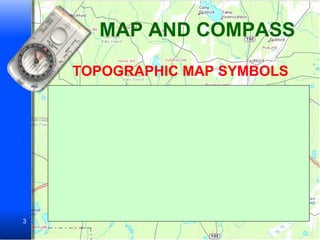
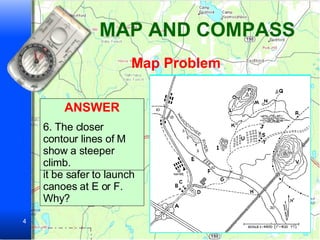
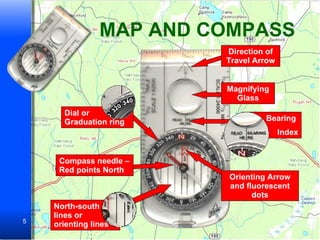
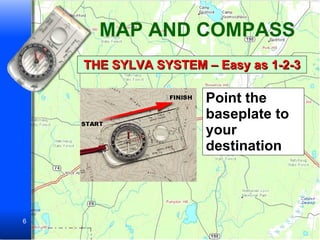
The document provides information on how to use maps and compasses to navigate terrain. It discusses key features of topographic maps like highways, railroads, bridges and landmarks. It then presents sample navigation problems asking the reader to determine the best routes and locations based on map symbols and terrain. The final sections explain the basic steps to use a compass to determine headings and directions of travel.