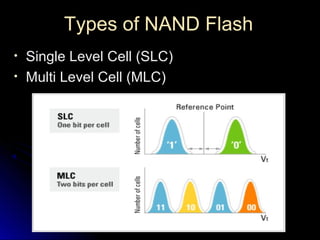
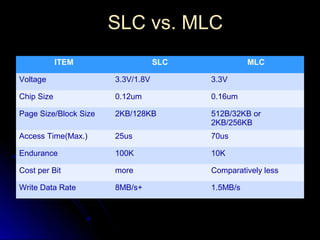
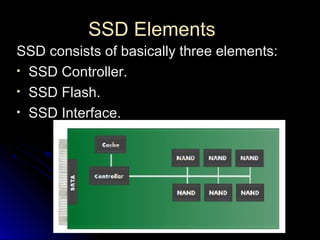
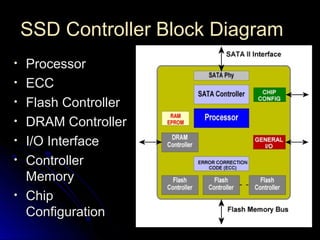
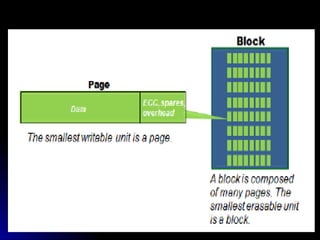
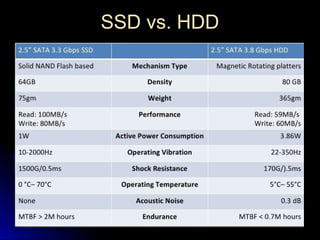
SSDs use solid state memory like NAND flash instead of spinning disks to store data. SSDs access data much faster than hard disk drives and have no moving parts, providing benefits like higher reliability, lower power consumption, and silent operation. An SSD contains a controller, flash memory, and an interface to connect to a computer or device. The controller manages the flash memory by mapping data to pages and blocks. SSDs are being used increasingly in devices like laptops, servers, and cameras due to their faster speeds and reliability compared to HDDs.