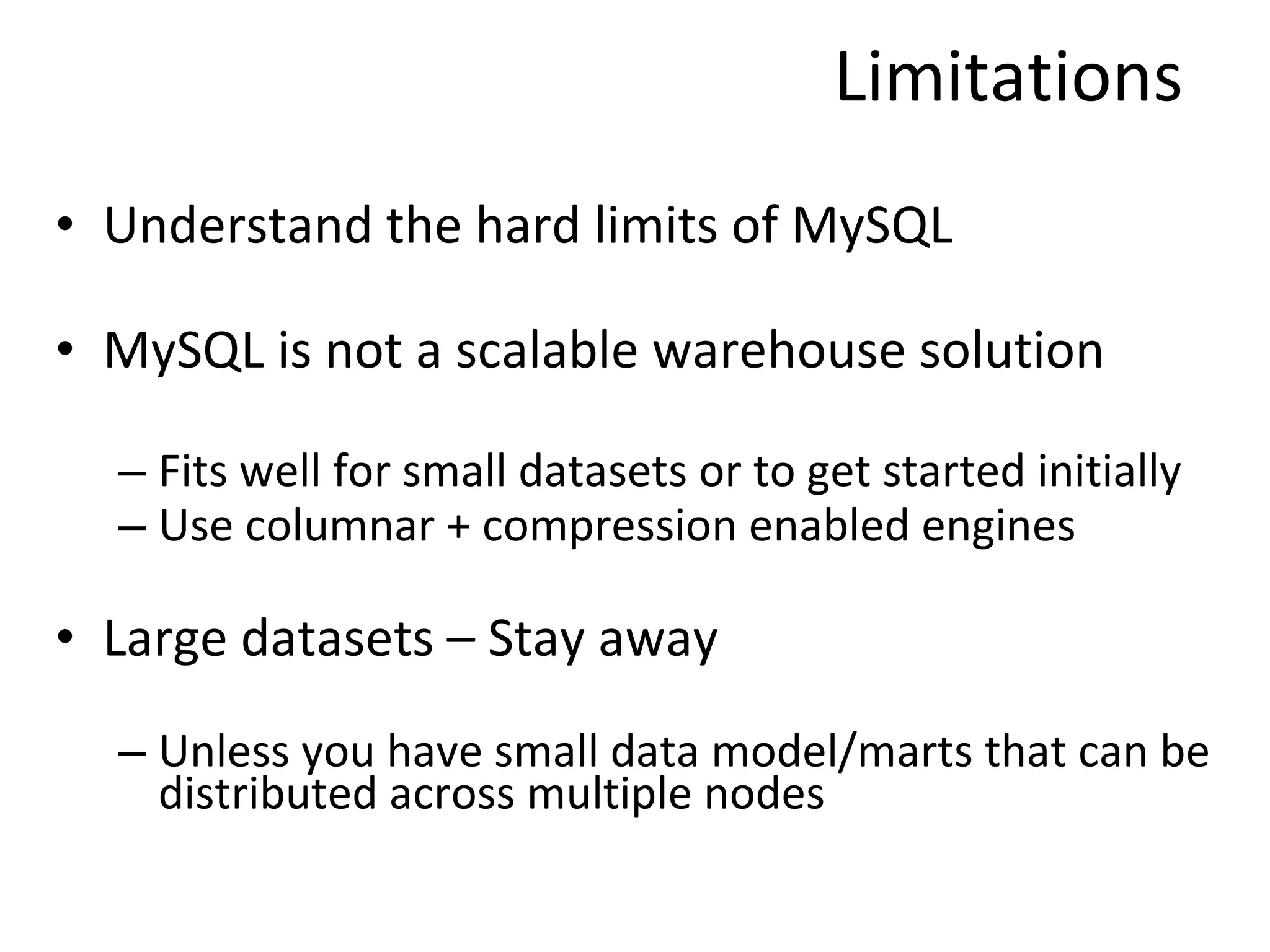
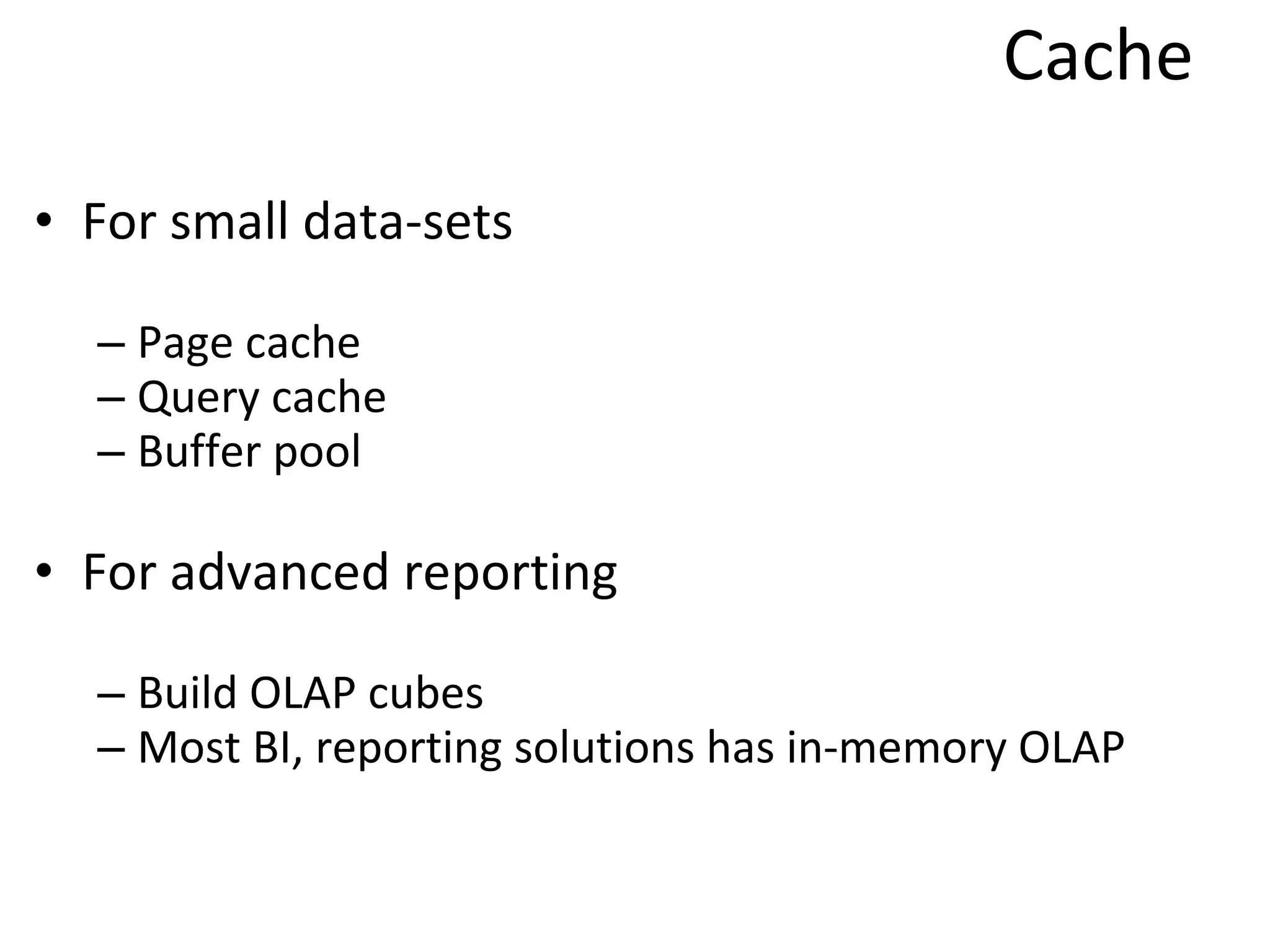
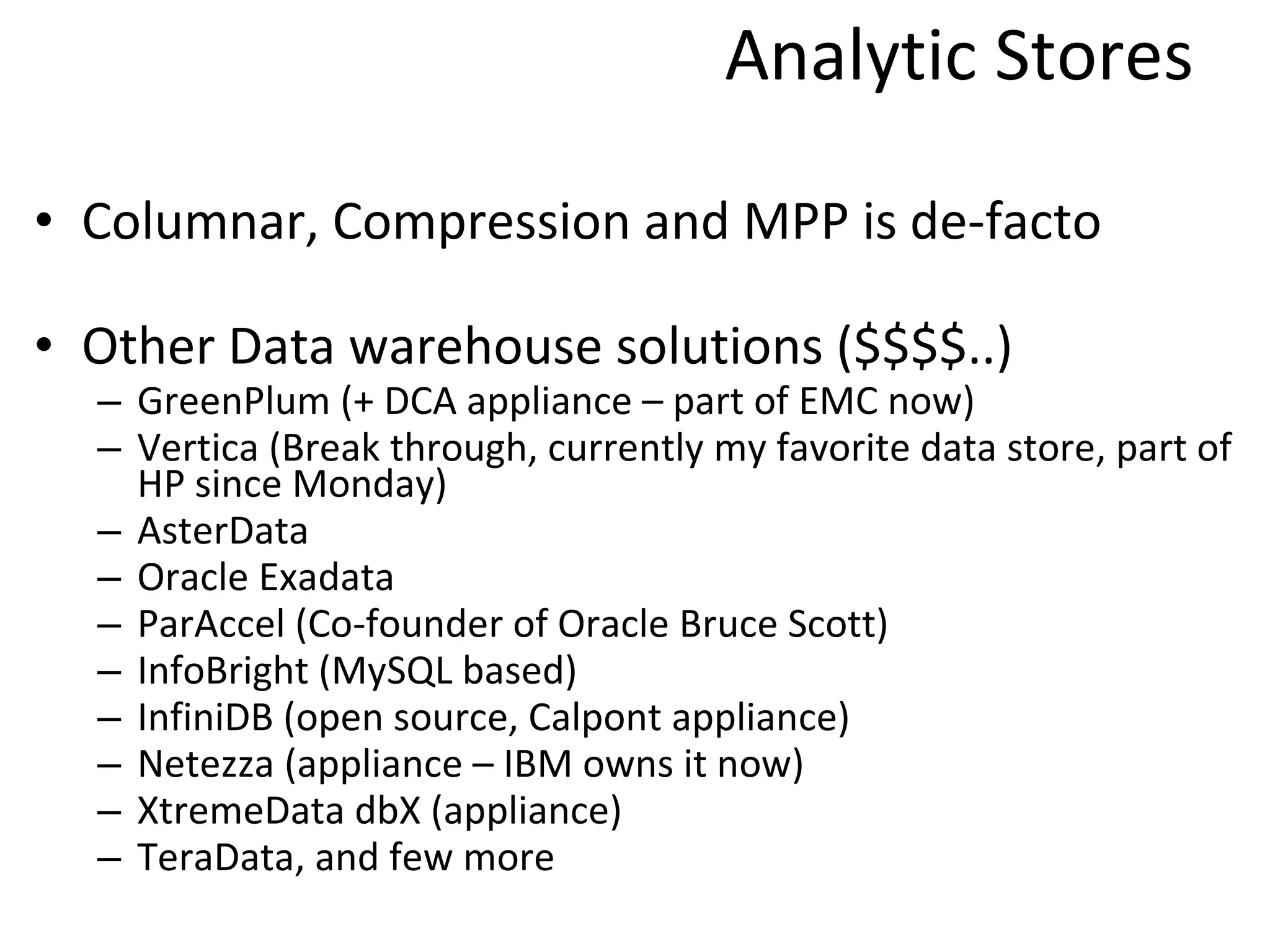
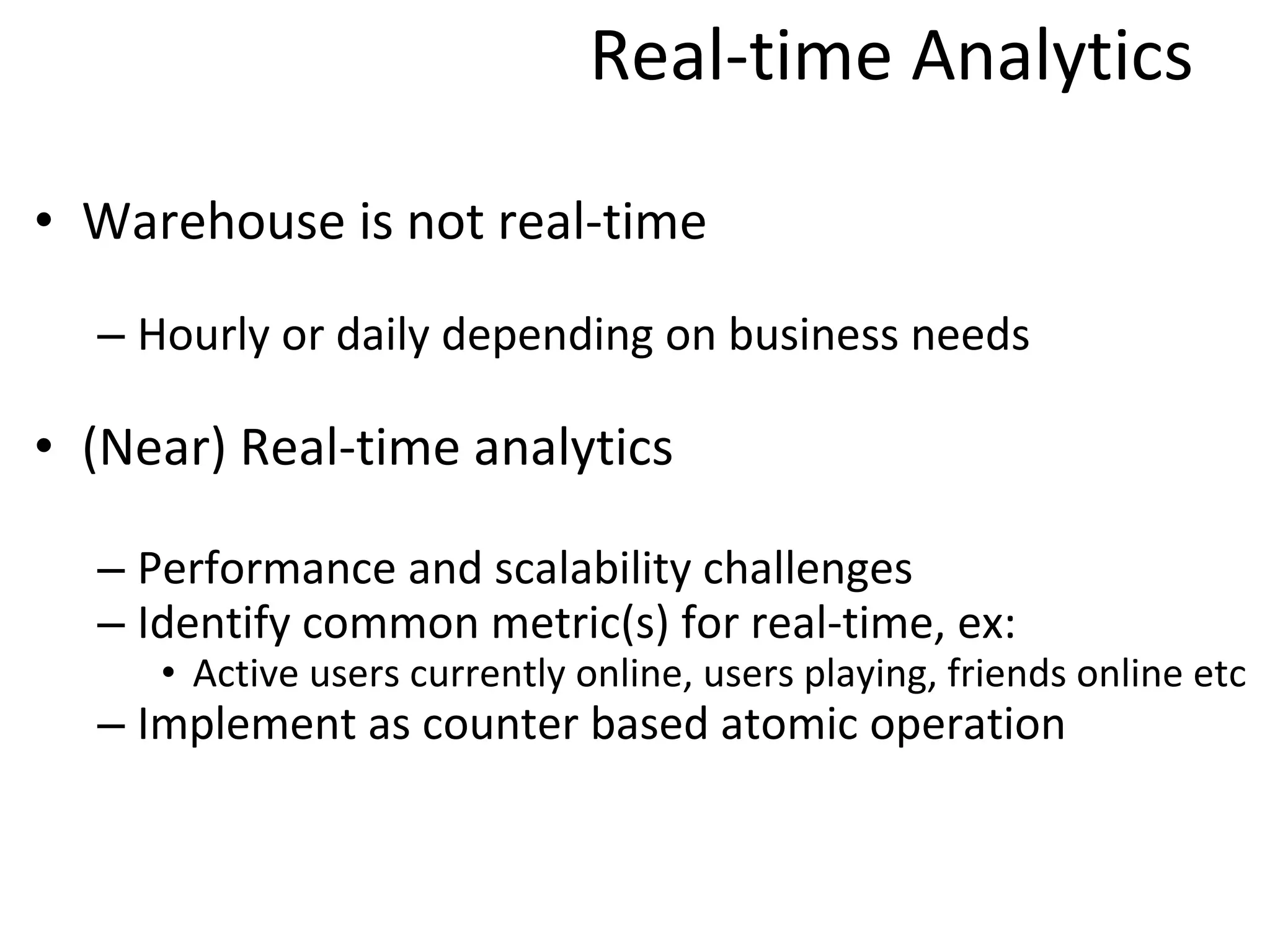
The document discusses the role of MySQL in data analytics and data warehousing. It describes how MySQL is widely used by many companies for online transaction processing (OLTP) and is the de facto standard for developers. While MySQL can be used for small data warehousing and analytics tasks, the document recommends using column-oriented databases with compression for large datasets due to MySQL's limitations in scalability for data warehousing. It provides tips on optimizing MySQL for analytics workloads and discusses using OLAP cubes and real-time analytics for near real-time insights.





![MySQL Widely Adopted Simple, easy to learn and adopt Widely in use for 10+ yrs Very large community Most developers knows how to use MySQL Lot of domain experts All most all tools support MySQL Highly optimal and scalable [if you use it right] It is even available on the cloud Used by all most all big companies When people do not know what data store to choose – defaults to MySQL](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mysql-warehouse-analytics-110217124057-phpapp02/75/Role-of-MySQL-in-Data-Analytics-Warehousing-10-2048.jpg)




![Questions ? http://venublog.com/ [email_address] Twitter: @vanuganti](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mysql-warehouse-analytics-110217124057-phpapp02/75/Role-of-MySQL-in-Data-Analytics-Warehousing-27-2048.jpg)