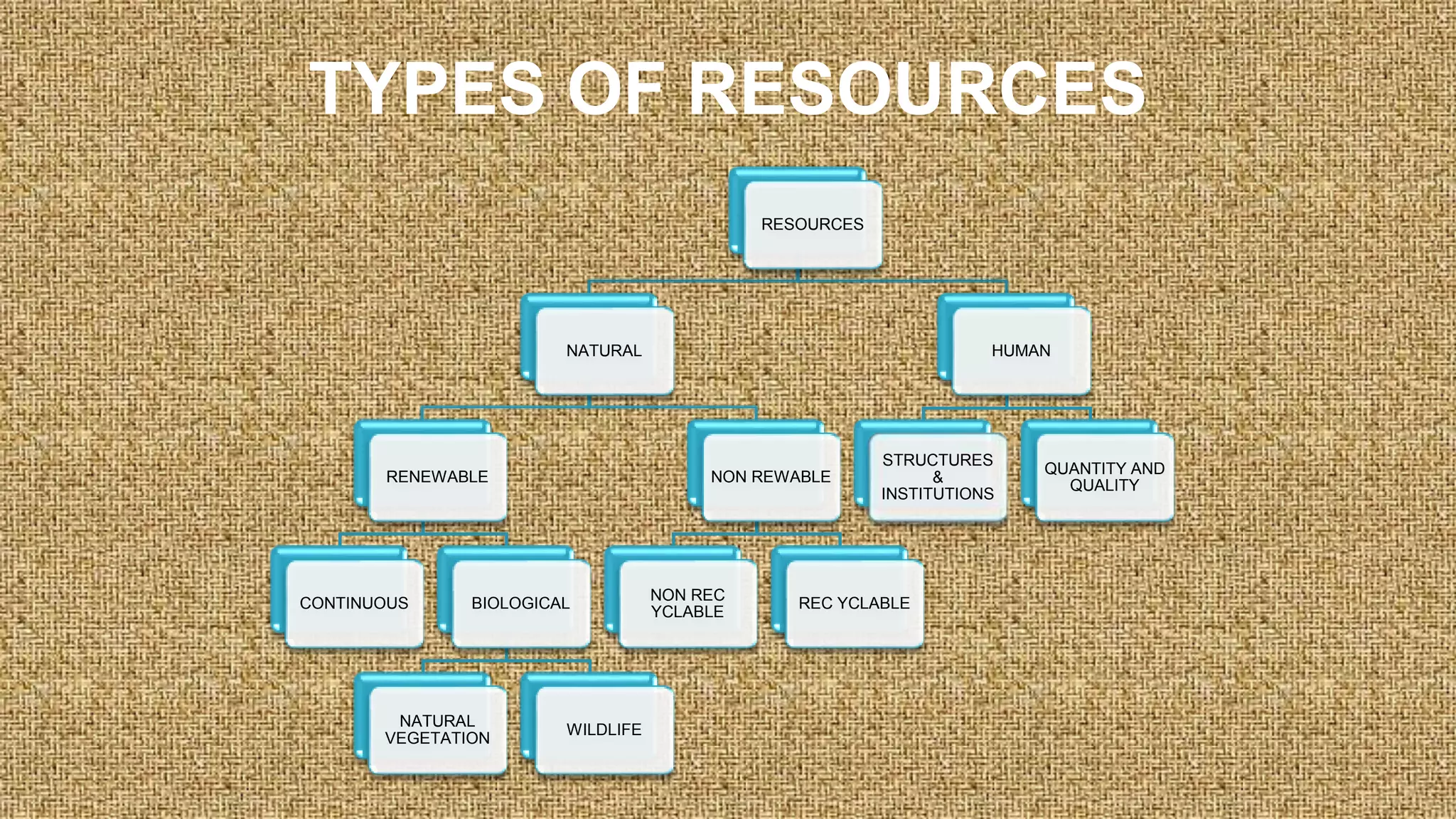
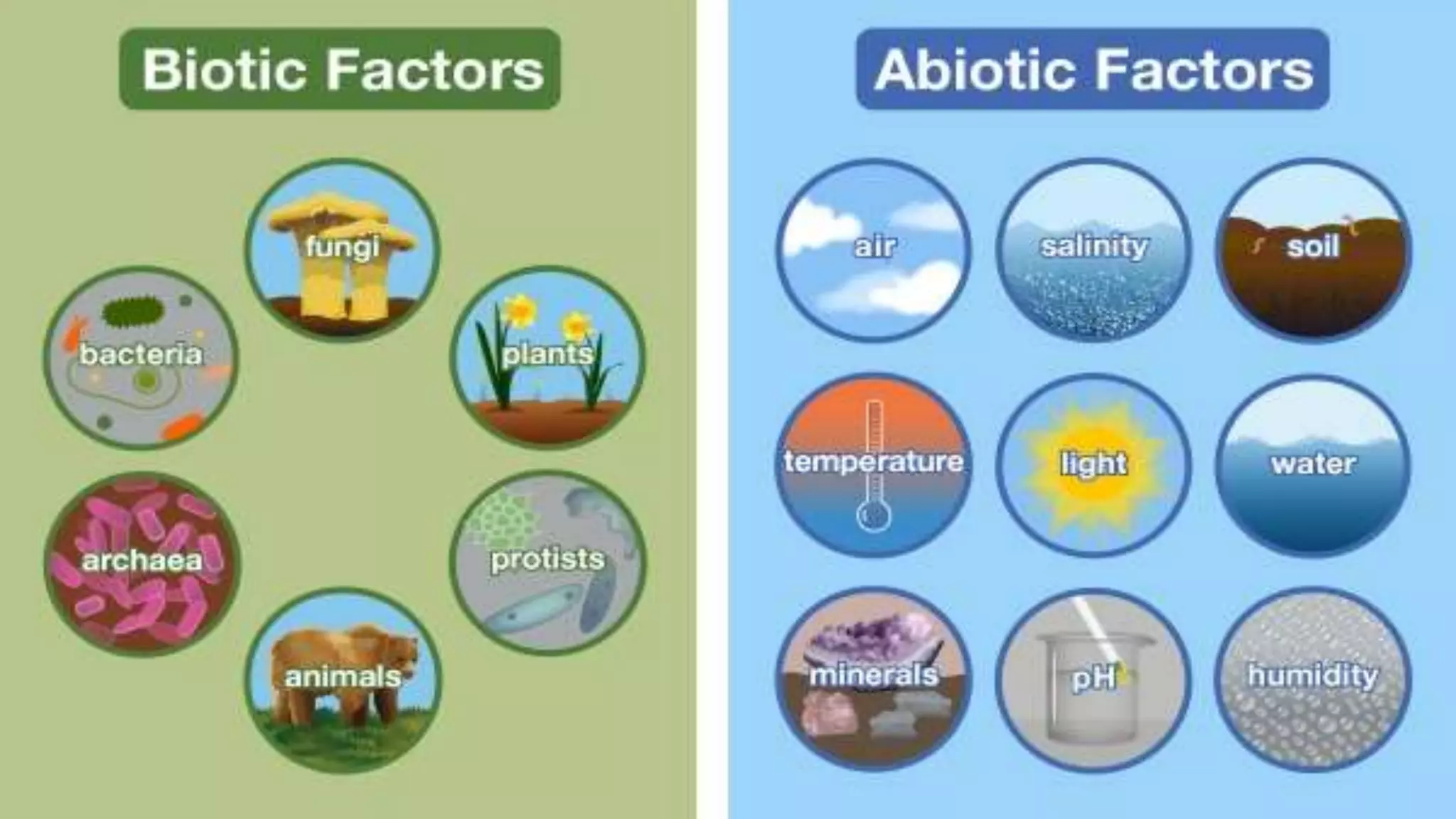
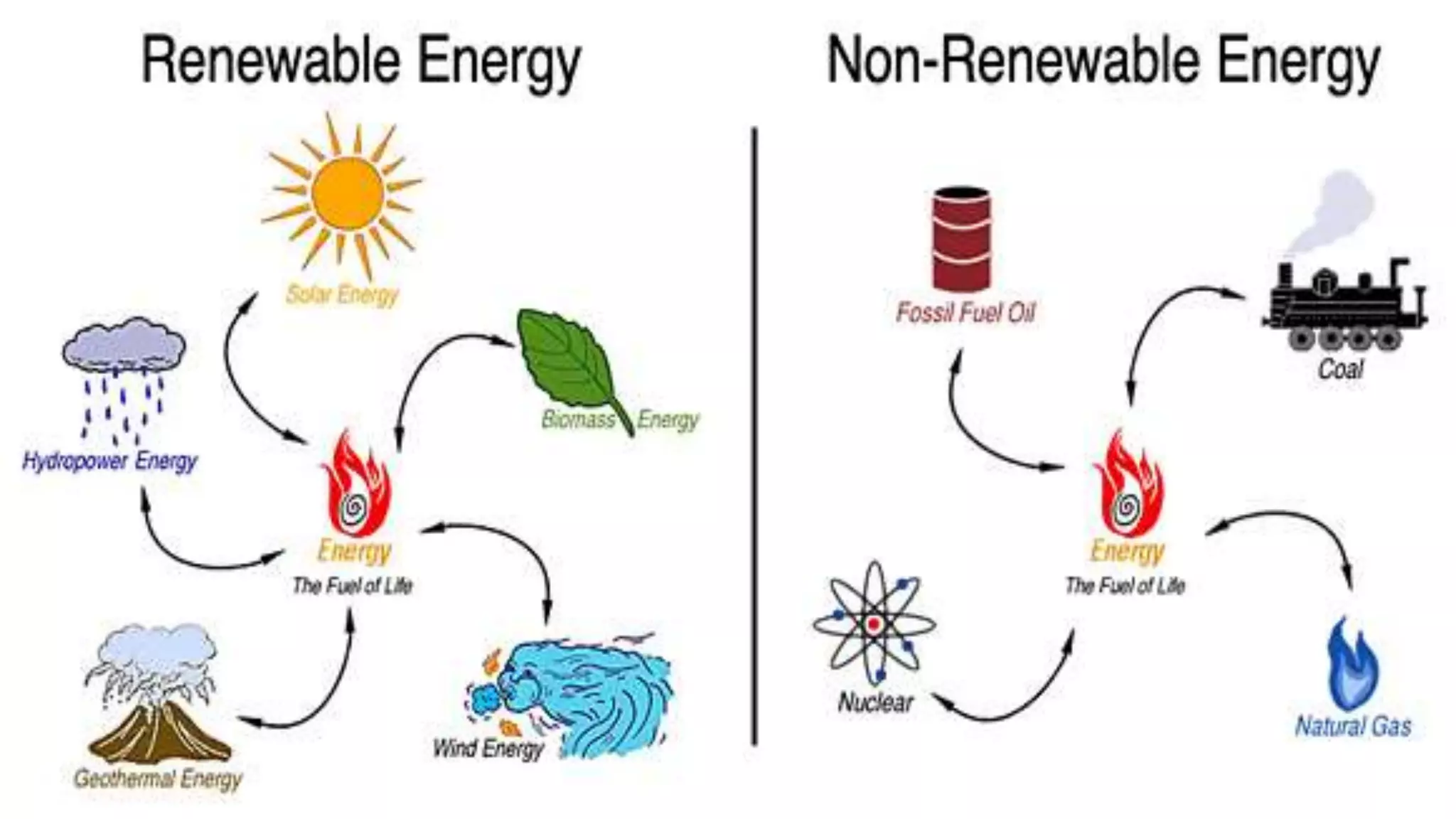
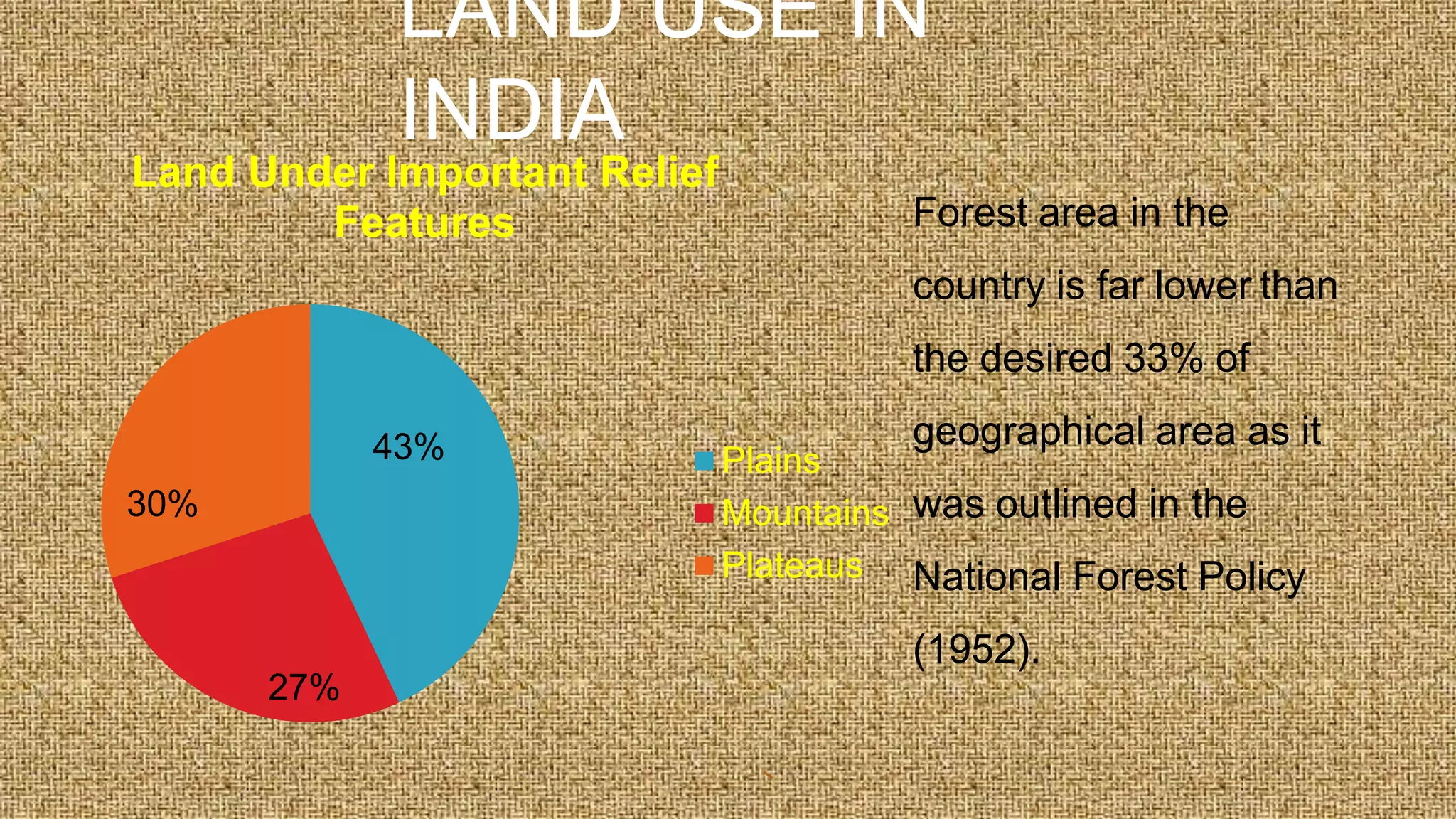
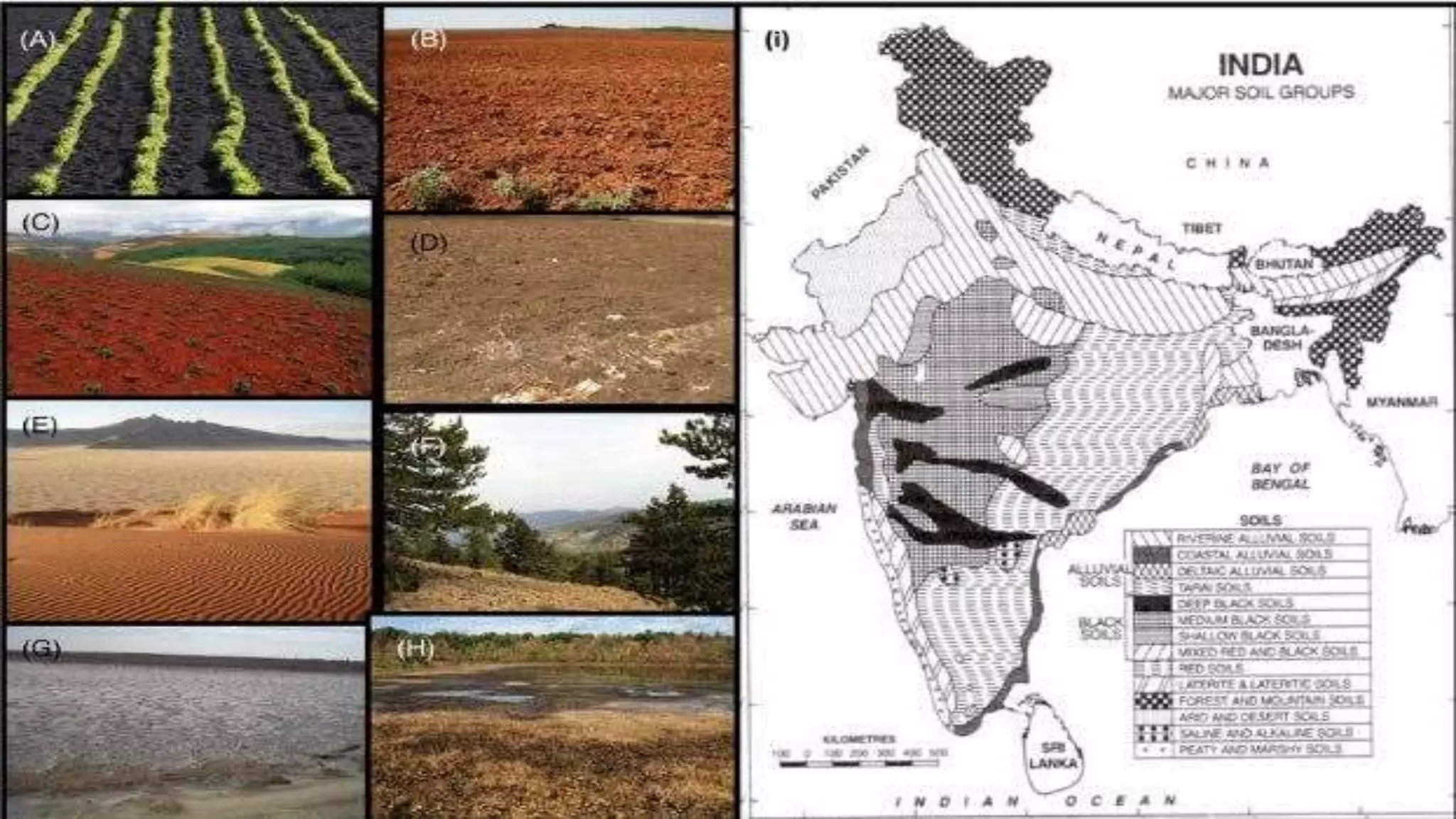
The document is a geography project discussing various types of natural resources, including their classification based on origin, exhaustibility, ownership, and development status. It emphasizes the importance of resource planning and sustainable development, particularly in the context of India. The document also details different types of soil and their relevance to agriculture and human needs.