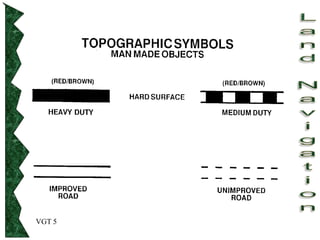
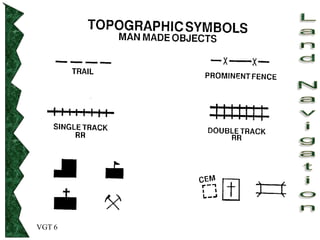
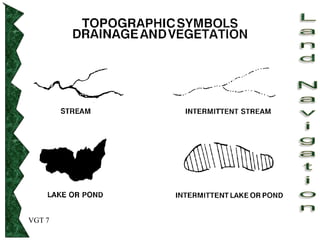
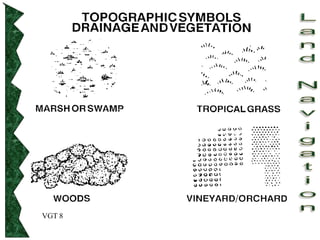
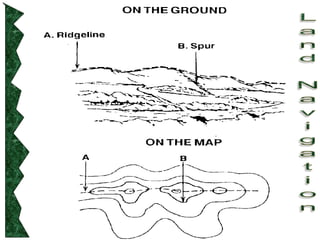
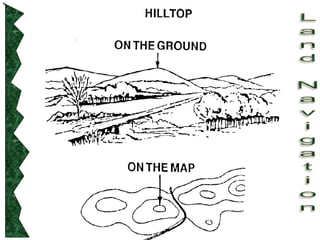
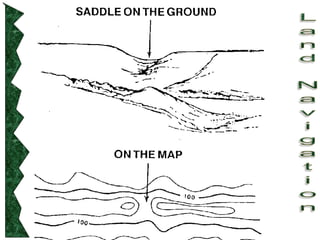
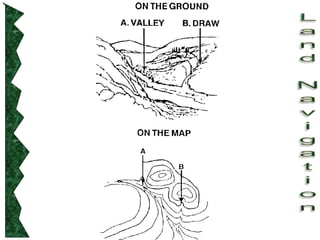
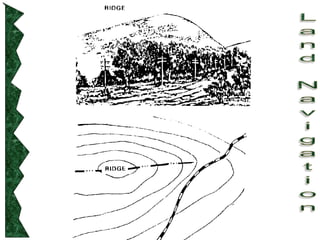
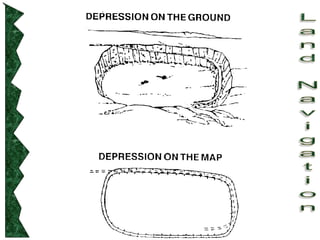
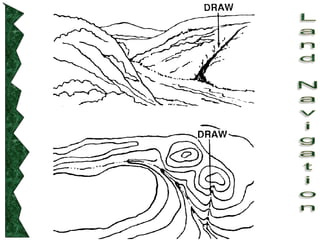
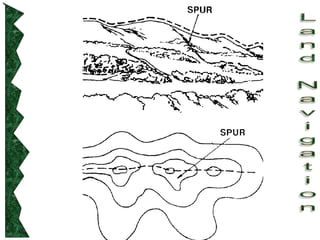
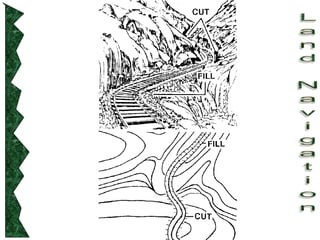
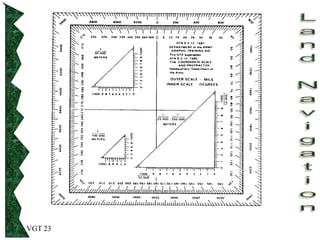
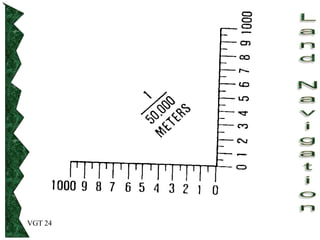
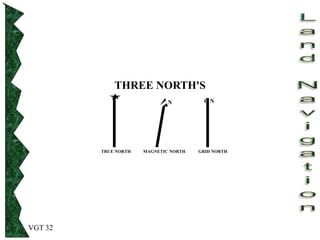
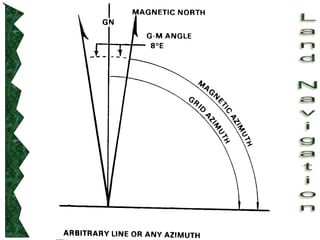
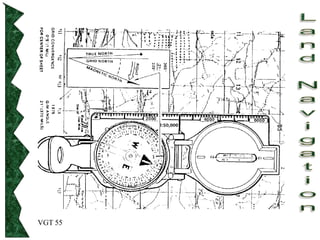
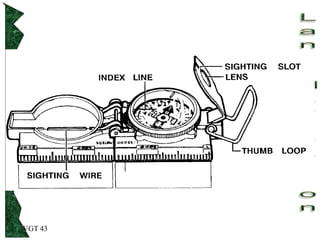
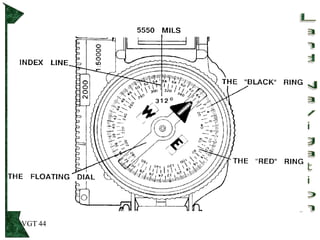
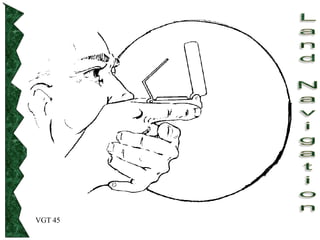
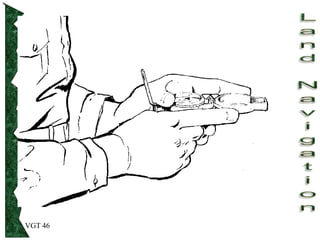
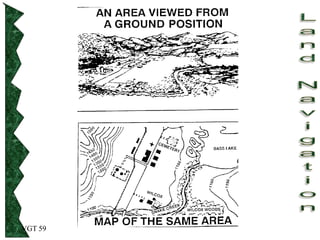
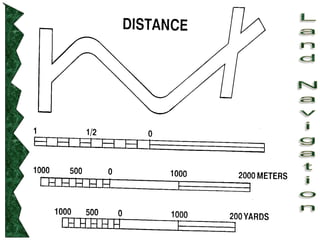
The document outlines basic map reading skills necessary for land navigation, including identifying map colors, symbols, marginal information, and terrain features. It explains how to determine grid and elevation, as well as how to calculate azimuths and distances using various methods. The content includes practical exercises to strengthen understanding of these navigation techniques.