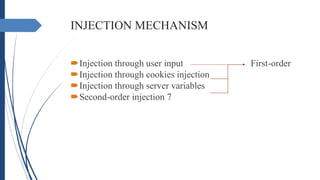
This document discusses SQL injection attacks and how they work. SQL injection occurs when user-supplied data is included in an SQL query in a way that allows the user's input to be interpreted as SQL code rather than data. An attacker can exploit this by crafting malicious SQL statements in their input to extract or manipulate data in the database or bypass authentication checks. The document covers the goals of cyber attacks, types of SQL injection attacks like first-order and second-order injections, and steps to perform an SQL injection on a vulnerable website.






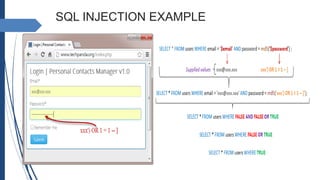


![STEPS FOR SQL INJECTION
Step1- open techpanda.org page (any vulnerable site)
Step2 – use following inputs for login
Email id- xxx@xxx.xxx
Password - xxx') OR 1 = 1 -- ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sqlinjection-181028165004/85/Sql-injection-11-320.jpg)
