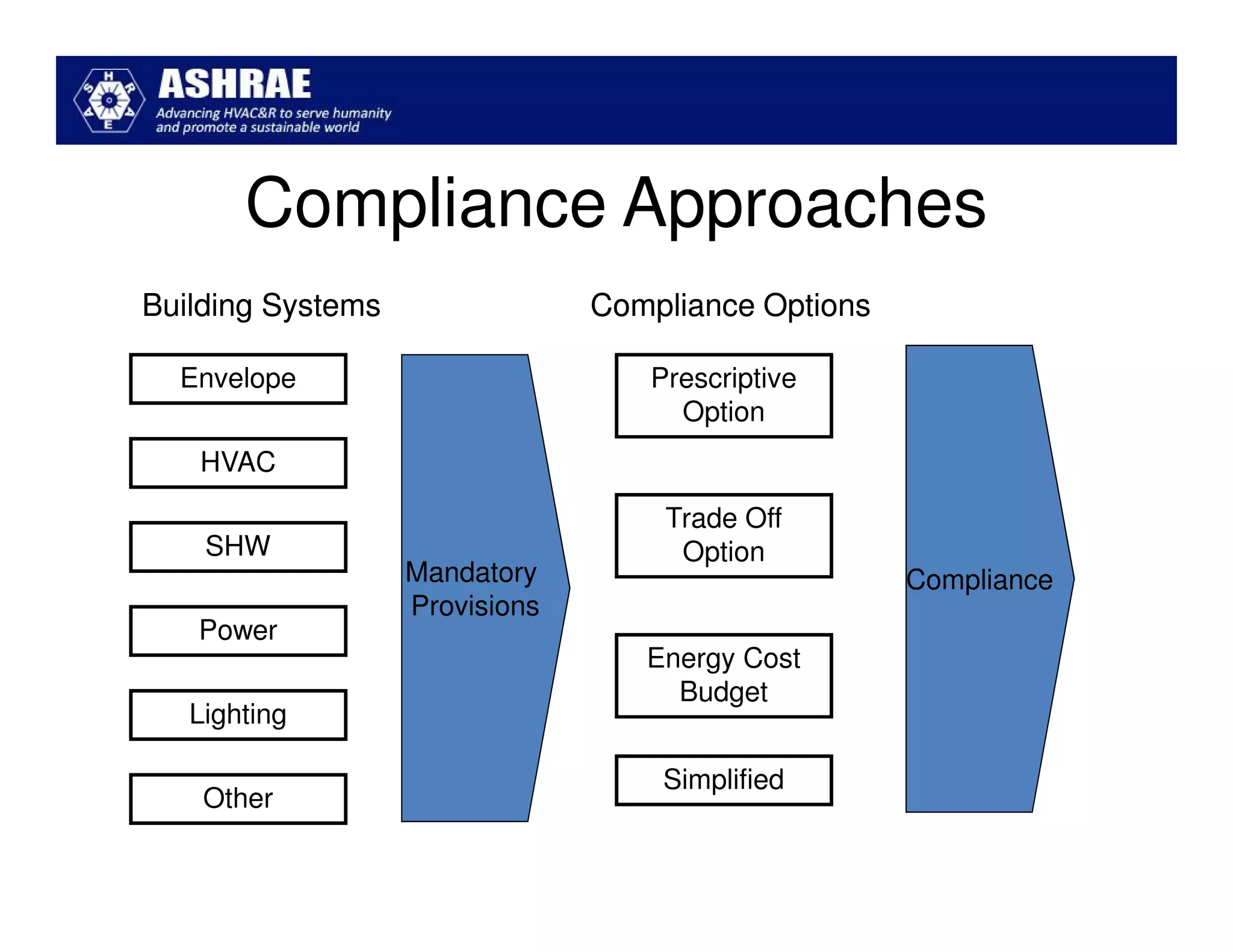
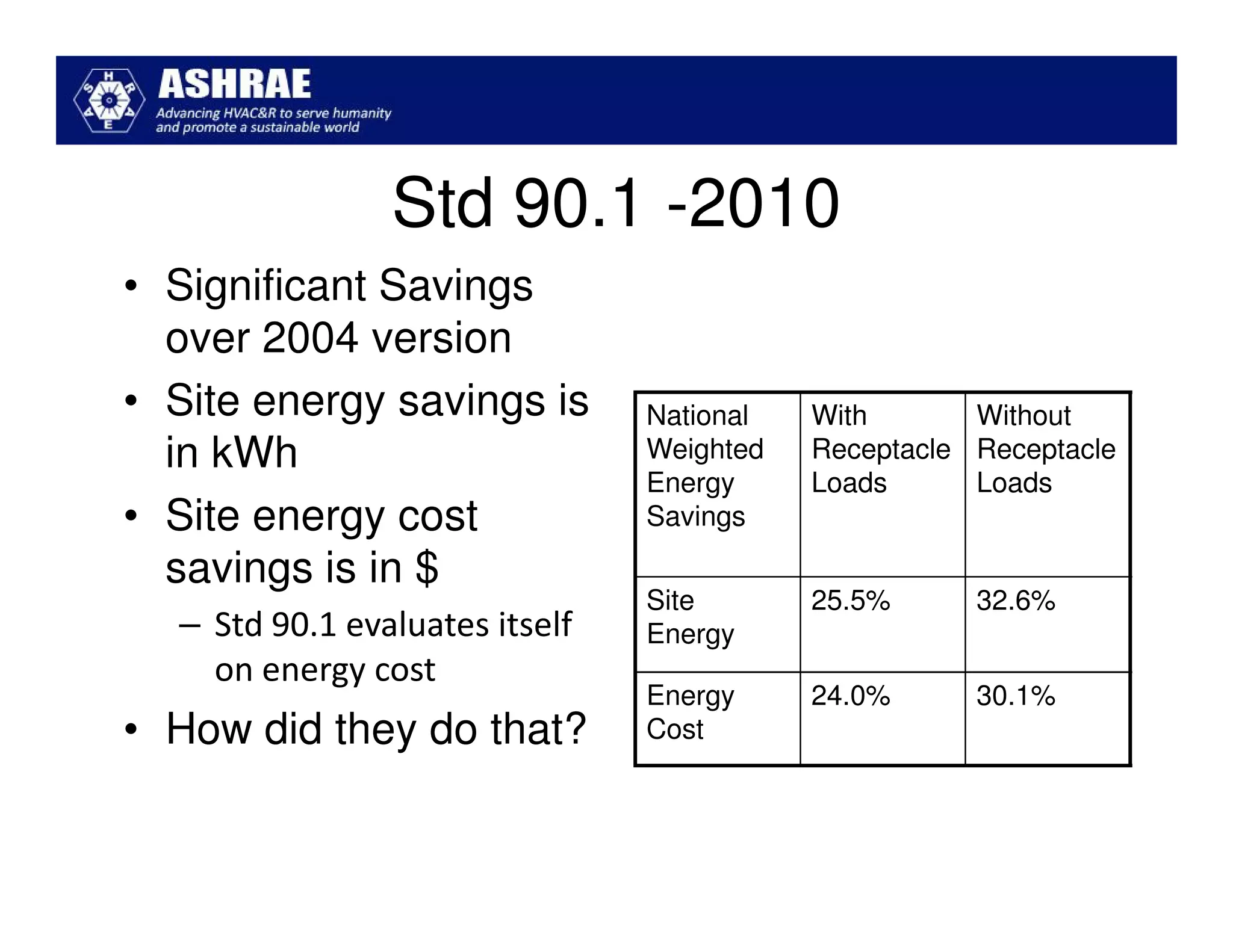
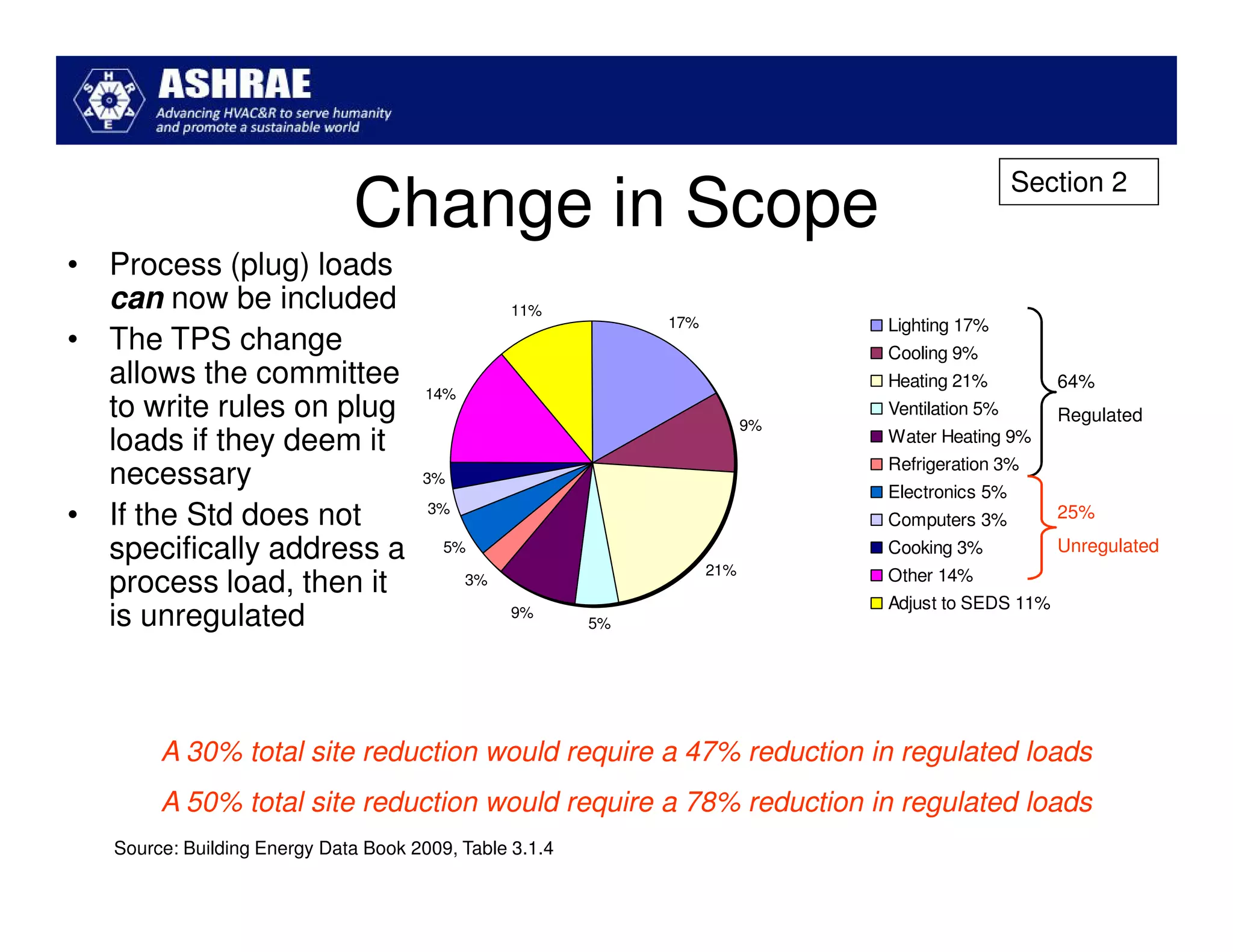
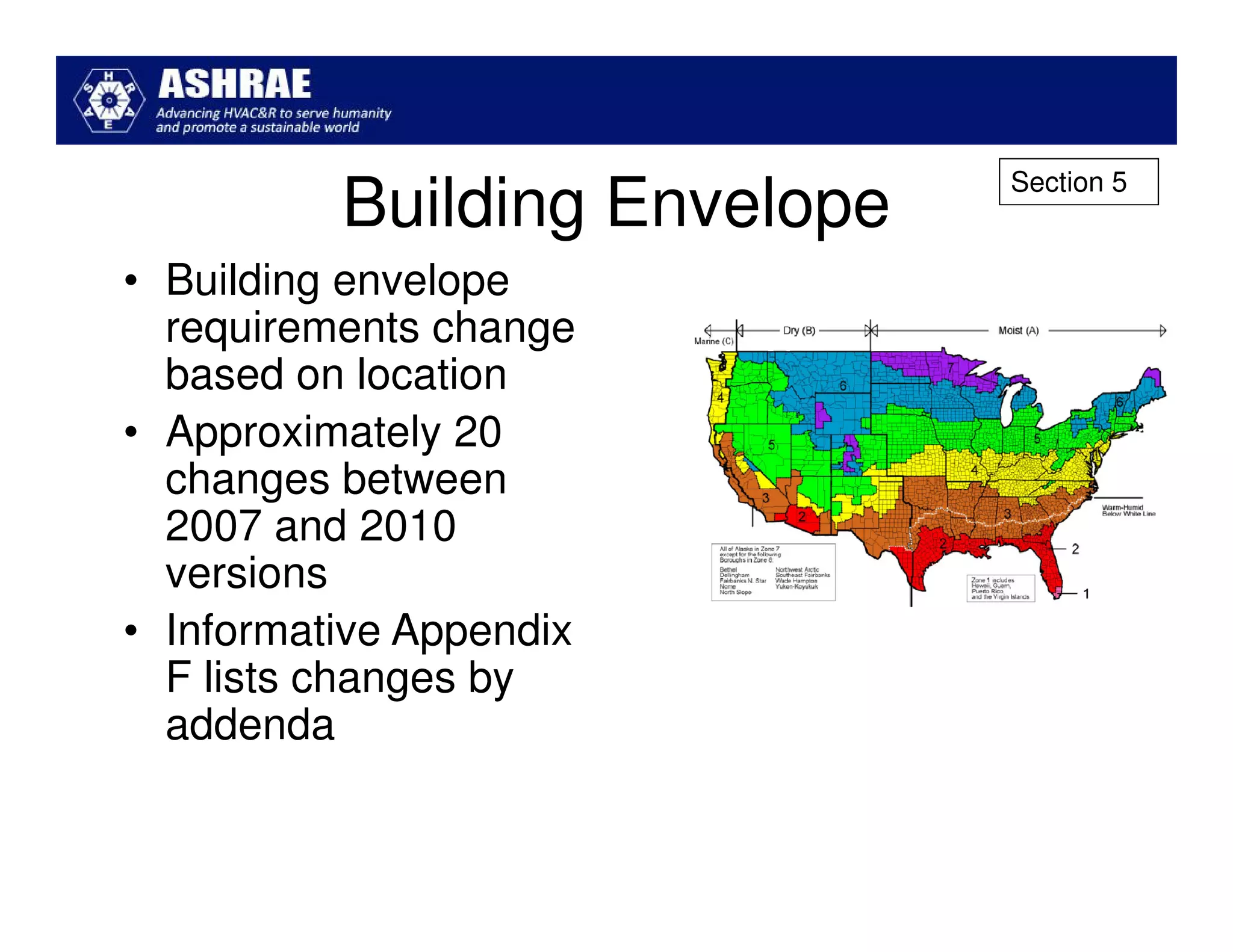
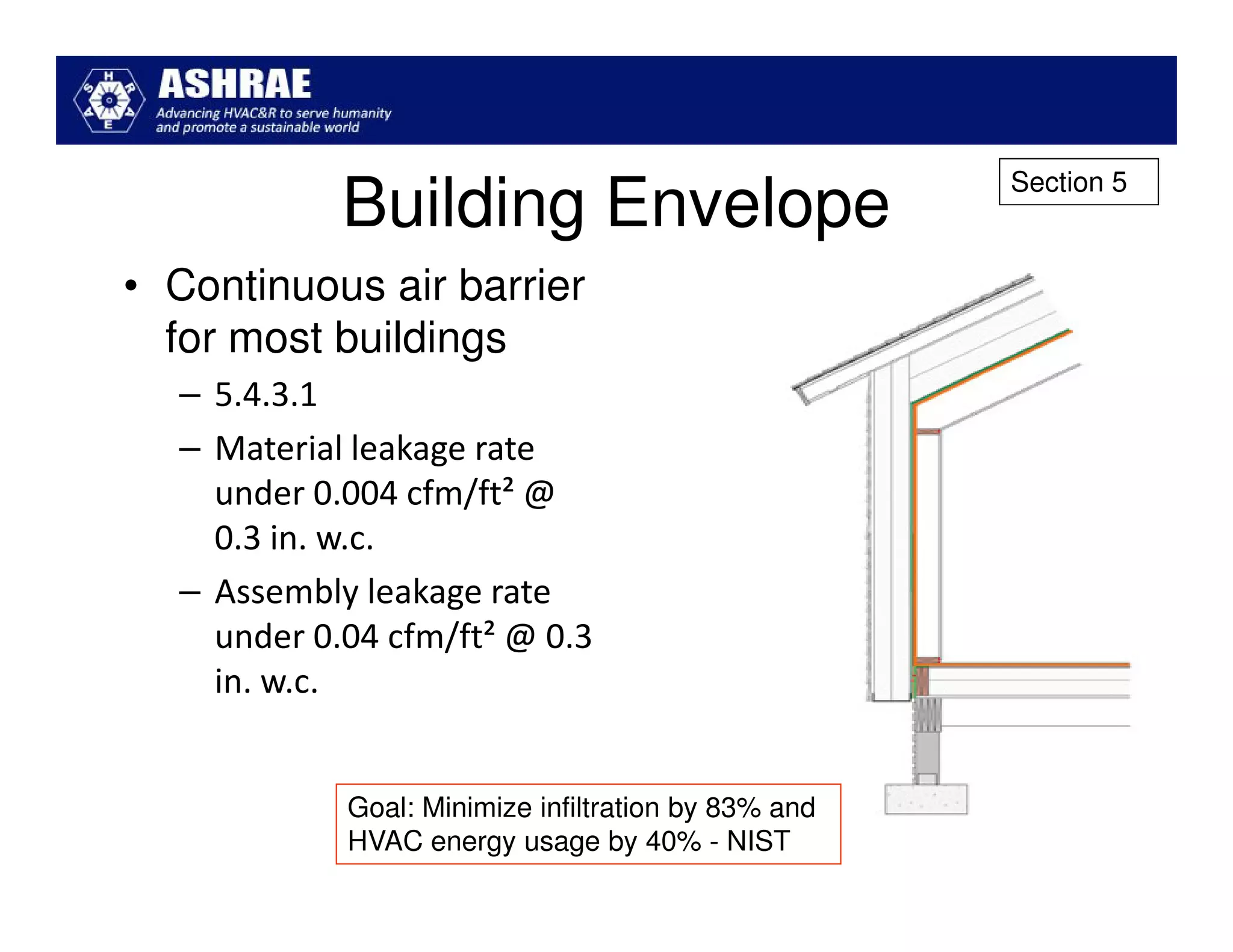
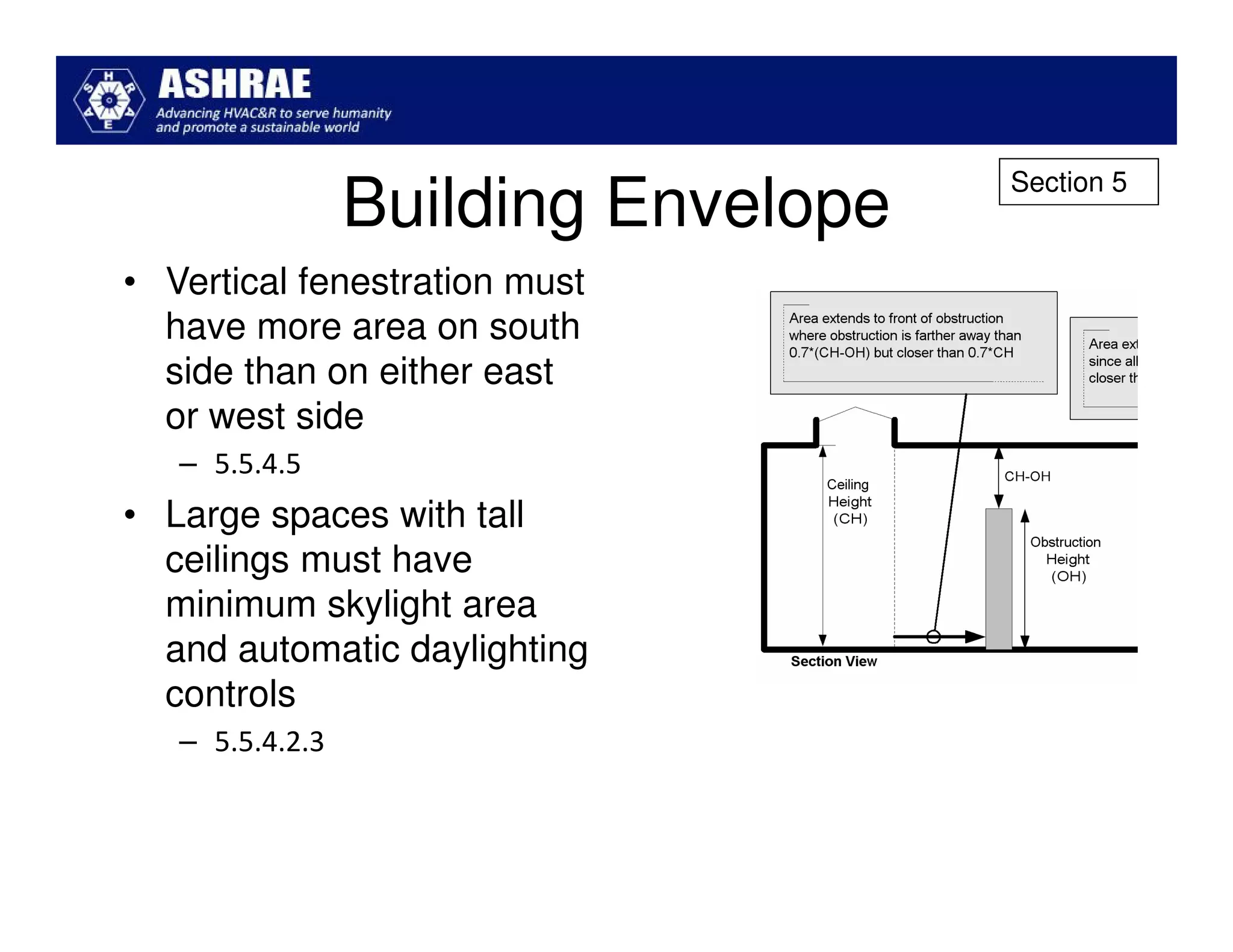
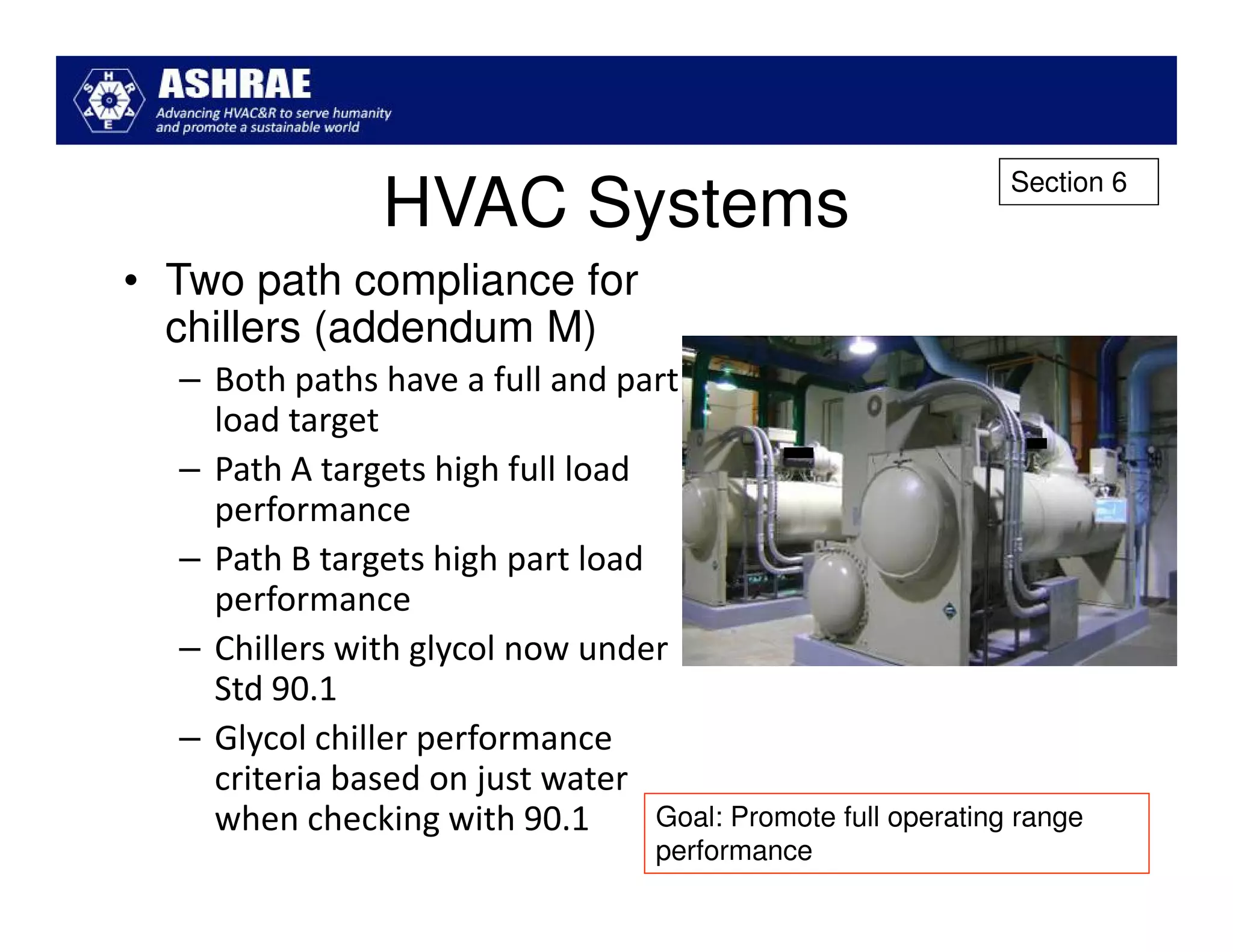
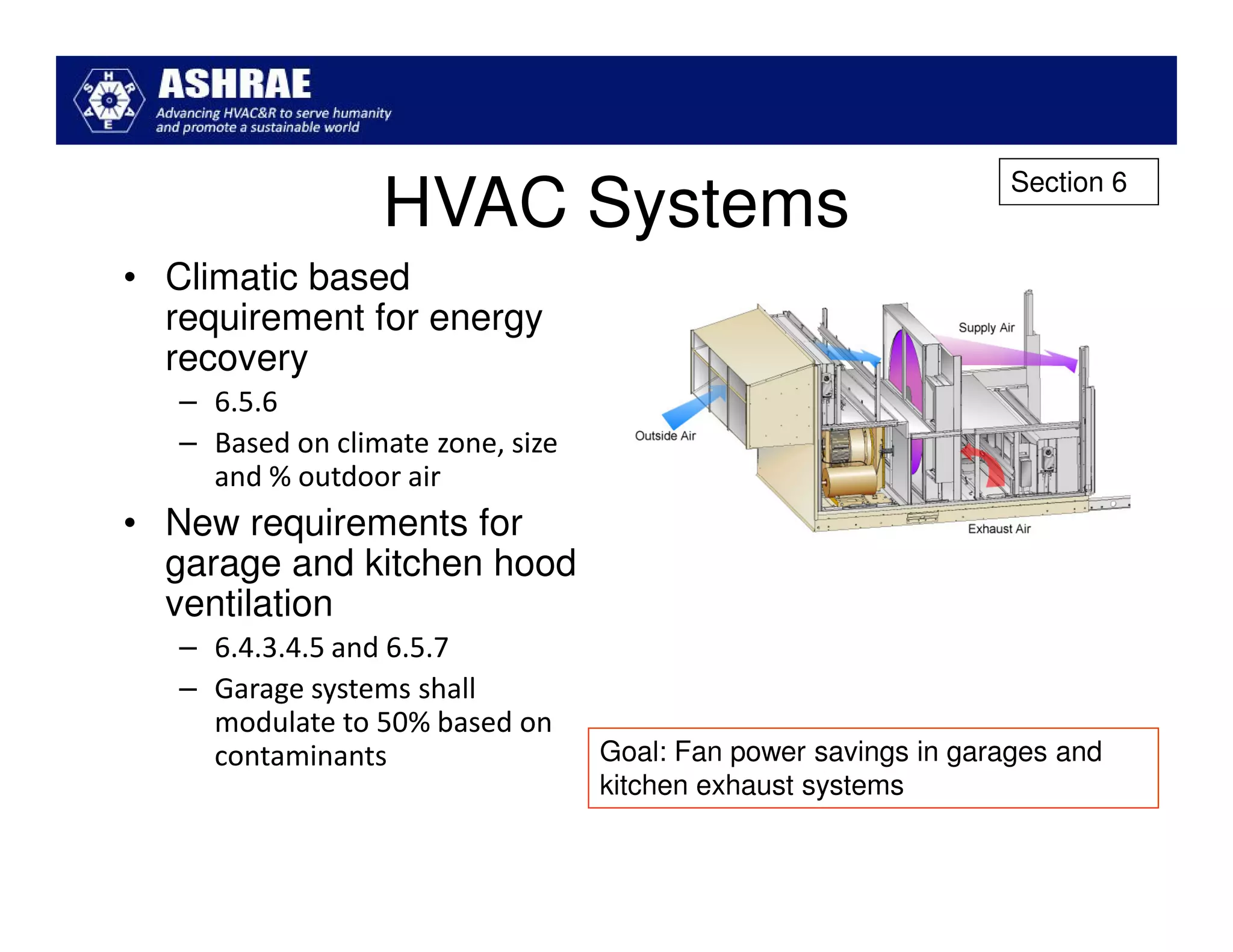
ASHRAE Standard 90.1-2010 made significant improvements in energy efficiency over the 2004 version. It expanded the scope to include process loads and established new requirements in key areas like building envelopes, HVAC systems, and lighting. The standard evaluates savings based on both site energy and energy cost reductions. Compliance can be met through prescriptive requirements or through a trade-off option. The presentation reviewed many of the changes introduced in key sections between the 2007 and 2010 versions.