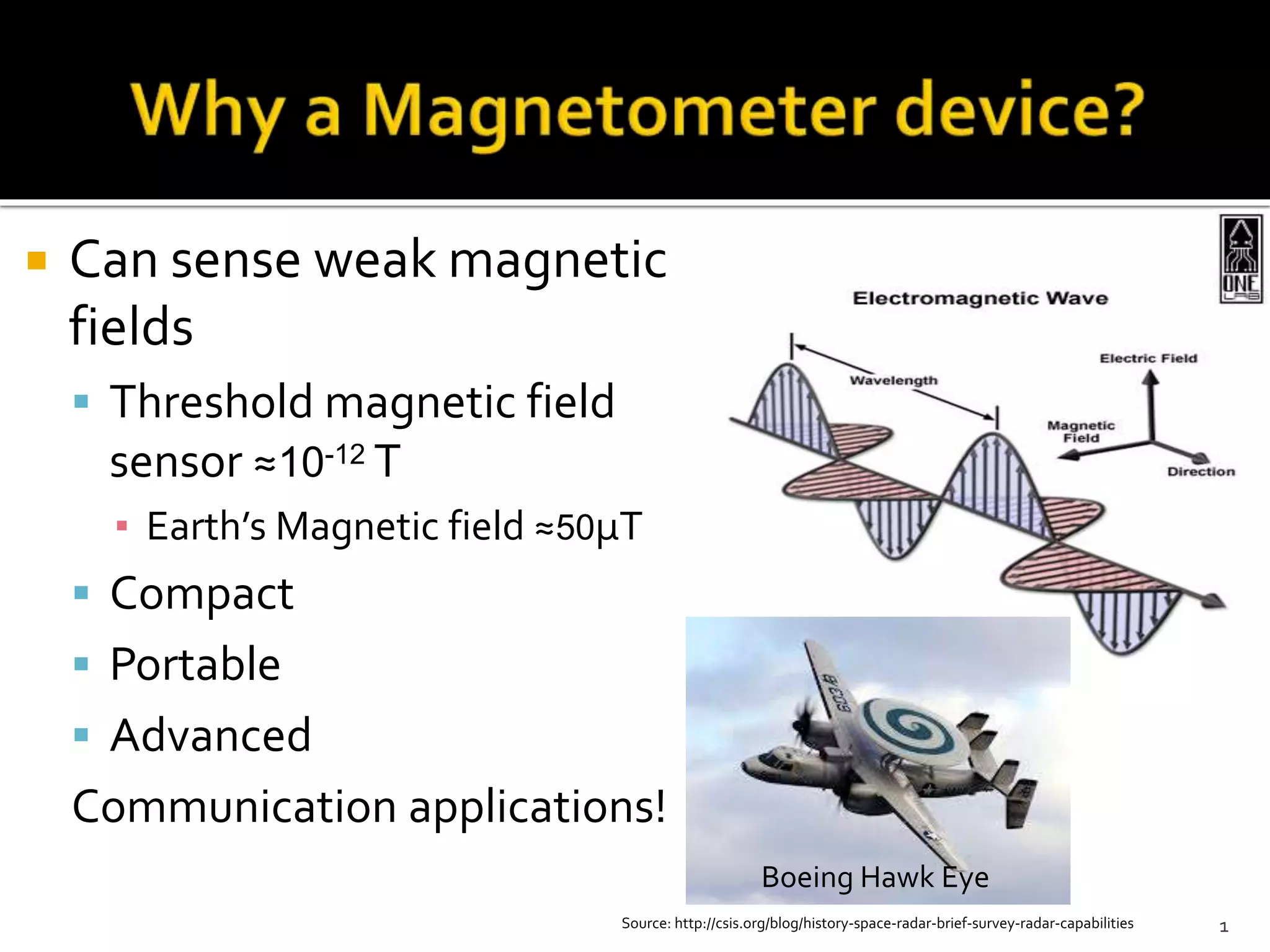
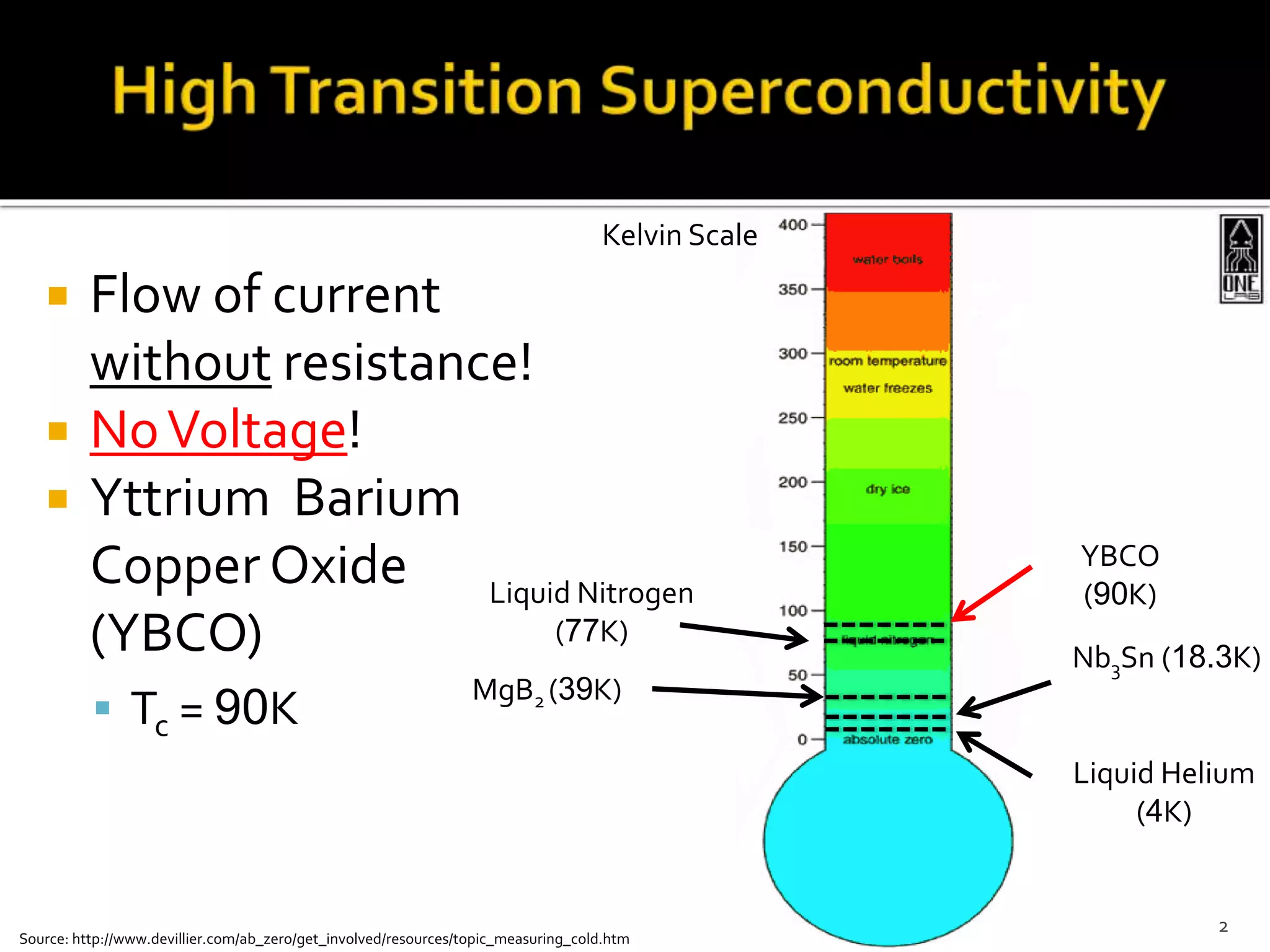
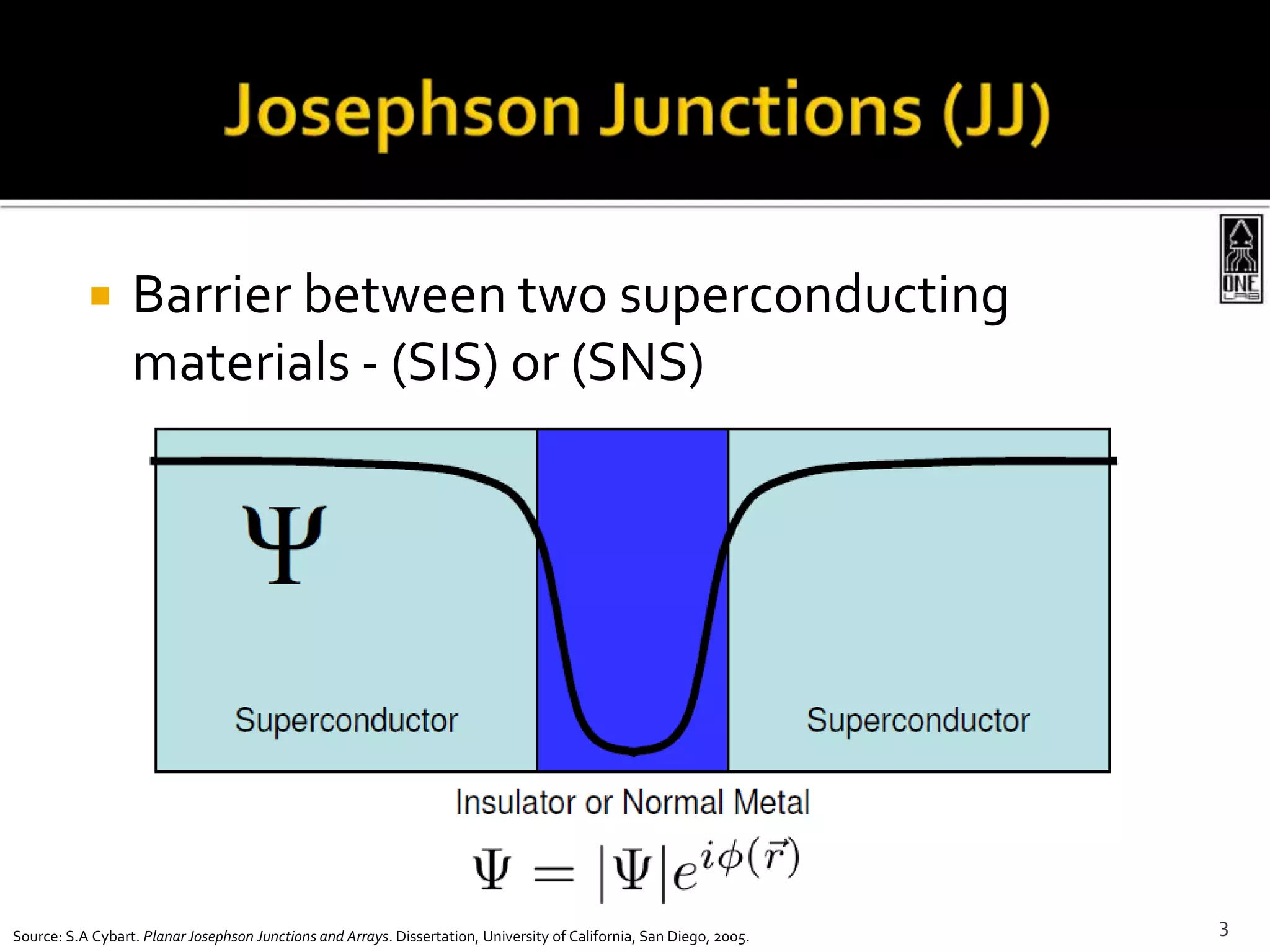
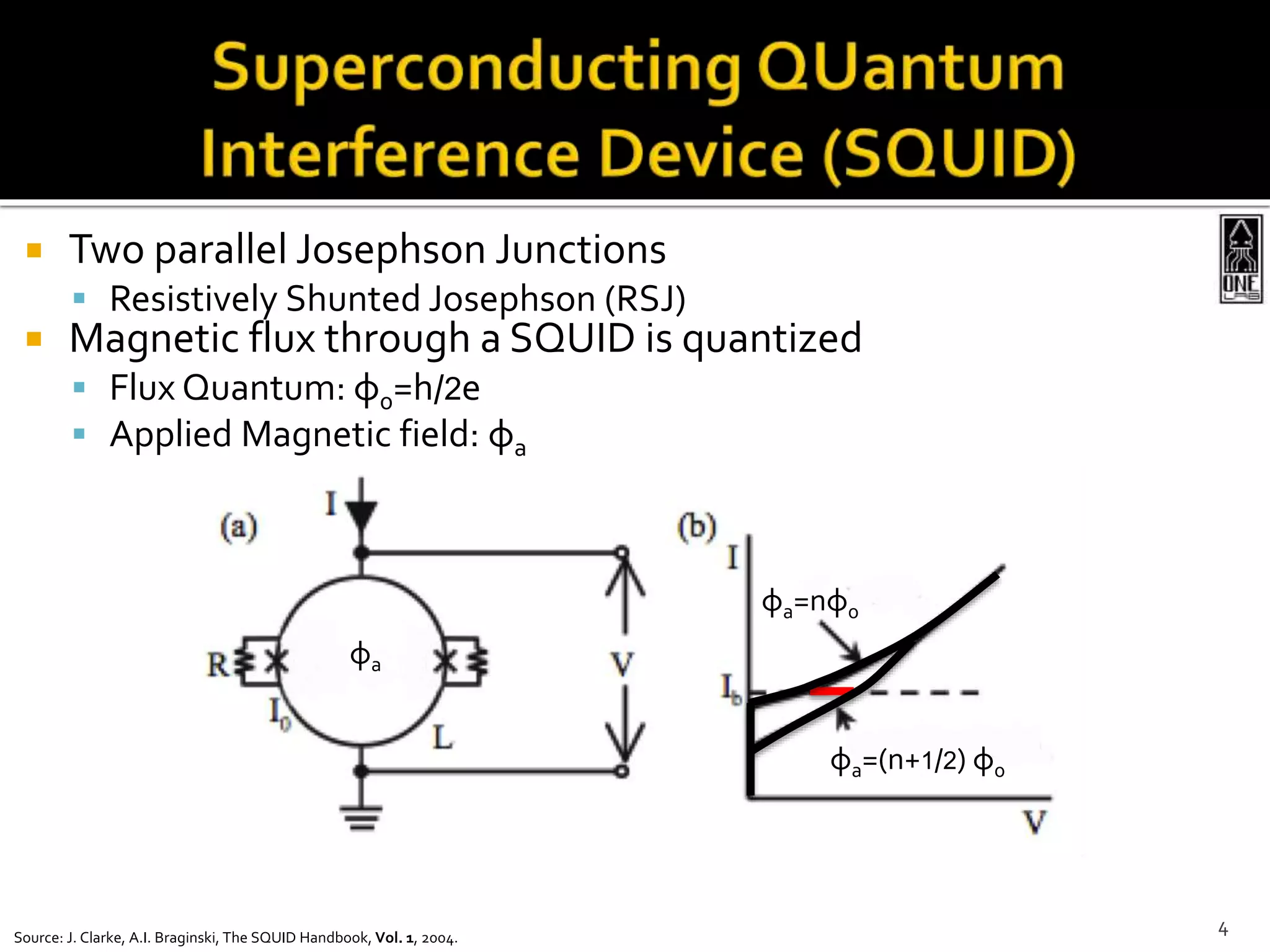
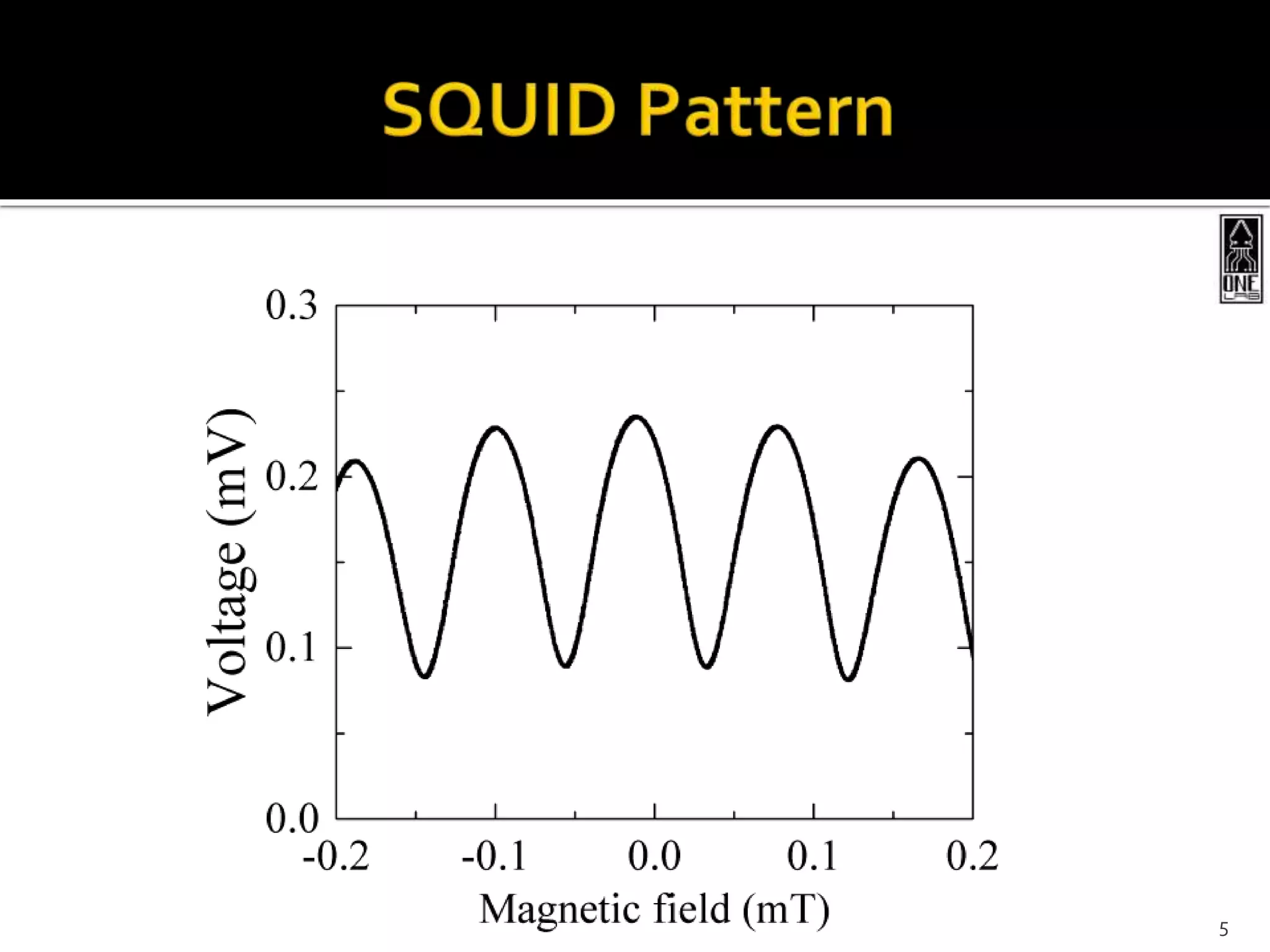
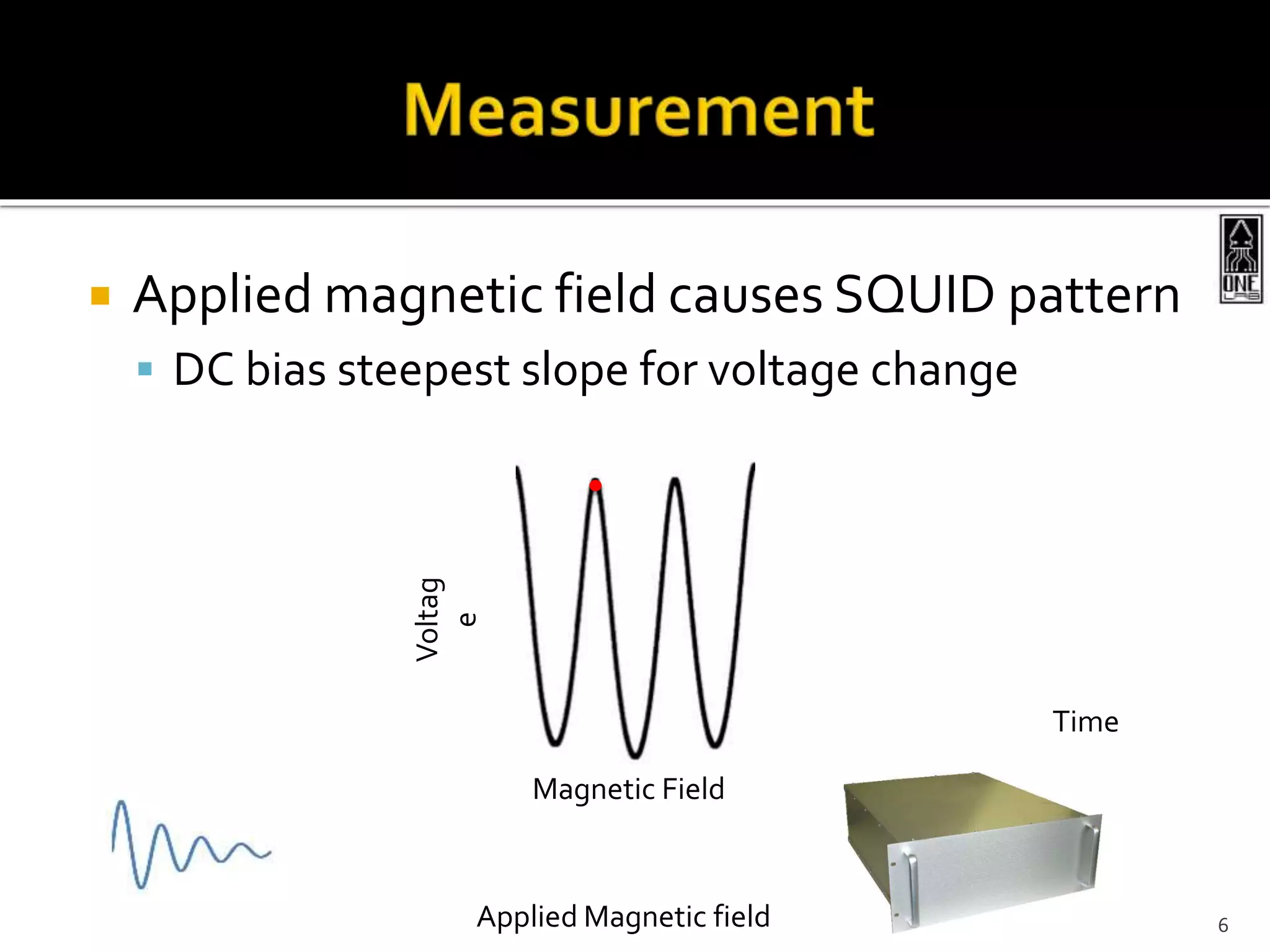
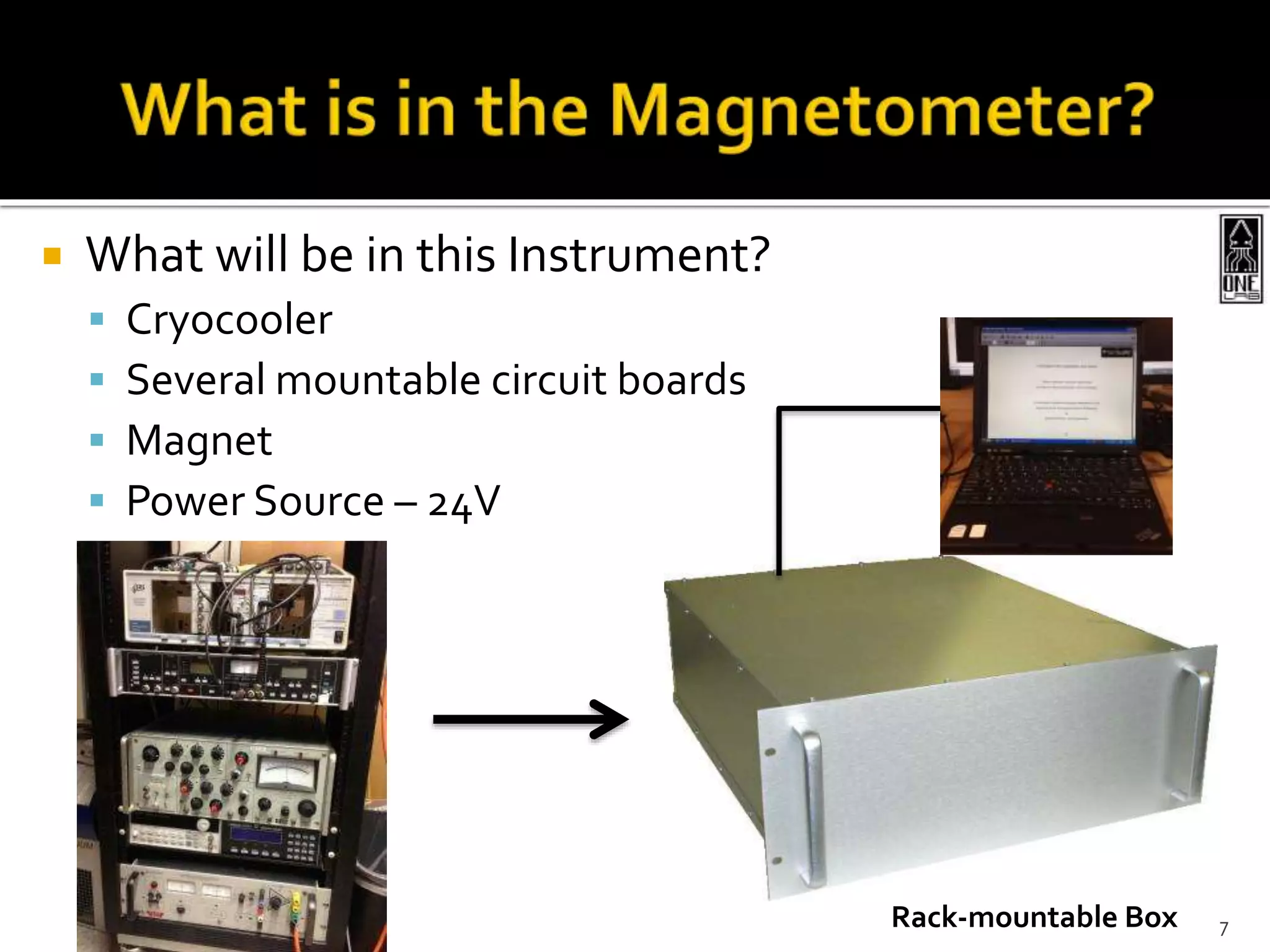
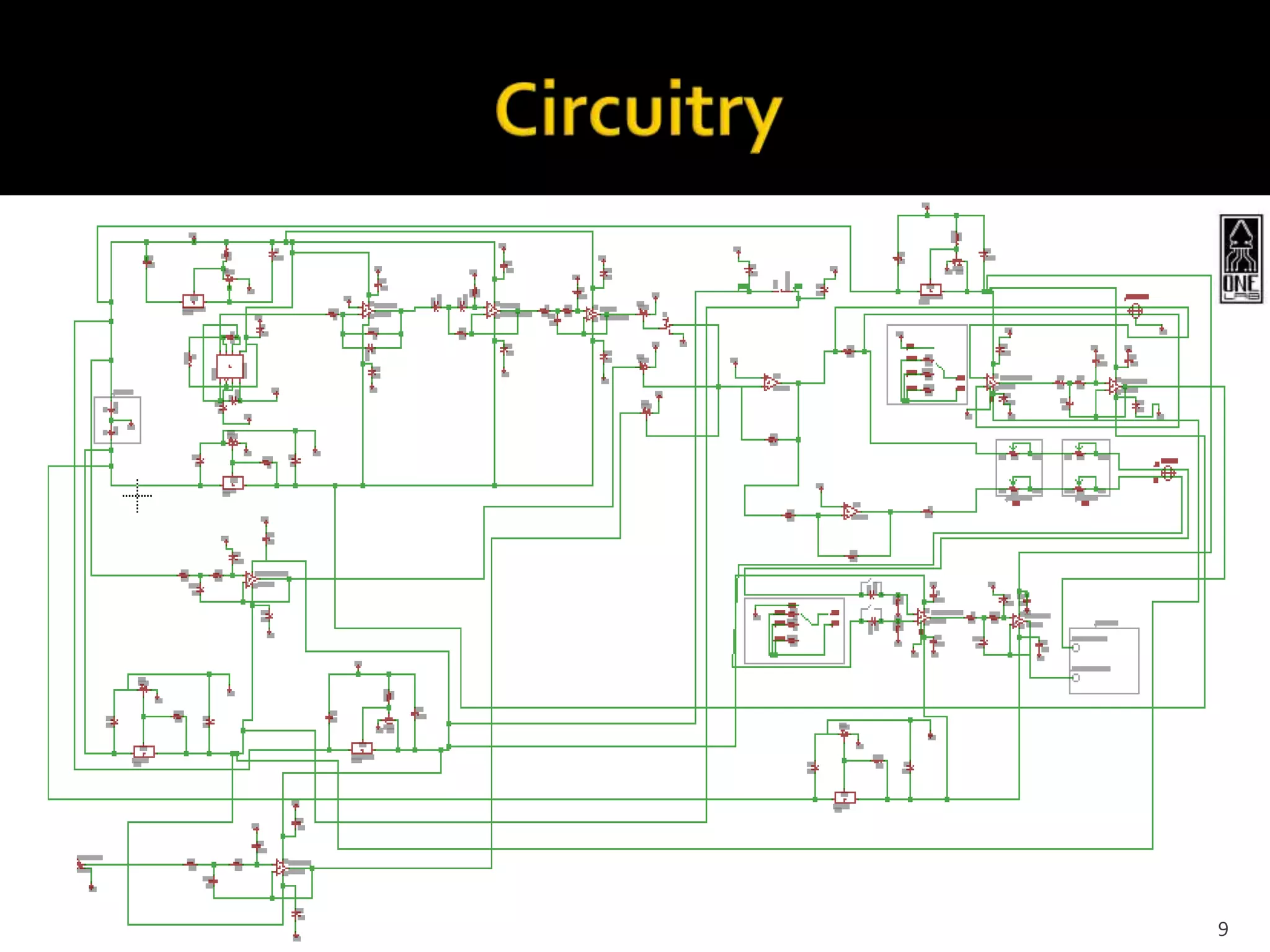
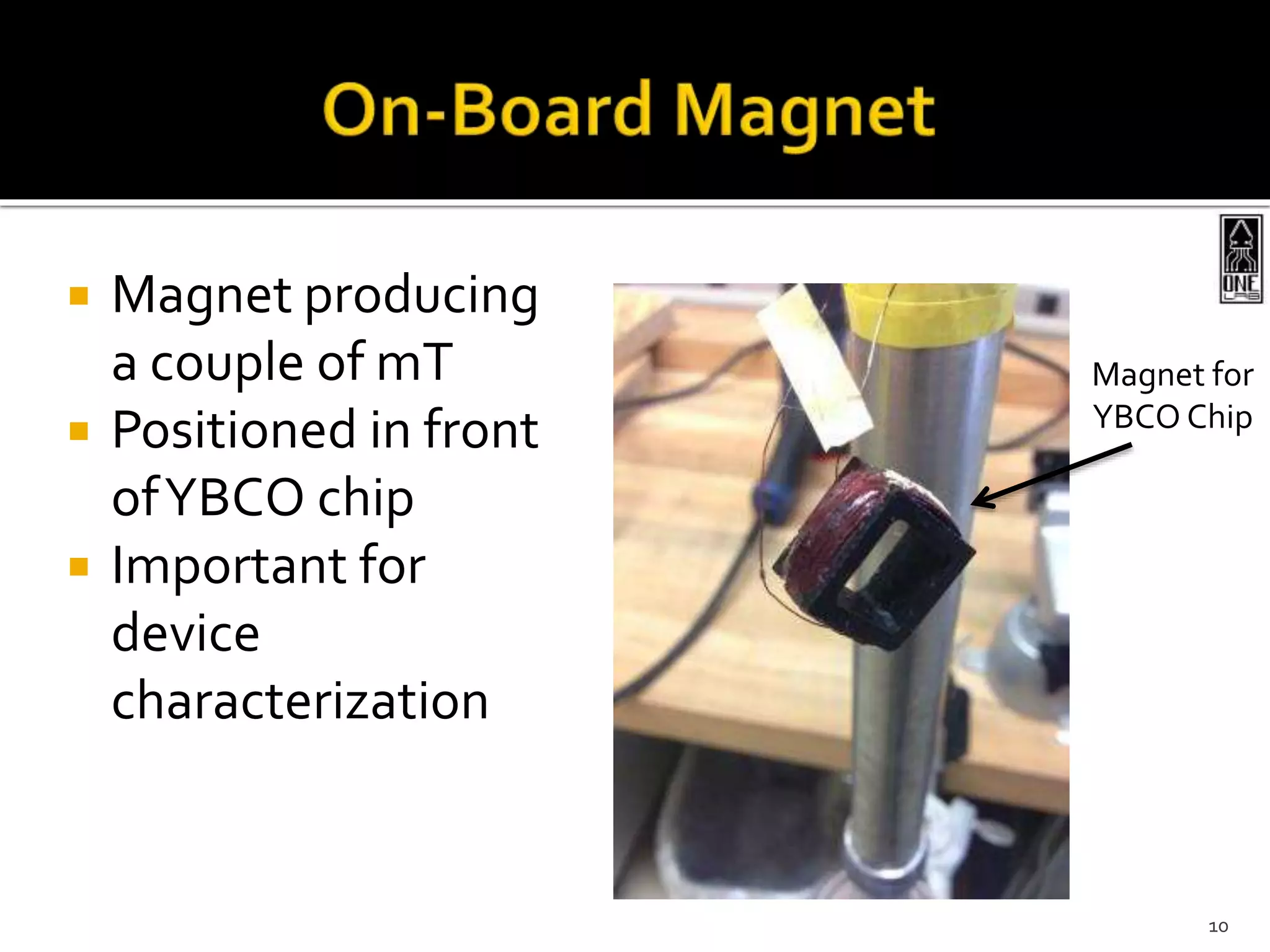
This document summarizes the development of a portable magnetoencephalography (MEG) instrument using high-temperature superconducting quantum interference devices (SQUIDs). The instrument will contain a cryocooler to cool the yttrium barium copper oxide (YBCO) SQUID sensors to 90K, printed circuit boards containing the SQUID electronics, a magnet to generate a magnetic field for device characterization, and a power source. The compact, efficient design will allow for applications such as MEG to measure brain activity outside of a laboratory setting. The project is led by Professor Robert Dynes and involves a team of researchers and students.