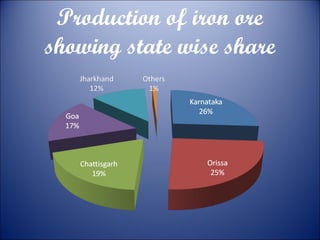
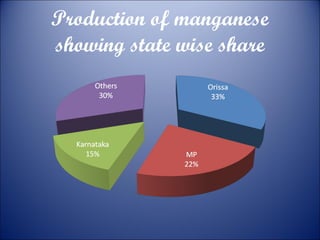
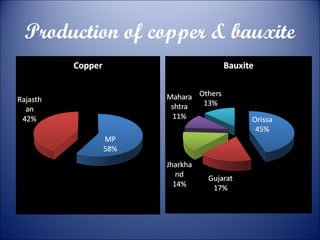
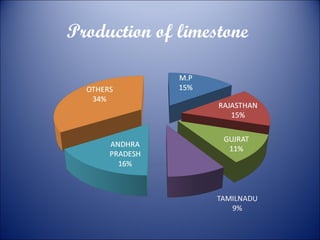
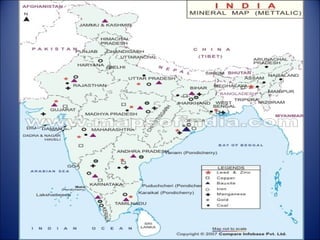
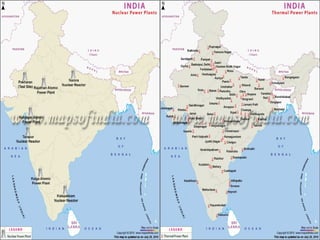
Minerals are naturally occurring substances with a defined internal structure. They are essential to life and used widely in industry. Minerals can be metallic like iron, manganese, copper, or non-metallic like mica, salt, and limestone. India has major deposits of important minerals like iron ore, manganese, bauxite, and coal. Energy resources include conventional sources like coal, petroleum, and electricity as well as non-conventional sources like solar, wind, and nuclear power. Conservation efforts include using energy-efficient appliances and recycling waste to reduce resource usage.