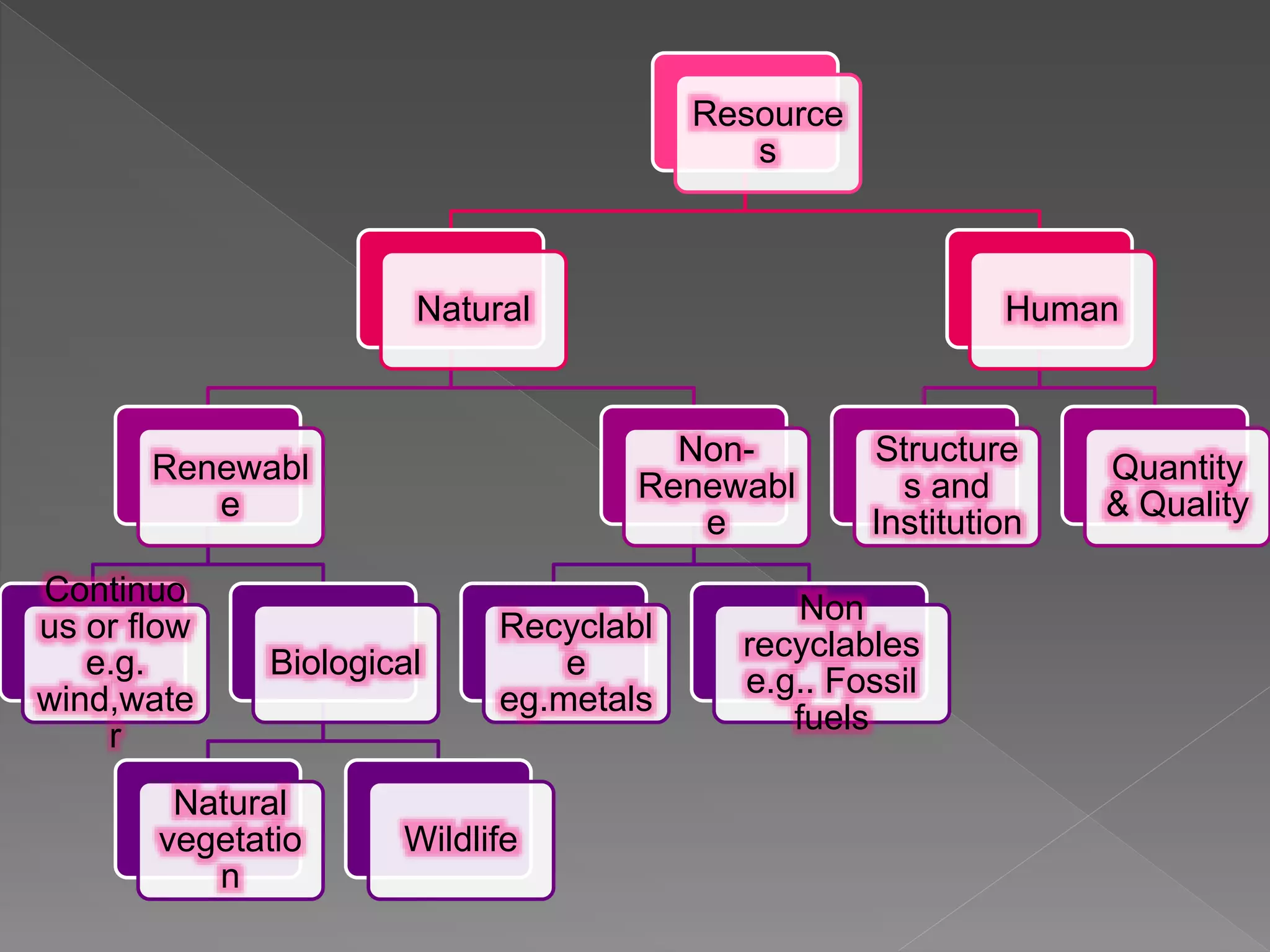
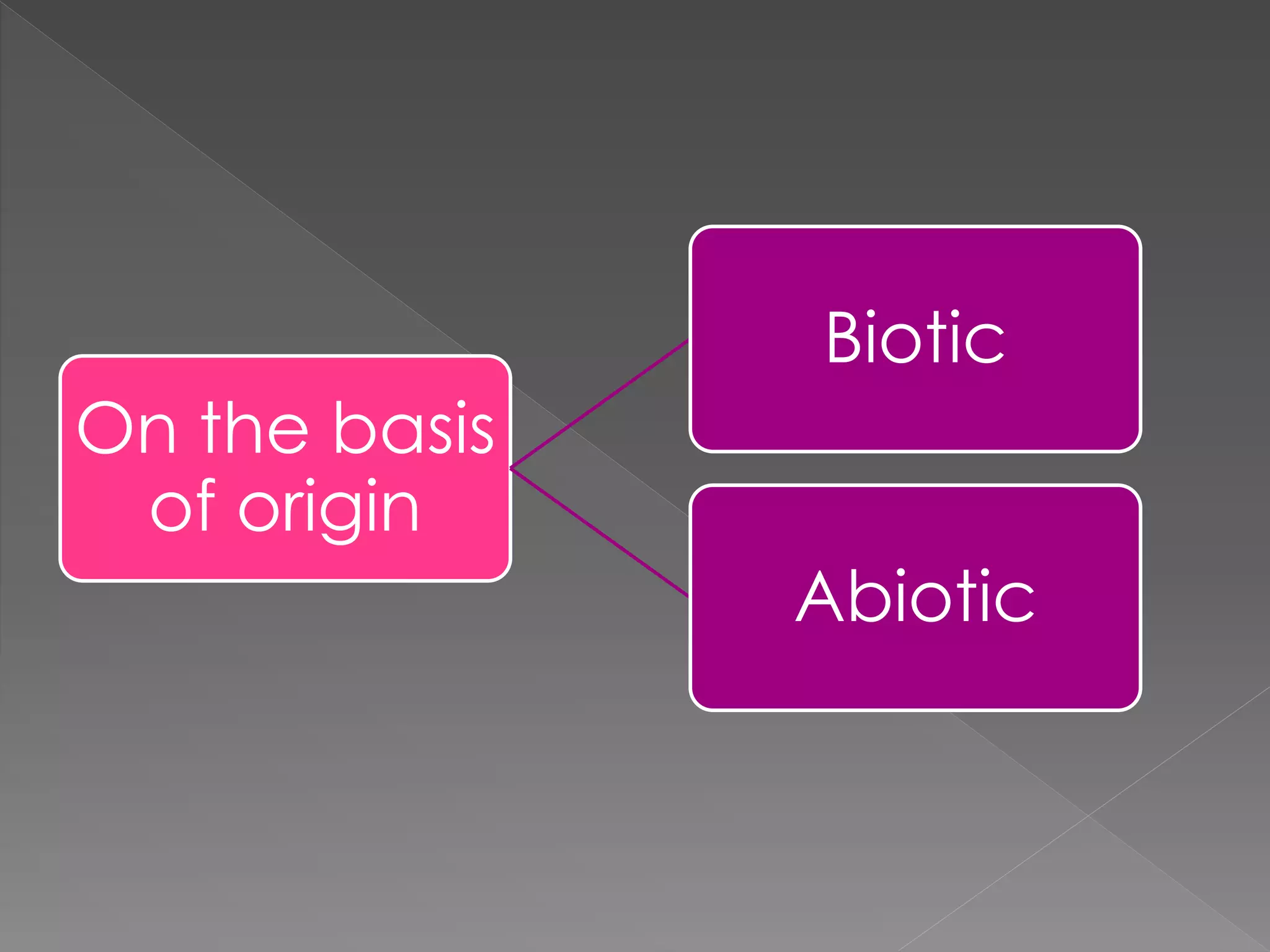
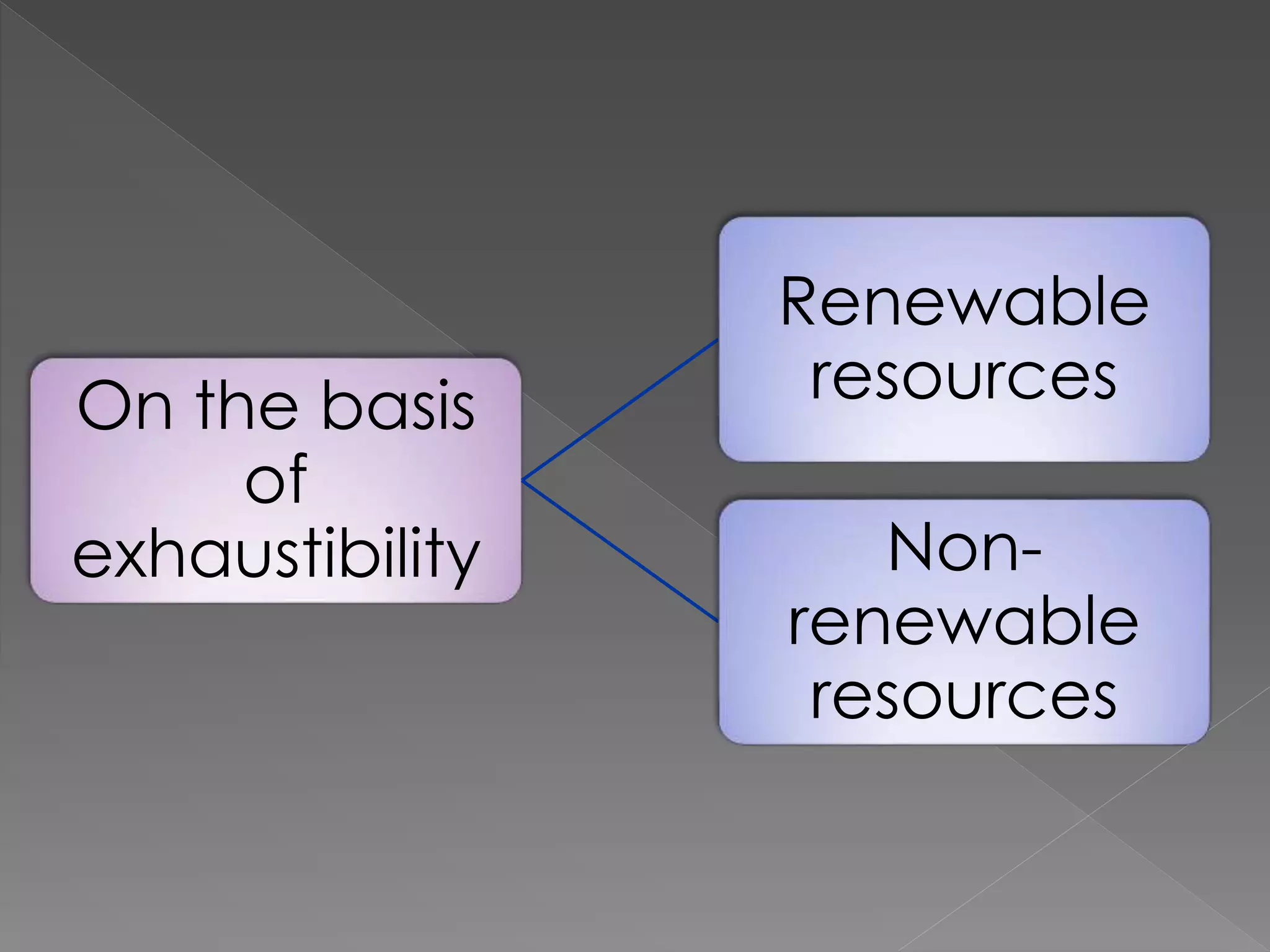
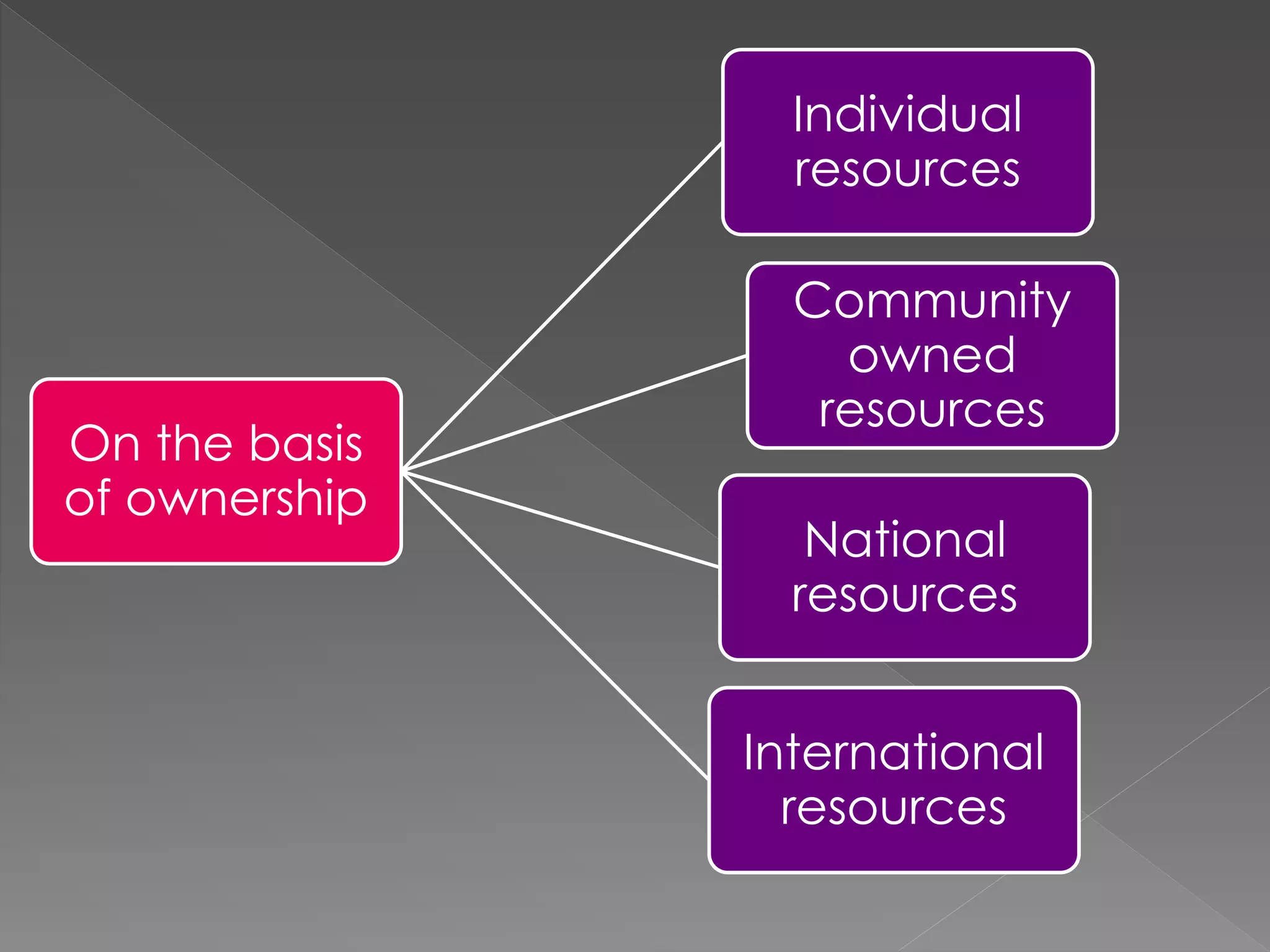
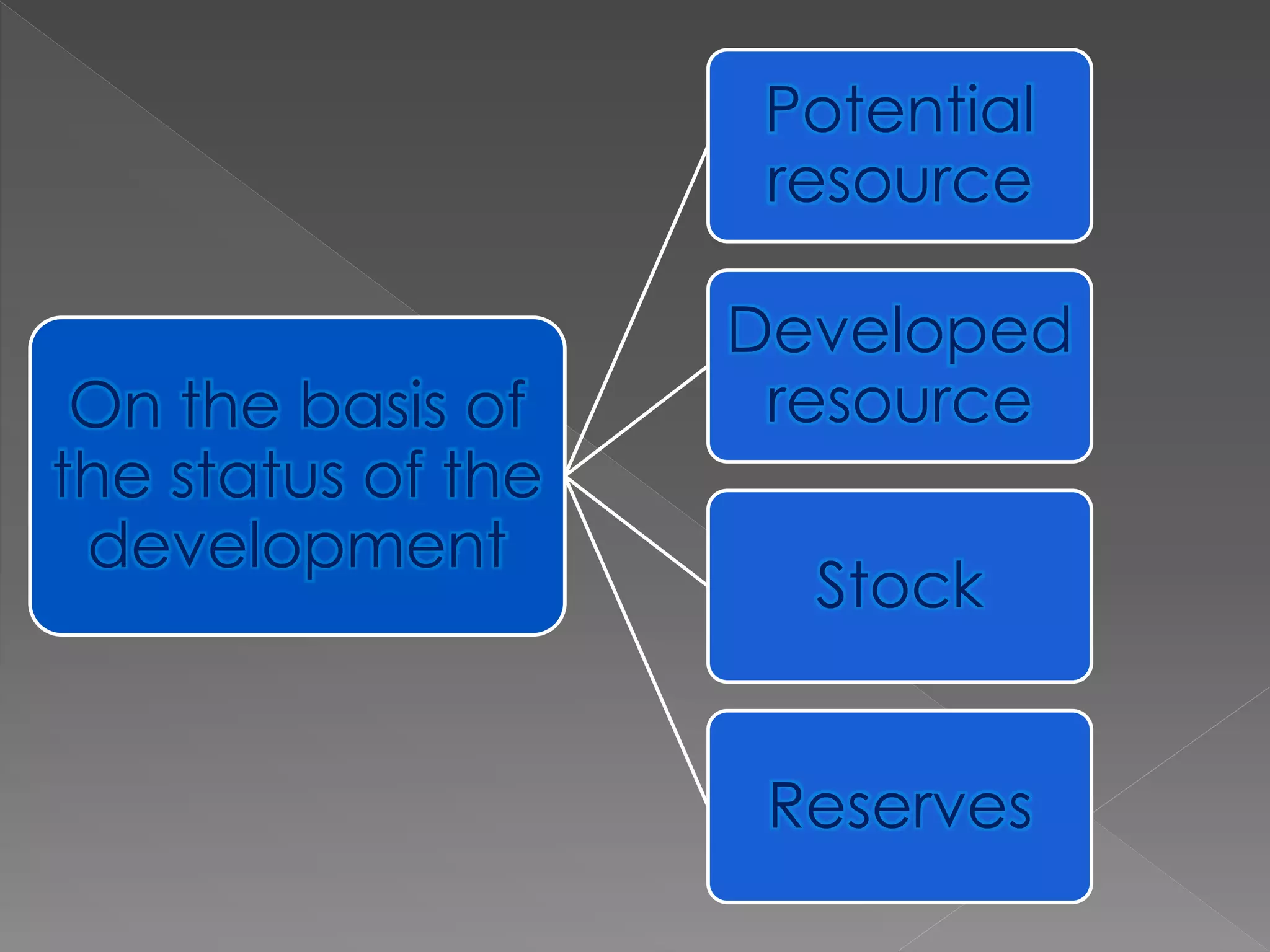
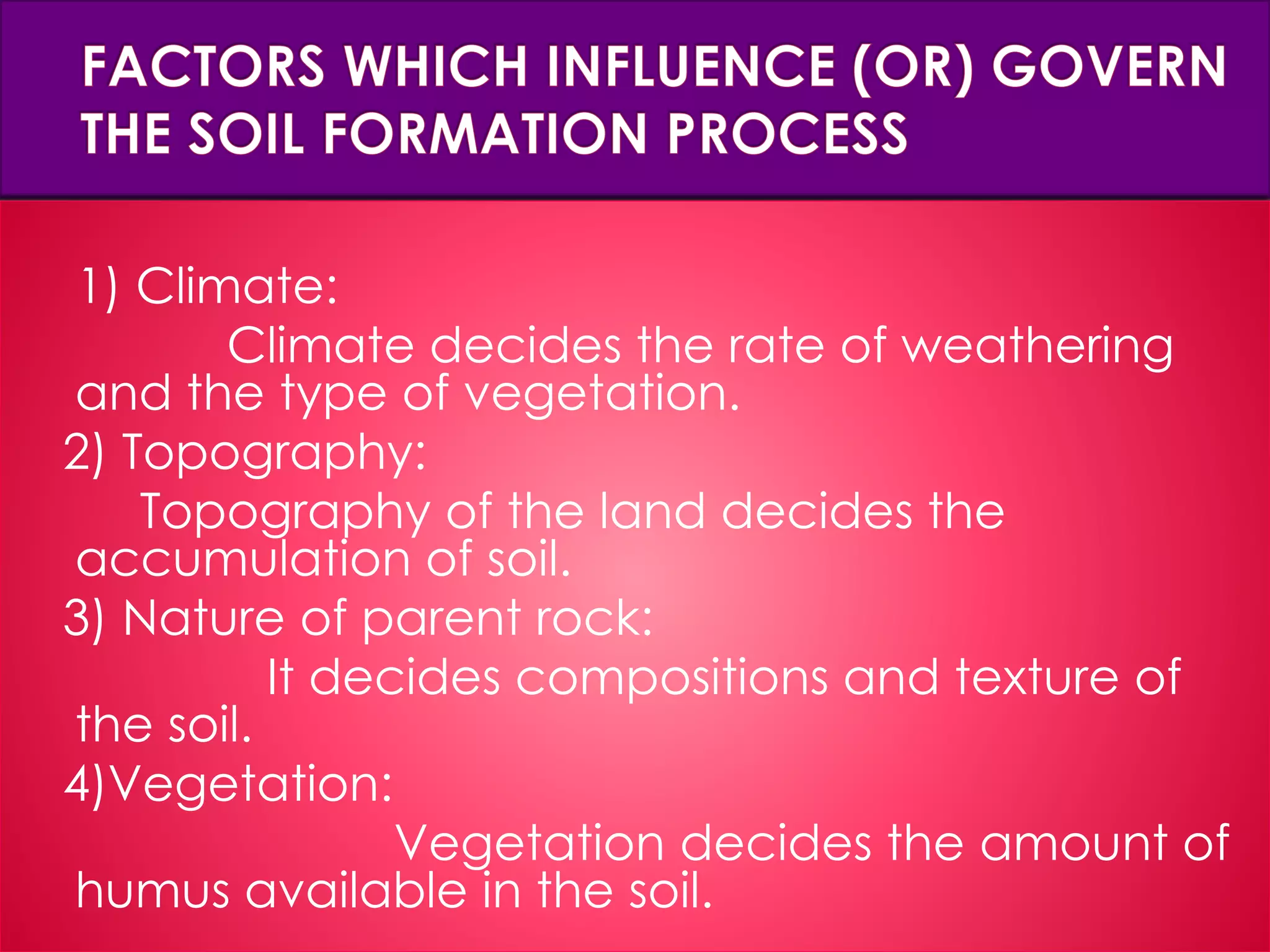
The document discusses different types of resources and their classification. It defines resources as materials or substances obtained from the environment that satisfy human needs and wants. Resources are classified based on their origin (biotic, abiotic), renewability (renewable, non-renewable), ownership (individual, community, national, international), development status (potential, developed, reserves), and depletion issues from overconsumption. Soil is an important resource for agriculture that is influenced by climate, topography, parent rock and vegetation, and soil erosion negatively impacts food production.




















![i). Alluvial soil is the most fertile and wide
spread soil found in India.
ii). It is formed due to the deposition of fine silt
called alluvium by the rivers.
iii). It is found in the northern plains, Gujarat
plains and the coastal plains.
iv). It consists of sand, silt and clay.
v). It is divided into khadar and Bangar [new
alluvium and old alluvium] It contains soil
nutrients such as potash, phosphoric acid and
lime. So, it is fertile and good for the growth of
sugarcane, rice, wheat and pulses.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sspptonresources-140621225710-phpapp02/75/Ss-ppt-on-resources-fro-class-10-28-2048.jpg)














