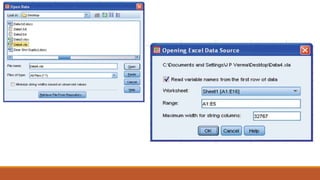
The document is an introduction to SPSS, a statistical software used for data analysis across various fields such as education and market research. It outlines the steps to analyze data, including data entry, defining variables, and selecting procedures for statistical tests. Additionally, it details methods for descriptive analysis, correlation, regression, and data sourcing from different file types like spreadsheets.