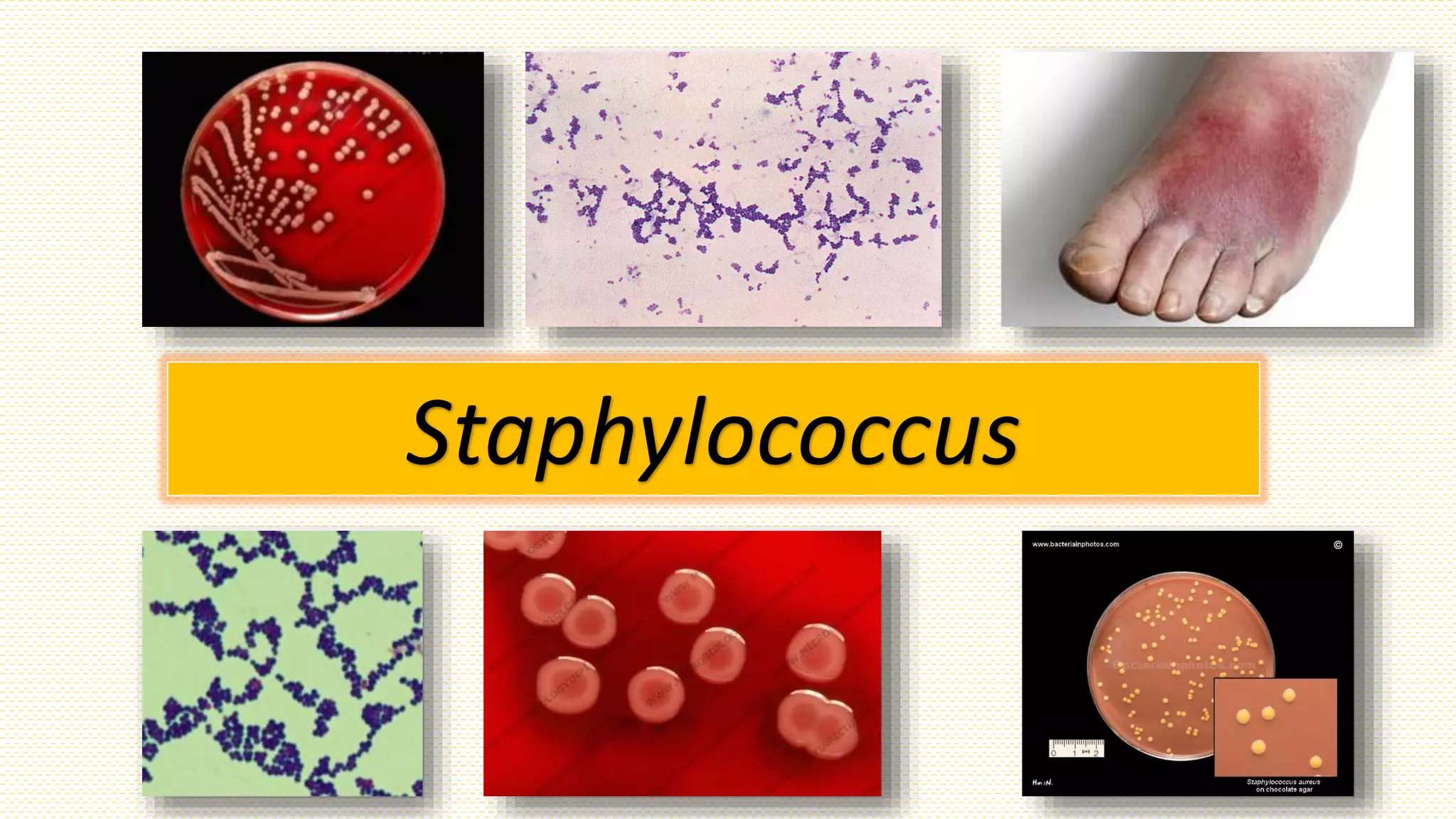
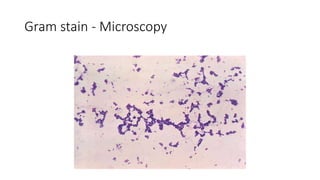
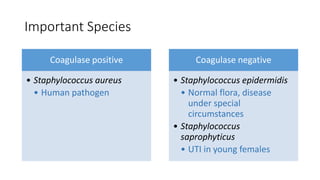
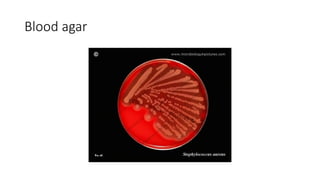
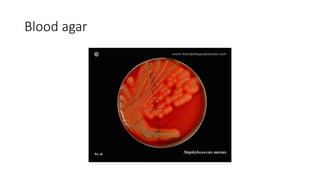
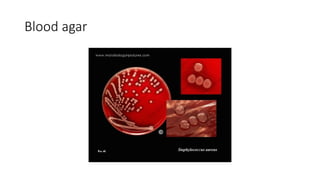
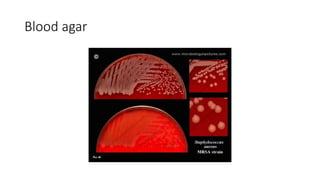
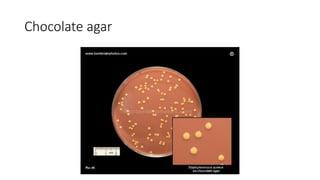
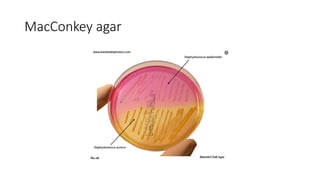
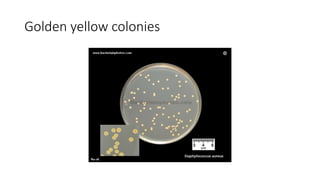
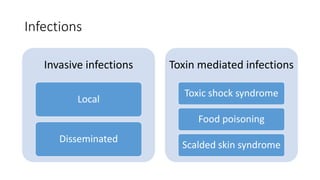
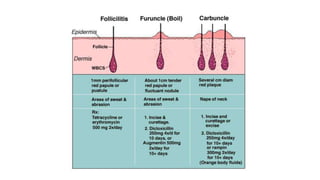
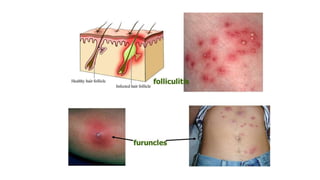
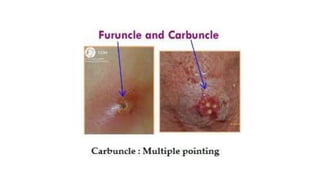
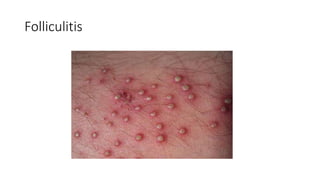
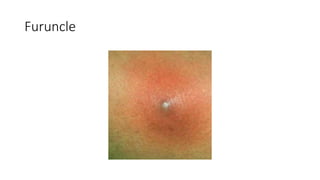
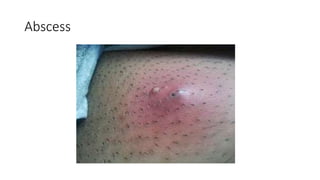
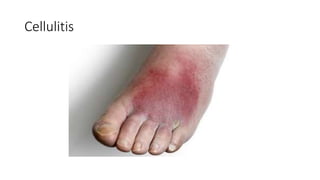
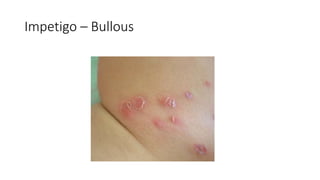
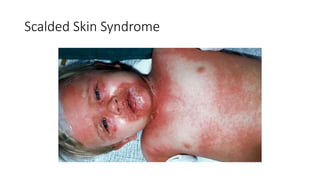
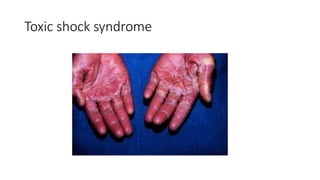
The document provides an overview of Staphylococcus species, detailing coagulase-positive Staphylococcus aureus as a human pathogen and coagulase-negative species like Staphylococcus epidermidis, which are part of normal flora. It outlines the characteristics, virulence factors, and infections associated with these bacteria, including local and disseminated infections, as well as toxin-mediated conditions like toxic shock syndrome and food poisoning. Additionally, it lists first-line and second-line antibiotics for treatment.